VMware SD-WAN Edges typically get deployed in a Transit VPC on Amazon Web Services (AWS). AWS introduced the support for AWS TGW (Transit Gateway) Connect Service for SD-WAN appliances to connect to the Transit Gateway. VMware SD-WAN Edge now has a feature (BGP over GRE support on LAN), which enables support on the VMware SD-WAN Edges to use the AWS TGW Connect Service for connectivity to the AWS Transit Gateway.
For the AWS TGW Connect Service, the Edge provisioned in the Transit VPC needs to use the LAN (routed, non-WAN) interface to set up the GRE tunnel. This effectively uses the Private IP configured on the Edge Intelligence (EI) to set up the GRE tunnel to the Transit Gateway.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) Configuration Procedure
- In the AWS portal, provision an AWS Transit Gateway in a particular region. This same region must have the Transit VPC, where the VMware SD-WAN Edge is provisioned.
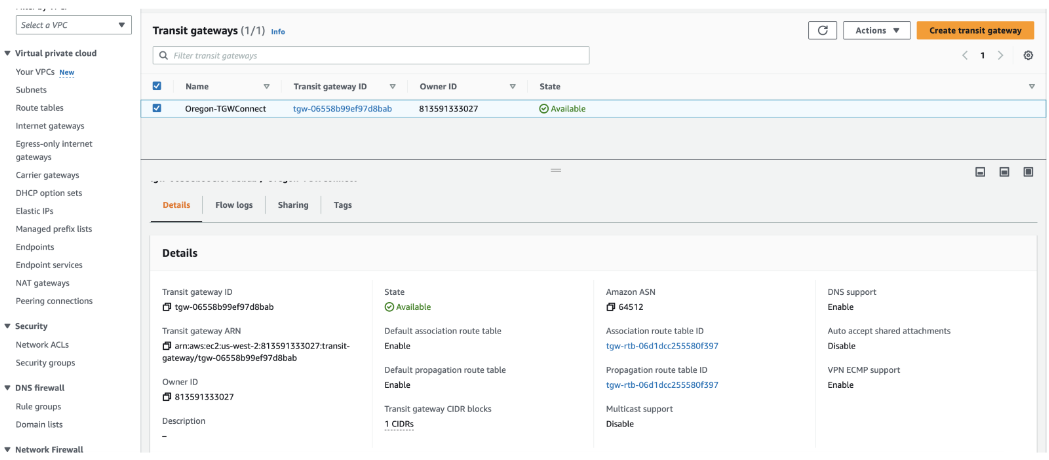 Check for the Transit Gateway CIDR block to be configured, as shown in the image below.Note: An IP from this block is used for the GRE endpoint on the AWS TGW. The Amazon ASN is used later in the BGP configuration on the VMware SD-WAN Edge.
Check for the Transit Gateway CIDR block to be configured, as shown in the image below.Note: An IP from this block is used for the GRE endpoint on the AWS TGW. The Amazon ASN is used later in the BGP configuration on the VMware SD-WAN Edge.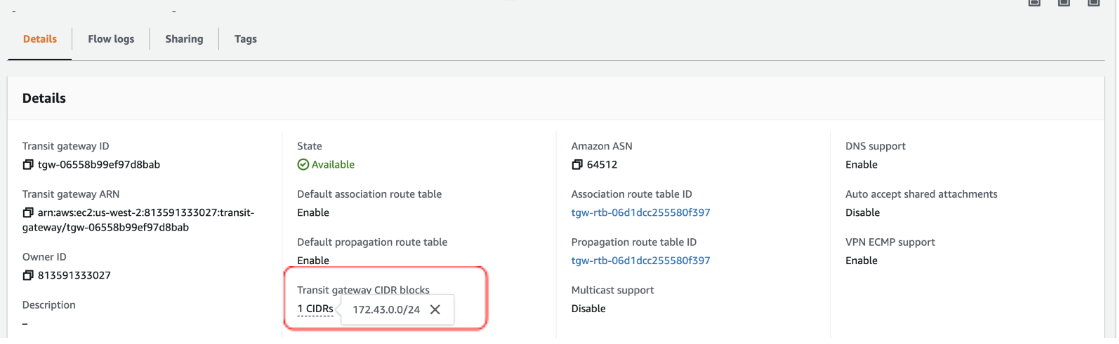
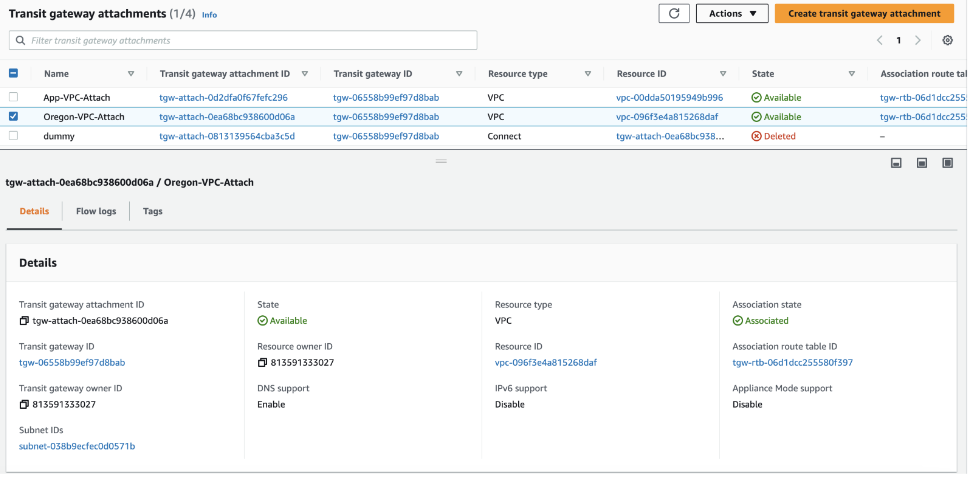
- Create a VPC Attachment for the Transit VPC specifying the Subnets where the LAN interface of the Edge or EI resides.
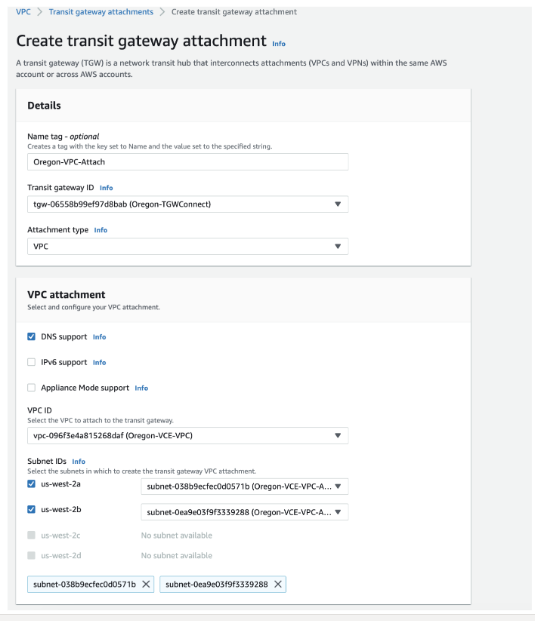
After the VPC Attachment is created, Available will display in the State column.
- Create a Connect Attachment using the VPC Attachment.
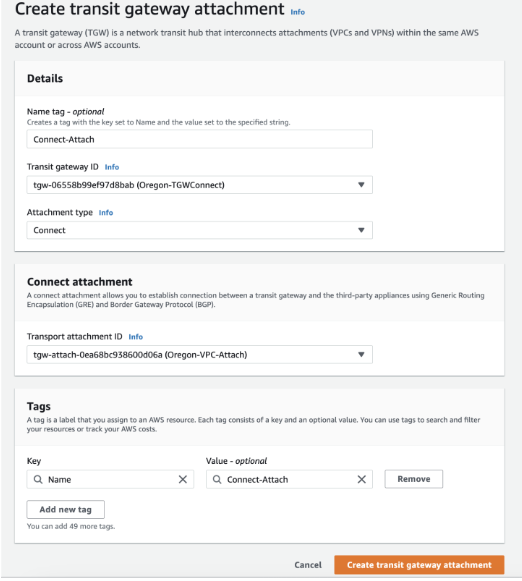
After the Connect Attachment is created, Available will display in the State column.
