This service allows you to create VPN tunnel configurations to access one or more Non SD-WAN Destinations. VMware provides the configuration required to create the tunnel(s) – including creating IKE IPsec configuration and generating a pre-shared key.
Overview
The following figure shows an overview of the VPN tunnels that can be created between VMware and a Non SD-WAN Destination.
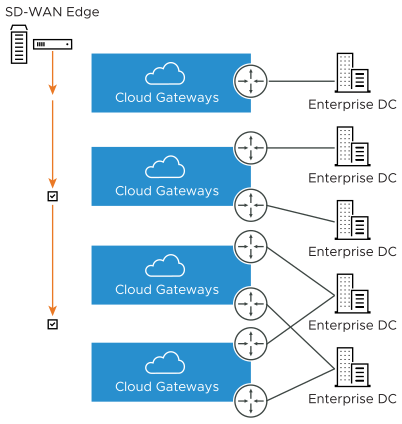
Optionally, an IP address can be specified for a Secondary VPN Gateway to form a Secondary VPN Tunnel between an SD-WAN Gateway and the Secondary VPN Gateway. Redundant VPN Tunnels can be specified for any VPN tunnels you create.
Configure a Non SD-WAN Destination of type AWS VPN Gateway
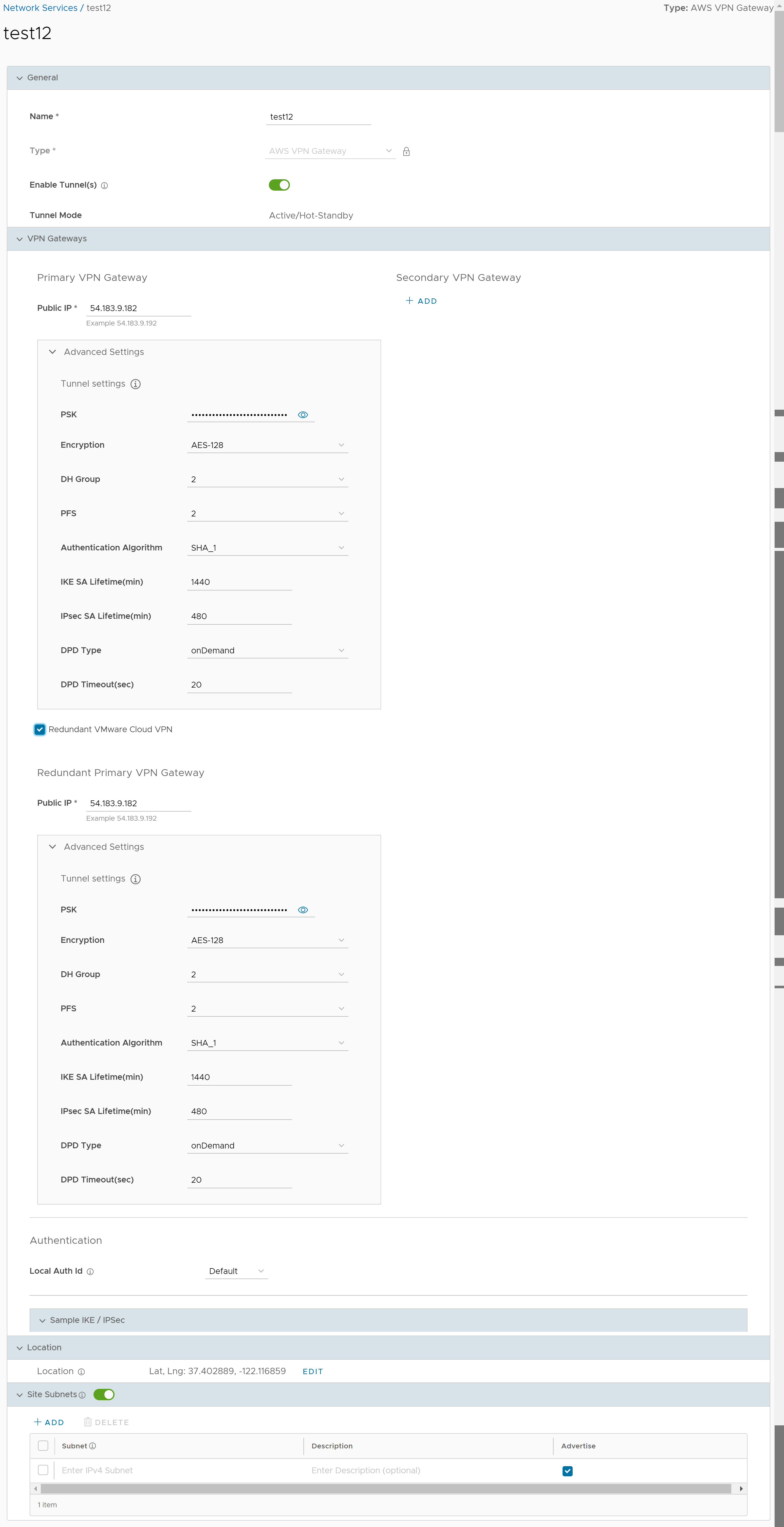
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| General | |
| Name | You can edit the previously entered name for the Non SD-WAN Destination. |
| Type | Displays the type as AWS VPN Gateway. You cannot edit this option. |
| Enable Tunnel(s) | Click the toggle button to initiate the tunnel(s) from the SD-WAN Gateway to the AWS VPN Gateway. |
| Tunnel Mode | Displays Active/Hot-Standby, indicating that if the Active tunnel goes down, the Standby (Hot-Standby) tunnel takes over and becomes the Active tunnel. |
| Primary VPN Gateway | |
| Public IP | Displays the IP address of the Primary VPN Gateway. |
| PSK | The Pre-Shared Key (PSK) is the security key for authentication across the tunnel. The SASE Orchestrator generates a PSK by default. If you want to use your own PSK or password, enter it in the text box. |
| Encryption | Select either AES-128 or AES-256 as the AES algorithm key size to encrypt data. The default value is AES-128. |
| DH Group | Select the Diffie-Hellman (DH) Group algorithm from the drop-down menu. This is used for generating keying material. The DH Group sets the strength of the algorithm in bits. The supported DH Groups are 2, 5, and 14. The default value is 2. |
| PFS | Select the Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS) level for additional security. The supported PFS levels are deactivated, 2, and 5. The default value is 2. |
| Authentication Algorithm | Select the authentication algorithm for the VPN header. Select one of the supported Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) functions from the drop-down menu:
The default value is SHA 1. |
| IKE SA Lifetime(min) | Time when Internet Key Exchange (IKE) rekeying is initiated for SD-WAN Edges. The minimum IKE lifetime is 10 minutes and maximum is 1440 minutes. The default value is 1440 minutes. |
