What is the Purpose of This Test
To check the active tunnel paths between local WAN links and each peer, and gateway status.
When Can You Run This Test
Whenever you face site-to-site communication issues or Gateway traffic issues, run this test to check if the tunnel is UP for destination.
For instructions on how to run a remote diagnostic test on Edges, see Run Remote Diagnostic Tests on Edges.
What to Check in the Test Output
Following is an example of the test output:
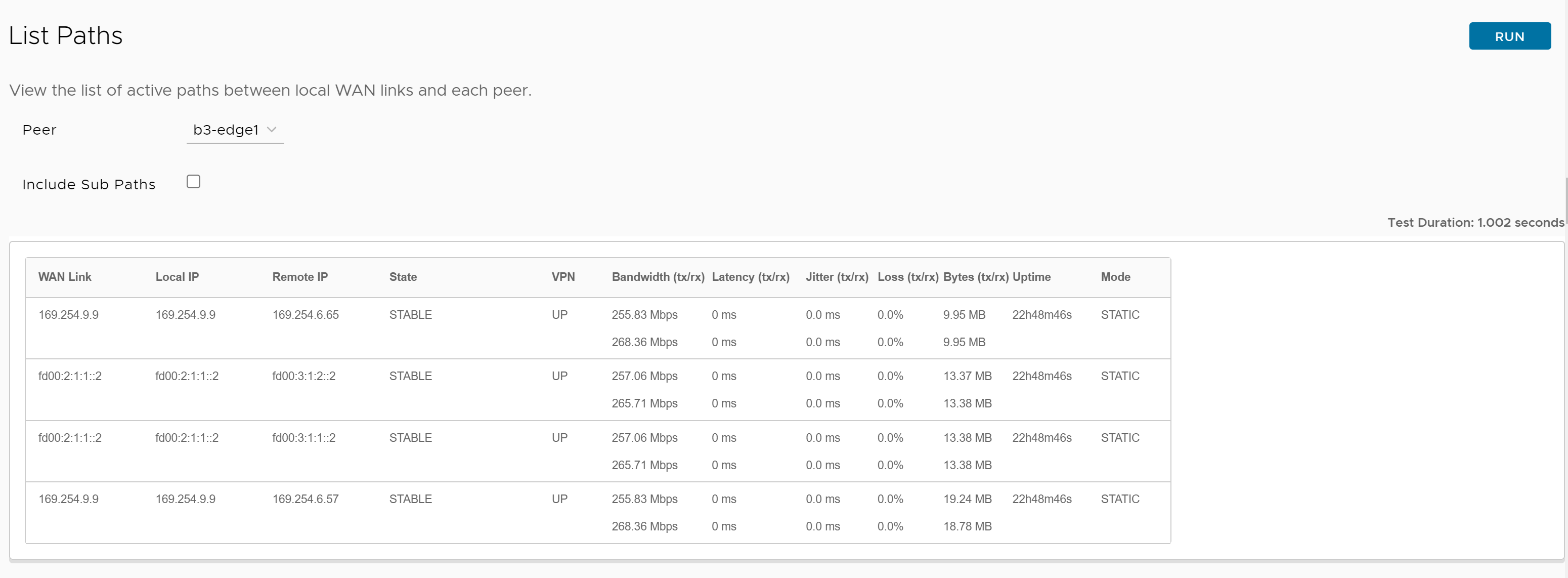
The Remote Diagnostics output displays the following information:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| WAN Link | Specifies the WAN link IP used to form tunnel. |
| Local IP | Specifies the Physical Interface IP for the WAN link. |
| Remote IP | Specifies the Peer IP to which tunnel is formed. |
| State | Specifies the tunnel state. The state can be any of the following:
|
| VPN | Specifies the VPN state and it should be UP for good tunnel. |
| Bandwidth (tx/rx) | Indicates the bandwidth of the tunnel. |
| Latency (tx/rx) | Indicates the latency of the tunnel. |
| Jitter (tx/rx) | Indicates the jitterness of the tunnel. |
| Loss (tx/rx) | Indicates the packet loss of the tunnel. |
| Bytes (tx/rx) | Indicates the bytes of the tunnel in MB. |
| Uptime | Indicates the duration of tunnel uptime. |
| Mode | Specifies the mode of the tunnel:
|