This topic tells you about on-demand services, including VMware SQL with MySQL for Tanzu Application Service.
Service network requirement
When you deploy VMware Tanzu Application Service for VMs (TAS for VMs), you must create a statically defined network to host the component VMs that make up the infrastructure. Components, such as Cloud Controller and UAA, run on this infrastructure network.
On-Demand services might require you to host them on a separate network from the default network. You can also deploy on-demand services on a separate service networks to meet your own security requirements.
TAS for VMs supports dynamic networking. You can use dynamic networking with asynchronous service provisioning to define dynamically-provisioned service networks. For more information, see Default network and service network.
On-Demand services are enabled by default on all networks. You can create separate networks to host services in BOSH Director, if required. You can select which network hosts on-demand service instances when you configure the tile for that service.
Default network and service network
On-demand VMware SQL with MySQL for TAS services use BOSH to dynamically deploy VMs and create single-tenant service instances in a dedicated network. On-demand services use the dynamically-provisioned service network to host single-tenant worker VMs. These worker VMs run as service instances within development spaces.
This on-demand architecture has the following advantages:
- Developers can provision IaaS resources for their services instances when the instances are created. This removes the need for operators to pre-provision a fixed amount of IaaS resources when they deploy the service broker.
- Service instances run on a dedicated VM and do not share VMs with unrelated processes. This removes the “noisy neighbor” problem, where an app monopolizes resources on a shared cluster.
- Single-tenant services can support regulatory compliances where sensitive data must be separated across different machines.
An on-demand service separates operations between the default network and the service network. Shared service components, such as executive controllers and databases, Cloud Controller, UAA, and other on-demand components, run on the default network. Worker pools deployed to specific spaces run on the service network.
The following diagram shows worker VMs in an on-demand service instance running on a separate services network, while other components run on the default network.
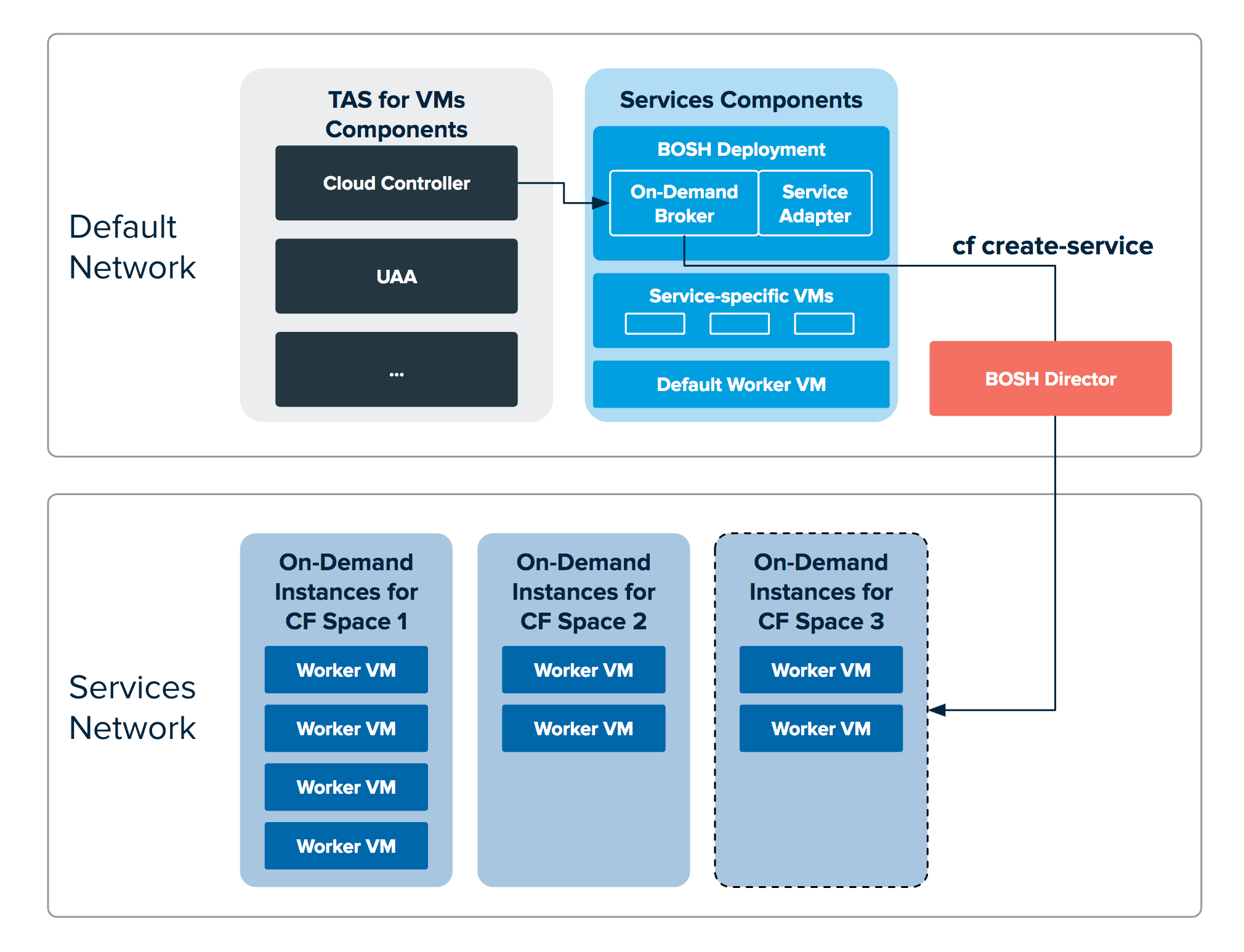
Required networking rules for on-demand services
Before deploying a service tile that uses the on-demand service broker (ODB), you must create networking rules to enable components to communicate with ODB. For instructions for creating networking rules, see the documentation for your IaaS.