| IPsec SA Lifetime(min) | Time when Internet Security Protocol (IPsec) rekeying is initiated for Edges. The minimum IPsec lifetime is 3 minutes and maximum is 480 minutes. The default value is 480 minutes. |
| DPD Type | The Dead Peer Detection (DPD) method is used to detect if the Internet Key Exchange (IKE) peer is alive or dead. If the peer is detected as dead, the device deletes the IPsec and IKE Security Association. Select either Periodic or onDemand from the drop-down menu. The default value is onDemand. |
| DPD Timeout(sec) | Enter the DPD timeout value. The DPD timeout value will be added to the internal DPD timer, as described below. Wait for a response from the DPD message before considering the peer to be dead (Dead Peer Detection).
Prior to the 5.1.0 release, the default value is 20 seconds. For the 5.1.0 release and later, see the list below for the default value.
Note: Prior to the 5.1.0 release, you can deactivate DPD by configuring the DPD timeout timer to 0 seconds. However, for the 5.1.0 release and later, you cannot deactivate DPD by configuring the DPD timeout timer to 0 seconds. The DPD timeout value in seconds will get added onto the default minimum value of 47.5 seconds).
|
| Secondary VPN Gateway | Click the Add button, and then enter the IP address of the Secondary VPN Gateway. Click Save Changes. The Secondary VPN Gateway is immediately created for this site and provisions a VMware VPN tunnel to this Gateway. |
| Redundant VMware Cloud VPN | Select the check box to add redundant tunnels for each VPN Gateway. Changes made to Encryption, DH Group, or PFS of Primary VPN Gateway also apply to the redundant VPN tunnels, if configured. |
| Local Auth Id | Local authentication ID defines the format and identification of the local gateway. From the drop-down menu, choose from the following types and enter a value:
Note: If you do not specify a value,
Default is used as the local authentication ID.
|
| Sample IKE / IPsec | Click to view the information needed to configure the Non SD-WAN Destination Gateway. The Gateway administrator should use this information to configure the Gateway VPN tunnel(s). |
| Location | Click Edit to set the location for the configured Non SD-WAN Destination. The latitude and longitude details are used to determine the best Edge or Gateway to connect to in the network. |
| Site Subnets | Use the toggle button to activate or deactivate the Site Subnets. Click Add to add subnets for the Non SD-WAN Destination. If you do not need subnets for the site, select the subnet and click Delete.
Note:
|