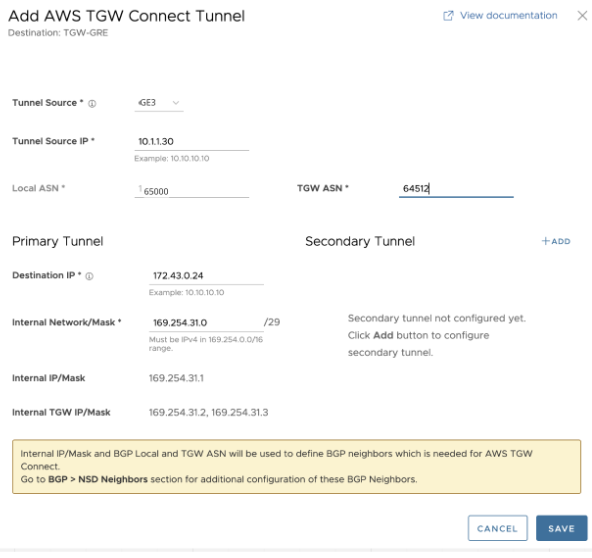
- Create a Connect peer, which will translate to a GRE Tunnel. Specify the following parameters: the Transit Gateway GRE Address, the Peer GRE Address, the BGP Inside CIDR block, and the Peer ASN.
Note: The BGP Inside CIDR block and the Peer ASN must match what is configured on the VMware SD-WAN Edge.
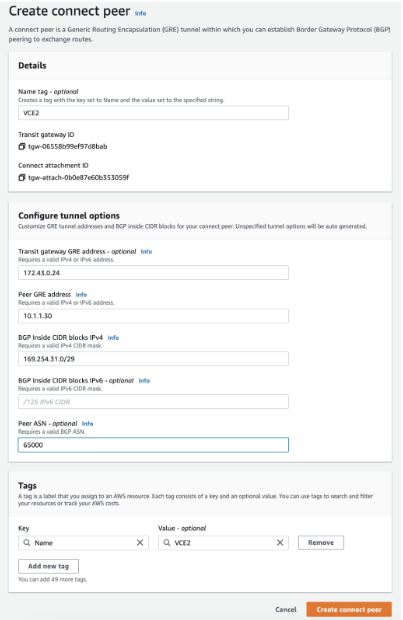 In the above example:
In the above example:- 172.43.0.24 is the GRE Outside IP address on the AWS TGW, this IP is allocated from the Transit Gateway CIDR block.
- 10.1.1.30 is the GRE Outside IP address on the VMware SD-WAN Edge.
- 169.254.31.0/29 is the Inside CIDR Block. The addresses from this block are used for the BGP neighbor.
- 169.254.31.1 is the IP address on the VMware SD-WAN Edge.
- 169.254.31.2 and 169.254.31.3 are addresses used for the BGP on the AWS TGW.
- 64512 is the BGP ASN configured on the AWS TGW.
- 65000 is the BGP ASN configured on the VMware SD-WAN Edge.
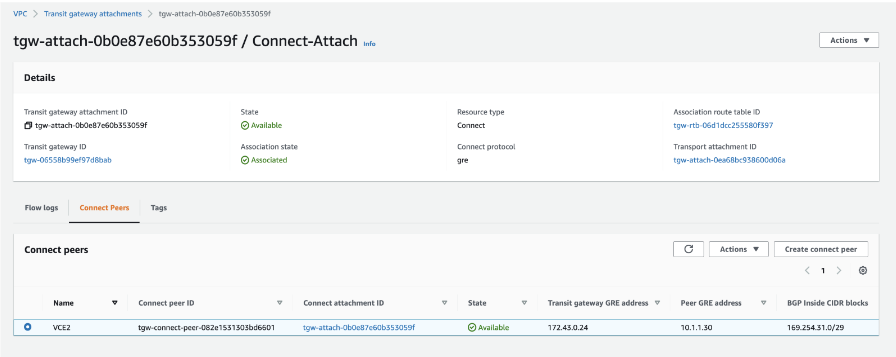 The VPC Resource Map for the Transit VPC lists the LAN side subnet with the Route table, as shown in the image below.
