Route Summarization or route aggregation is a method to minimize the number of routes that a router advertises to its neighbor. It consolidates selected route prefixes into a single route advertisement. This differentiates it from regular routing, in which every unique route prefix in a route table is advertised to the neighbor.
Overview
Route Summarization or supernetting advertises a single route prefix instead of sending a bunch of contiguous route prefixes. However, with route summarization, there is a need to design the networks with summarization in mind, else, there is a possibility for introducing suboptimal routing and forwarding traffic for unused networks. Similarly, if the router does not find a matching destination route prefix in its routing table for which it advertised the summary prefix, it would drop traffic.
When using the Route Summarization feature, the network administrator must take into consideration the network design before he or she specifies the summarized prefix, which needs to be advertised to its neighbor.
Route Summarization Use Case
In the below topology a router is learning route prefixes from multiple sources. When the router advertises route prefixes to its neighbor via BGP, it advertises the unique route prefixes. In the example below, it is advertising eight unique route prefixes. Instead, with route summarization, the router can advertise a single summary prefix to its neighbor via BGP. See image below.
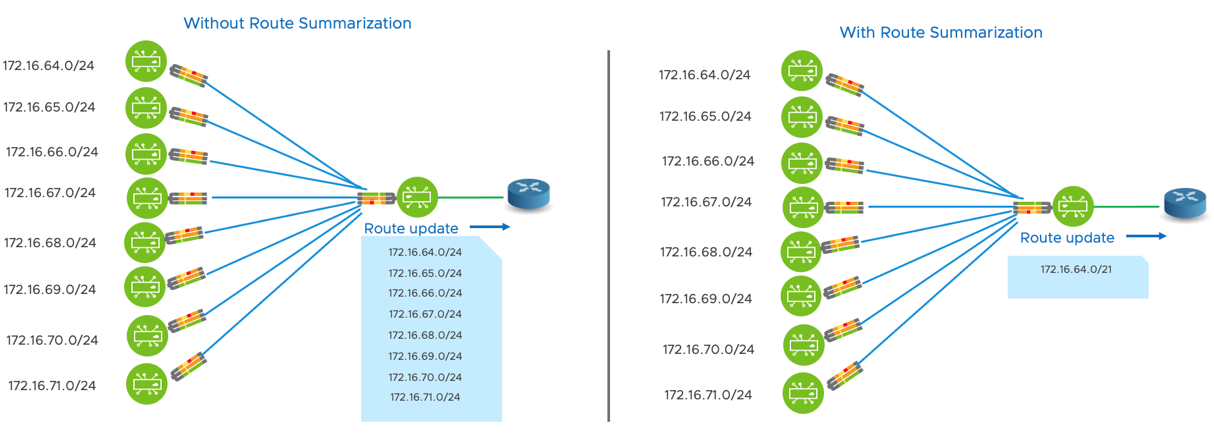
Route summarization is a functionality introduced on the VMware SD-WAN Edge and the Gateway.
- In the case of the VMware SD-WAN Edge:
- Summary prefix via BGP to a neighbor setup over Routed (LAN) interface
- Summary prefix via BGP to a neighbor setup over NSD (IPsec/BGP) tunnel
- Summary prefix via OSPF to a neighbor setup over Routed (LAN) interface
- In the case of the VMware SD-WAN Gateway:
- Summary prefix via BGP to a neighbor setup over NSD (IPsec/BGP) tunnel
- Summary prefix via BGP to a Partner Hand off router over the Partner Hand off Interface
Black Hole Routing
A black hole route, also known as a null route, is a network route where traffic gets discarded. In reference to Route Summarization, black hole routing is used to drop traffic to a destination that is a part of a summary route, but not a part of the prefixes that are learned locally. From the 5.2 release, this process is required because when a summary route is advertised to the peer, all of the traffic is destined to the whole supernet summary route, including the destination prefix that is not present in the Edge/Gateway. Whenever a summary route is configured, a black hole route for summary prefix is automatically installed in the route table, and it remains until it's unconfigured.