Bitnami package for Valkey Cluster
Valkey is an open source (BSD) high-performance key/value datastore that supports a variety workloads such as caching, message queues, and can act as a primary database.
Trademarks: This software listing is packaged by Bitnami. The respective trademarks mentioned in the offering are owned by the respective companies, and use of them does not imply any affiliation or endorsement.
TL;DR
helm install my-release oci://REGISTRY_NAME/REPOSITORY_NAME/valkey-cluster
Note: You need to substitute the placeholders
REGISTRY_NAMEandREPOSITORY_NAMEwith a reference to your Helm chart registry and repository.
Introduction
This chart bootstraps a Valkey deployment on a Kubernetes cluster using the Helm package manager.
Bitnami charts can be used with Kubeapps for deployment and management of Helm Charts in clusters.
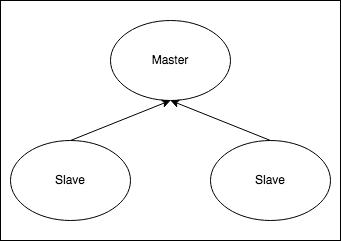
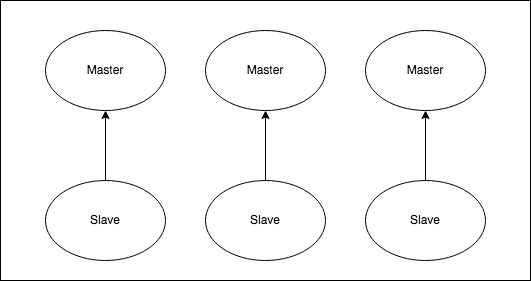
Choose between Valkey Helm Chart and Valkey Cluster Helm Chart
You can choose any of the two Valkey Helm charts for deploying a Valkey cluster. While Valkey Helm Chart will deploy a master-slave cluster using Valkey Sentinel, the Valkey Cluster Helm Chart will deploy a Valkey Cluster with sharding. The main features of each chart are the following:
| Valkey | Valkey Cluster |
|---|---|
| Supports multiple databases | Supports only one database. Better if you have a big dataset |
| Single write point (single master) | Multiple write points (multiple masters) |
 |
 |
Prerequisites
- Kubernetes 1.23+
- Helm 3.8.0+
- PV provisioner support in the underlying infrastructure
Installing the Chart
To install the chart with the release name my-release:
helm install my-release oci://REGISTRY_NAME/REPOSITORY_NAME/valkey-cluster
Note: You need to substitute the placeholders
REGISTRY_NAMEandREPOSITORY_NAMEwith a reference to your Helm chart registry and repository. For example, in the case of Bitnami, you need to useREGISTRY_NAME=registry-1.docker.ioandREPOSITORY_NAME=bitnamicharts.
The command deploys Valkey on the Kubernetes cluster in the default configuration. The Parameters section lists the parameters that can be configured during installation.
NOTE: if you get a timeout error waiting for the hook to complete increase the default timeout (300s) to a higher one, for example:
helm install --timeout 600s myrelease oci://REGISTRY_NAME/REPOSITORY_NAME/valkey-cluster
Note: You need to substitute the placeholders
REGISTRY_NAMEandREPOSITORY_NAMEwith a reference to your Helm chart registry and repository. For example, in the case of Bitnami, you need to useREGISTRY_NAME=registry-1.docker.ioandREPOSITORY_NAME=bitnamicharts. Tip: List all releases usinghelm list
Configuration and installation details
Resource requests and limits
Bitnami charts allow setting resource requests and limits for all containers inside the chart deployment. These are inside the resources value (check parameter table). Setting requests is essential for production workloads and these should be adapted to your specific use case.
To make this process easier, the chart contains the resourcesPreset values, which automatically sets the resources section according to different presets. Check these presets in the bitnami/common chart. However, in production workloads using resourcePreset is discouraged as it may not fully adapt to your specific needs. Find more information on container resource management in the official Kubernetes documentation.