The VPC Resource Map for the Transit VPC lists the LAN side subnet with the Route table, as shown in the image below.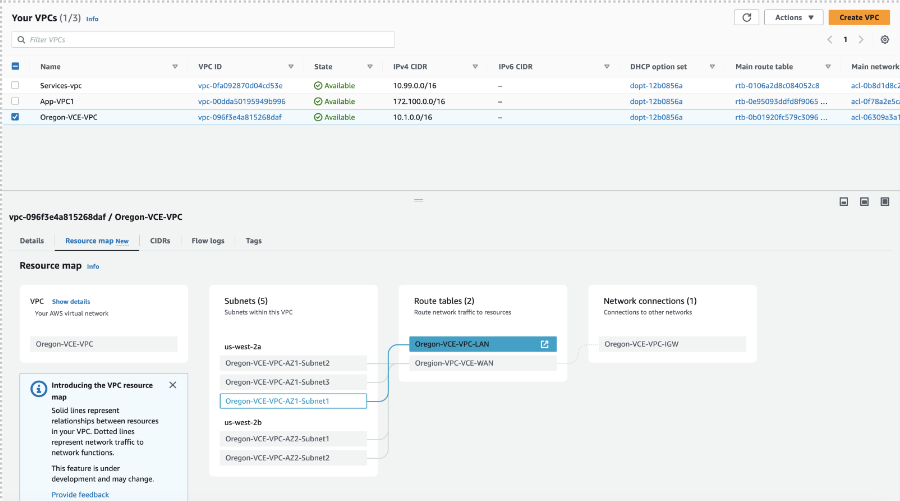
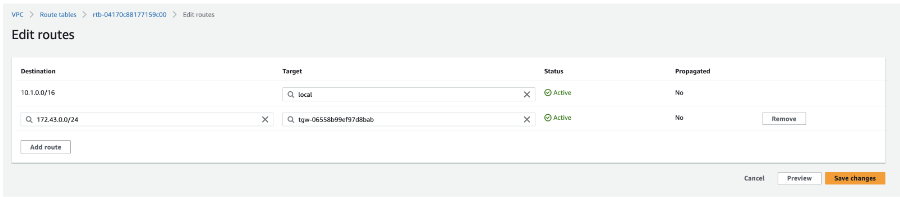
- In the Transit VPC route table, add a route for the TGW CIDR block with Target or Next Hop as the VPC Attachment.
Note: For example, 172.43.0.0/24 is the AWS TGW CIDR block.
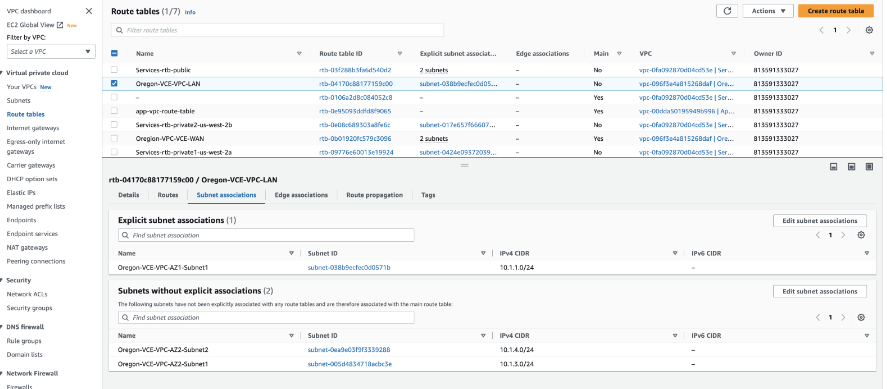
- In the same route table, verify that the LAN EI subnet has an explicit Subnet association.
VMware SASE Orchestrator Configuration Procedure
- On the VMware SASE Orchestrator, go to Network Services > Non SD-WAN Destinations via Edge and configure the GRE Tunnel with the AWS Transit Gateway Connect.
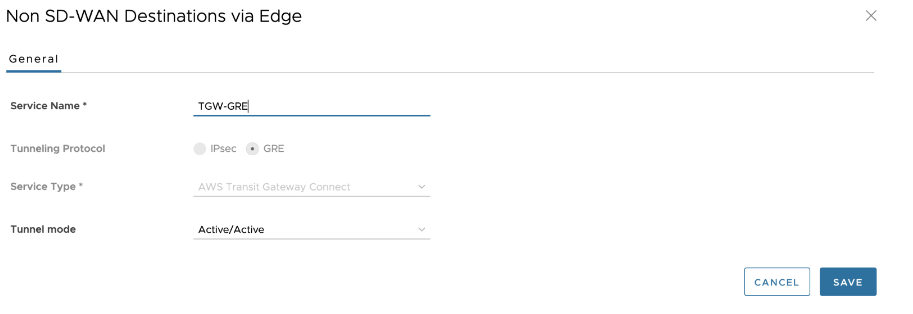 Note: When configuring the GRE Tunnel with the AWS Transit Gateway Connect service, see the following important notes:
Note: When configuring the GRE Tunnel with the AWS Transit Gateway Connect service, see the following important notes:- The only Tunnel Mode parameter that can be configured is Active/Active.
