Describes how to configure a Non SD-WAN Destination of type Microsoft Azure Virtual Hub from SD-WAN Gateway.
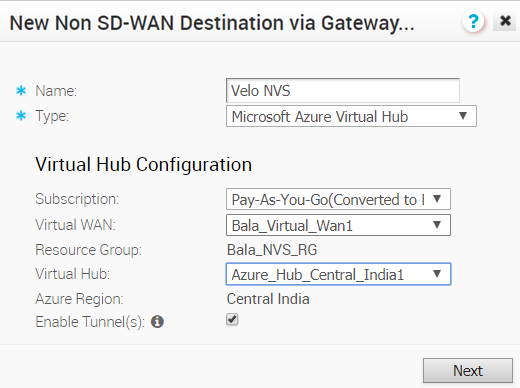
To configure a Non SD-WAN Destination of type Microsoft Azure Virtual Hub from SD-WAN Gateway:
Prerequisites
- Ensure you have configured a Cloud subscription. For steps, see Configure a Cloud Subscription Network Service.
- Ensure you have created Virtual WAN and Hubs in Azure. For steps, see Configure Azure Virtual WAN for Branch-to-Azure VPN Connectivity.
Procedure
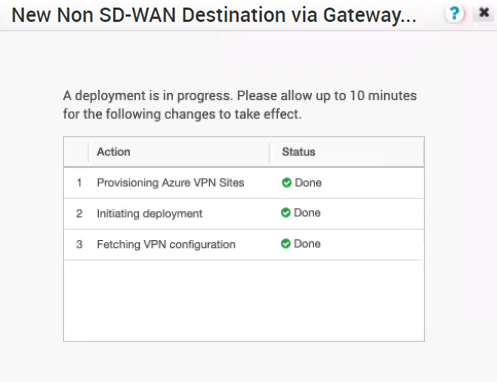
Results
Once the Azure VPN sites are provisioned at the SD-WAN Orchestrator side, you can view the VPN sites (Primary and Redundant) in the Azure portal by navigating to your Virtual WAN page > Virtual WAN architecture > VPN sites.
What to do next
- Associate the Microsoft Azure Non SD-WAN Destination to a Profile to establish a tunnel between a branch and Azure Virtual Hub. For more information, see Associate a Microsoft Azure Non SD-WAN Destination to a Profile.
- You must add SD-WAN routes into Azure network manually. For more information, see Edit a VPN Site.
- After associating a Profile to the Microsoft Azure Non SD-WAN Destination, you can return to the Non SD-WAN Destinations via Gateway section by navigating to and configure the BGP settings for the Non SD-WAN Destination. Scroll to the name of your Non SD-WAN Destination, and then click the Edit link in the BGP column. For more information, see Configure BGP over IPsec from Gateways.
- In the Non SD-WAN Destinations via Gateway area, click the Edit link in the BFD column for a Non SD-WAN Destination, to configure the BFD settings. For more information, see Configure BFD for Gateways.
For information about Azure Virtual WAN Gateway Automation, see Configure SD-WAN Orchestrator for Azure Virtual WAN IPsec Automation from SD-WAN Gateway.