Rolling VS Immutable tags
It is strongly recommended to use immutable tags in a production environment. This ensures your deployment does not change automatically if the same tag is updated with a different image.
Bitnami will release a new chart updating its containers if a new version of the main container, significant changes, or critical vulnerabilities exist.
Use a different Valkey version
To modify the application version used in this chart, specify a different version of the image using the image.tag parameter and/or a different repository using the image.repository parameter.
Cluster topology
To successfully set the cluster up, it will need to have at least 3 master nodes. The total number of nodes is calculated like- nodes = numOfMasterNodes + numOfMasterNodes * replicas. Hence, the defaults cluster.nodes = 6 and cluster.replicas = 1 means, 3 master and 3 replica nodes will be deployed by the chart.
By default the Valkey Cluster is not accessible from outside the Kubernetes cluster, to access the Valkey Cluster from outside you have to set cluster.externalAccess.enabled=true at deployment time. It will create in the first installation only 6 LoadBalancer services, one for each Valkey node, once you have the external IPs of each service you will need to perform an upgrade passing those IPs to the cluster.externalAccess.service.loadbalancerIP array.
The replicas will be read-only replicas of the masters. By default only one service is exposed (when not using the external access mode). You will connect your client to the exposed service, regardless you need to read or write. When a write operation arrives to a replica it will redirect the client to the proper master node. For example, using valkey-cli you will need to provide the -c flag for valkey-cli to follow the redirection automatically.
Using the external access mode, you can connect to any of the pods and the slaves will redirect the client in the same way as explained before, but the all the IPs will be public.
In case the master crashes, one of his slaves will be promoted to master. The slots stored by the crashed master will be unavailable until the slave finish the promotion. If a master and all his slaves crash, the cluster will be down until one of them is up again. To avoid downtime, it is possible to configure the number of Valkey nodes with cluster.nodes and the number of replicas that will be assigned to each master with cluster.replicas. For example:
cluster.nodes=9( 3 master plus 2 replicas for each master)cluster.replicas=2
Providing the values above, the cluster will have 3 masters and, each master, will have 2 replicas.
NOTE: By default
cluster.initwill be set totruein order to initialize the Valkey Cluster in the first installation. If for testing purposes you only want to deploy or upgrade the nodes but avoiding the creation of the cluster you can setcluster.inittofalse.
Adding a new node to the cluster
There is a job that will be executed using a post-upgrade hook that will allow you to add a new node. To use it, you should provide some parameters to the upgrade:
- Pass as
passwordthe password used in the installation time. If you did not provide a password follow the instructions from the NOTES.txt to get the generated password. - Set the desired number of nodes at
cluster.nodes. - Set the number of current nodes at
cluster.update.currentNumberOfNodes. - Set to true
cluster.update.addNodes.
The following will be an example to add one more node:
helm upgrade --timeout 600s <release> --set "password=${VALKEY_PASSWORD},cluster.nodes=7,cluster.update.addNodes=true,cluster.update.currentNumberOfNodes=6" oci://REGISTRY_NAME/REPOSITORY_NAME/valkey-cluster
Note: You need to substitute the placeholders
REGISTRY_NAMEandREPOSITORY_NAMEwith a reference to your Helm chart registry and repository. For example, in the case of Bitnami, you need to useREGISTRY_NAME=registry-1.docker.ioandREPOSITORY_NAME=bitnamicharts.
Where VALKEY_PASSWORD is the password obtained with the command that appears after the first installation of the Helm Chart. The cluster will continue up while restarting pods one by one as the quorum is not lost.