- There are no Keepalive mechanisms for the GRE tunnel with the AWS Transit Gateway Service.
- BGP will be configured by default for the GRE tunnels. BGP Keepalive(s) are used for the BGP neighbor status.
- The Edge does not support ECMP across multiple tunnels. Therefore, only one GRE Tunnel will be used for egress Traffic.
- Under Profile, enable CloudVPN, enable Non SD-WAN Destination via Edge, and choose NSD.
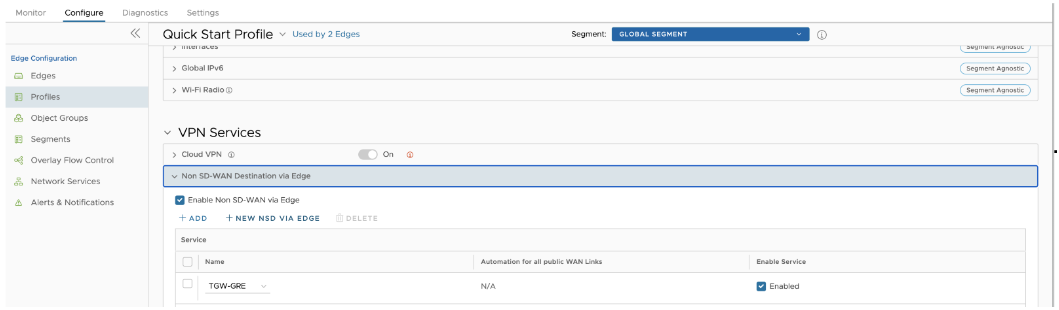
- Under the Edge configuration in the Non SD-WAN Destinations via Edge, select the configured NSD.
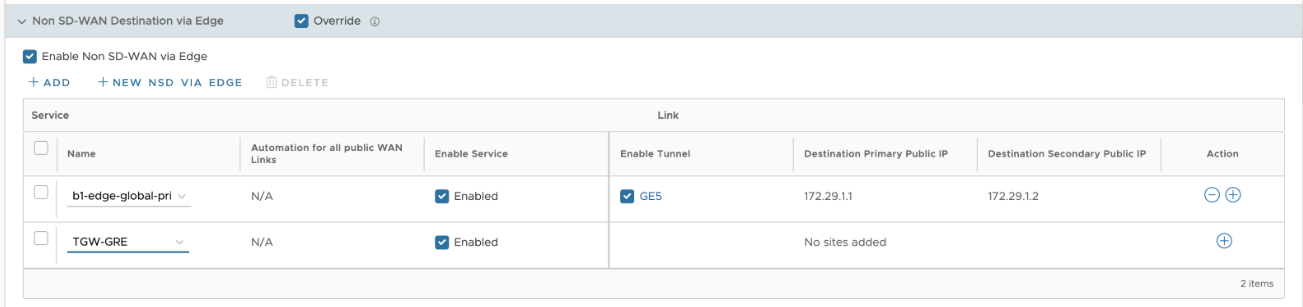
- For the specific NSD, configure the GRE tunnel parameters by selecting the + sign. Configure the following below:
- Tunnel Source as the LAN interface
- Tunnel Source IP as the IP address configured on the LAN interface, if specified dynamically use Remote Diagnostics > Interface Stats to obtain the IP address
- TGW ASN
- The Primary Tunnel parameters can be configured by providing, Destination IP, the IP address provided on the TGW Connect Peer
- The Internal Network/Mask must be the same as specified in the TGW Connect Peer Inside configuration.
- The Secondary Tunnel parameters can be configured for the Destination IP and Internal Network/Mask.
 Note: BGP will be enabled by default for this feature. Local ASN field will be pre-populated.
Note: BGP will be enabled by default for this feature. Local ASN field will be pre-populated.The Non SD-WAN via Edge configuration displays, as shown in the image.