The following table lists key components and their responsibilities in the on-demand architecture.
| Key Components | Component Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| BOSH Director | Creates and updates service instances as instructed by ODB. |
| BOSH Agent | Adds an agent on every VM that it deploys. The agent listens for instructions from the BOSH Director and executes those instructions. The agent receives job specifications from the BOSH Director and uses them to assign a role or job to the VM. |
| BOSH UAA | Issues OAuth2 tokens for clients to use when they act on behalf of BOSH users. |
| VMware Tanzu Application Service for VMs | Contains the apps that consume services. |
| ODB | Instructs BOSH to create and update services. Connects to services to create bindings. |
| Deployed service instance | Runs the given service. For example, a deployed VMware SQL with MySQL for TAS service instance runs the VMware SQL with MySQL for TAS service. |
Required networking rules for VMware SQL with MySQL for TAS
Regardless of the specific network layout, you must set network rules.
To ensure that connections are open, see the following table:
| Source component | Destination component | Default TCP port | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| BOSH Agent | BOSH Director | 4222 | The BOSH Agent runs on every VM in the system, including the BOSH Director VM. The BOSH Agent initiates the connection with the BOSH Director. The default port is not configurable. The communication between these components is two-way. |
| Broker and service instances | Doppler on VMware Tanzu Application Service for VMs (TAS for VMs) | 8082 | This port is for metrics. |
| Deployed apps on TAS for VMs | MySQL service instances | 3306 | This port is for general use, app-specific tasks. In addition to configuring your IaaS, create a security group for the MySQL service instance. |
| ODB | BOSH Director BOSH UAA |
25555 (BOSH Director) 8443 (UAA) 8844 (CredHub) |
The default ports are not configurable. |
| ODB | MySQL service instances | 8443 3306 |
This connection is for administrative tasks. Avoid opening general use, app-specific ports for this connection. |
| ODB | TAS for VMs | 8443 | The default port is not configurable. |
| TAS for VMs | ODB | 8080 | This port allows TAS for VMs to communicate with the ODB component. |
| TAS for VMs | ODB | 2345 | This port allows TAS for VMs to communicate with the ODB component so that the ApplicationDataBackupRestore (adbr) API can take backups. |
| Deployed apps on TAS for VMs | Runtime CredHub | 8844 | This port is needed if secure service binding credentials are enabled. For information, see Configure Security. |
| TAS for VMs | MySQL service instances | 8853 | This port is for DNS to run health checks against services instances. |
Required networking rules for leader-follower plans
If you are using a leader-follower service plan, you must set network rules in addition to the networking rules required for VMware SQL with MySQL for TAS.
To ensure that connections are open, see the following table:
| Source VM | Destination VM | Default TCP port | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leader VM | Follower VM | 8443 8081 |
This port is needed if leader-follower is enabled. For more information, see Networking Rules. The communication between these VMs is two-way. |
Required networking rules for highly available cluster plans
If you are using a HA cluster service plan, the operator must set network rules in addition to the networking rules required for VMware SQL with MySQL for TAS.
To ensure that connections are open, see the following table:
| Source VM | Destination VM | Default TCP port | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| TAS for VMs | MySQL service instances | 8083 | This port is needed to monitor cluster health with Switchboard. For more information, see Monitoring node health (HA cluster). |
| Jumpbox VM | TAS for VMs UAA | 8443 | This port is needed so that the replication canary can create a UAA client for sending email notifications. For more information, see About the replication canary. |
| HA cluster node | HA cluster node | 4567 4568 4444 |
This port is needed to maintain network connectivity between nodes in an HA cluster. For more information, see Firewall Configuration in the Percona documentation. The communication between these VMs is two way. |
| Galera healthcheck | Galera healthcheck | 9200 | This port is for monitoring the health of nodes in an HA cluster. The communication between these VMs is two way. |
Required networking rules for Multi‑Site Replication
If you are using multi‑site replication, you must set network rules for both foundations in addition to the networking rules required for VMware SQL with MySQL for TAS.
To ensure that connections are open in both foundations, see the following table:
| Source VM | Destination VM | Default TCP port | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leader VM | Follower VM | 8081 8443 18443 3306 |
These ports are needed to enable replication between services instance in two different foundations. The communication between these VMs is two way. |