External Access
If you are using external access, to add a new node you will need to perform two upgrades. First upgrade the release to add a new Valkey node and to get a LoadBalancerIP service. For example:
helm upgrade <release> --set "password=${VALKEY_PASSWORD},cluster.externalAccess.enabled=true,cluster.externalAccess.service.type=LoadBalancer,cluster.externalAccess.service.loadBalancerIP[0]=<loadBalancerip-0>,cluster.externalAccess.service.loadBalancerIP[1]=<loadbalanacerip-1>,cluster.externalAccess.service.loadBalancerIP[2]=<loadbalancerip-2>,cluster.externalAccess.service.loadBalancerIP[3]=<loadbalancerip-3>,cluster.externalAccess.service.loadBalancerIP[4]=<loadbalancerip-4>,cluster.externalAccess.service.loadBalancerIP[5]=<loadbalancerip-5>,cluster.externalAccess.service.loadBalancerIP[6]=,cluster.nodes=7,cluster.init=false oci://REGISTRY_NAME/REPOSITORY_NAME/valkey-cluster
Note: You need to substitute the placeholders
REGISTRY_NAMEandREPOSITORY_NAMEwith a reference to your Helm chart registry and repository. For example, in the case of Bitnami, you need to useREGISTRY_NAME=registry-1.docker.ioandREPOSITORY_NAME=bitnamicharts. Important here to provide the loadBalancerIP parameters for the new nodes empty to not get an index error.
As we want to add a new node, we are setting cluster.nodes=7 and we leave empty the LoadBalancerIP for the new node, so the cluster will provide the correct one. VALKEY_PASSWORD is the password obtained with the command that appears after the first installation of the Helm Chart. At this point, you will have a new Valkey Pod that will remain in crashLoopBackOff state until we provide the LoadBalancerIP for the new service. Now, wait until the cluster provides the new LoadBalancerIP for the new service and perform the second upgrade:
helm upgrade <release> --set "password=${VALKEY_PASSWORD},cluster.externalAccess.enabled=true,cluster.externalAccess.service.type=LoadBalancer,cluster.externalAccess.service.loadBalancerIP[0]=<loadbalancerip-0>,cluster.externalAccess.service.loadBalancerIP[1]=<loadbalancerip-1>,cluster.externalAccess.service.loadBalancerIP[2]=<loadbalancerip-2>,cluster.externalAccess.service.loadBalancerIP[3]=<loadbalancerip-3>,cluster.externalAccess.service.loadBalancerIP[4]=<loadbalancerip-4>,cluster.externalAccess.service.loadBalancerIP[5]=<loadbalancerip-5>,cluster.externalAccess.service.loadBalancerIP[6]=<loadbalancerip-6>,cluster.nodes=7,cluster.init=false,cluster.update.addNodes=true,cluster.update.newExternalIPs[0]=<load-balancerip-6>" oci://REGISTRY_NAME/REPOSITORY_NAME/valkey-cluster
Note: You need to substitute the placeholders
REGISTRY_NAMEandREPOSITORY_NAMEwith a reference to your Helm chart registry and repository. For example, in the case of Bitnami, you need to useREGISTRY_NAME=registry-1.docker.ioandREPOSITORY_NAME=bitnamicharts.
Note we are providing the new IPs at cluster.update.newExternalIPs, the flag cluster.update.addNodes=true to enable the creation of the Job that adds a new node and now we are setting the LoadBalancerIP of the new service instead of leave it empty.
NOTE: To avoid the creation of the Job that initializes the Valkey Cluster again, you will need to provide
cluster.init=false.
Scale down the cluster
To scale down the Valkey Cluster, follow these steps:
First perform a normal upgrade setting the cluster.nodes value to the desired number of nodes. It should not be less than 6 and the difference between current number of nodes and the desired should be less or equal to cluster.replicas to avoid removing master node an its slaves at the same time. Also it is needed to provide the password using the password. For example, having more than 6 nodes, to scale down the cluster to 6 nodes:
helm upgrade --timeout 600s <release> --set "password=${VALKEY_PASSWORD},cluster.nodes=6" .
The cluster will continue working during the update as long as the quorum is not lost.
NOTE: To avoid the creation of the Job that initializes the Valkey Cluster again, you will need to provide
cluster.init=false.