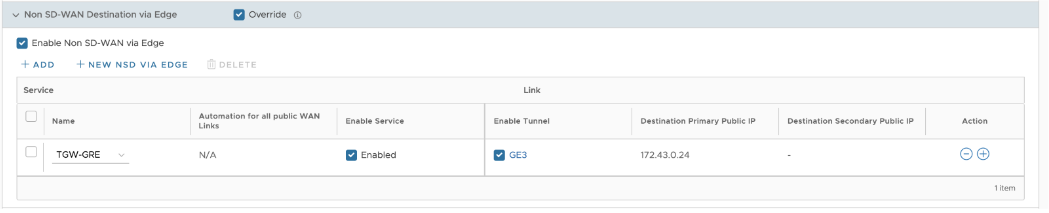
- The above configuration will automatically create the BGP configuration for the Neighbors. Each GRE Tunnel configuration towards the AWS Transit Gateway will automatically be created for two BGP Neighbors with information regarding the Link Name, Neighbor IP, Tunnel Type, and ASN.
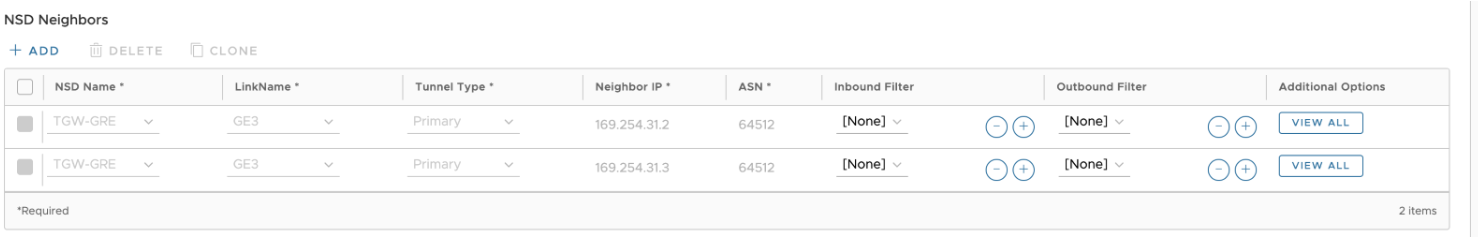 In Additional Options, the eBGP Max Hop is configured as 2, as this is a requirement for the TGW Connect Service. The additional parameters that are populated are Keepalive and Hold Timer based off the recommendation provided by AWS. The BGP Local IP is also pre-populated. These parameters cannot be modified.
In Additional Options, the eBGP Max Hop is configured as 2, as this is a requirement for the TGW Connect Service. The additional parameters that are populated are Keepalive and Hold Timer based off the recommendation provided by AWS. The BGP Local IP is also pre-populated. These parameters cannot be modified.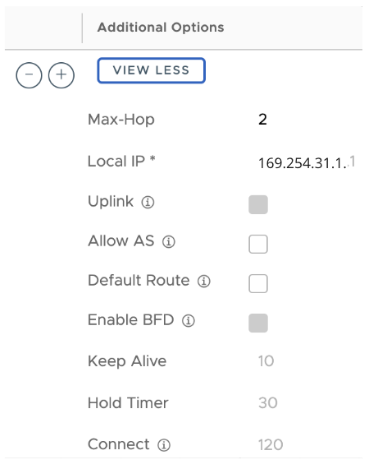 Note:
Note:- Two NSD BGP Neighbors will be automatically added.
- The Additional Options field will be modified for Max-Hop, Local IP, Keep Alive, and Hold Timer values.
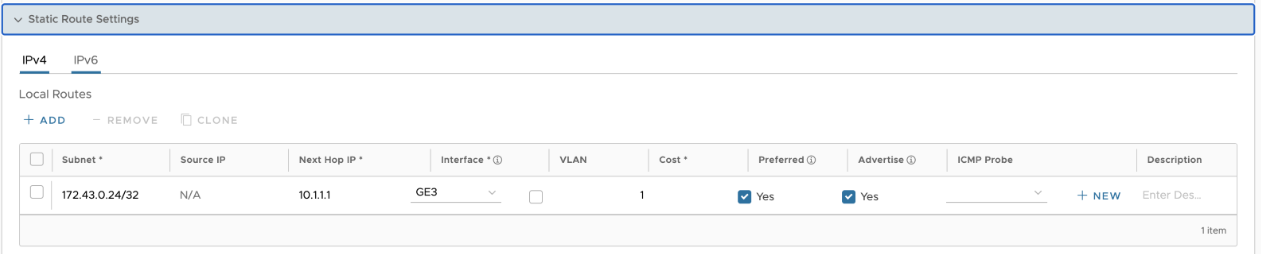
- For the GRE tunnel endpoint, configure a static route on the VMware SD-WAN Edge which specifies the Next-Hop to specify the Subnet Default Gateway and Interface as the LAN interface.