Once all the nodes are ready, get the list of nodes in the cluster using the CLUSTER NODES command. You will see references to the ones that were removed. Write down the node IDs of the nodes that show fail. In the following example the cluster scaled down from 7 to 6 nodes.
valkey-cli -a $VALKEY_PASSWORD CLUSTER NODES
...
b23bcffa1fd64368d445c1d9bd9aeb92641105f7 10.0.0.70:6379@16379 slave,fail - 1645633139060 0 0 connected
...
In each cluster node, execute the following command. Replace the NODE_ID placeholder.
valkey-cli -a $VALKEY_PASSWORD CLUSTER FORGET NODE_ID
In the previous example the commands would look like this in each cluster node:
valkey-cli -a $VALKEY_PASSWORD CLUSTER FORGET b23bcffa1fd64368d445c1d9bd9aeb92641105f7
Using password file
To use a password file for Valkey you need to create a secret containing the password.
NOTE: It is important that the file with the password must be called
valkey-password
And then deploy the Helm Chart using the secret name as parameter:
usePassword=true
usePasswordFile=true
existingSecret=valkey-password-secret
metrics.enabled=true
Securing traffic using TLS
TLS support can be enabled in the chart by specifying the tls. parameters while creating a release. The following parameters should be configured to properly enable the TLS support in the cluster:
tls.enabled: Enable TLS support. Defaults tofalsetls.existingSecret: Name of the secret that contains the certificates. No defaults.tls.certFilename: Certificate filename. No defaults.tls.certKeyFilename: Certificate key filename. No defaults.tls.certCAFilename: CA Certificate filename. No defaults.
For example:
First, create the secret with the certificates files:
kubectl create secret generic certificates-tls-secret --from-file=./cert.pem --from-file=./cert.key --from-file=./ca.pem
Then, use the following parameters:
tls.enabled="true"
tls.existingSecret="certificates-tls-secret"
tls.certFilename="cert.pem"
tls.certKeyFilename="cert.key"
tls.certCAFilename="ca.pem"
Sidecars and Init Containers
If you have a need for additional containers to run within the same pod as Valkey (e.g. an additional metrics or logging exporter), you can do so via the sidecars config parameter. Simply define your container according to the Kubernetes container spec.
sidecars:
- name: your-image-name
image: your-image
imagePullPolicy: Always
ports:
- name: portname
containerPort: 1234
Similarly, you can add extra init containers using the initContainers parameter.
initContainers:
- name: your-image-name
image: your-image
imagePullPolicy: Always
ports:
- name: portname
containerPort: 1234
Adding extra environment variables
In case you want to add extra environment variables (useful for advanced operations like custom init scripts), you can use the extraEnvVars property.
extraEnvVars:
- name: VALKEY_WHATEVER
value: value
Alternatively, you can use a ConfigMap or a Secret with the environment variables. To do so, use the extraEnvVarsCM or the extraEnvVarsSecret values.
Metrics
The chart optionally can start a metrics exporter for prometheus. The metrics endpoint (port 9121) is exposed in the service. Metrics can be scraped from within the cluster using something similar as the described in the example Prometheus scrape configuration. If metrics are to be scraped from outside the cluster, the Kubernetes API proxy can be utilized to access the endpoint.
Host Kernel Settings
Valkey may require some changes in the kernel of the host machine to work as expected, in particular increasing the somaxconn value and disabling transparent huge pages. To do so, you can set up a privileged initContainer with the sysctlImage config values, for example:
sysctlImage:
enabled: true
mountHostSys: true
command:
- /bin/sh
- -c
- |-
sysctl -w net.core.somaxconn=10000
echo never > /host-sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled
Alternatively, for Kubernetes 1.12+ you can set podSecurityContext.sysctls which will configure sysctls for master and slave pods. Example:
podSecurityContext:
sysctls:
- name: net.core.somaxconn
value: "10000"
Note that this will not disable transparent huge tables.
Helm Upgrade
By default cluster.init will be set to true in order to initialize the Valkey Cluster in the first installation. If for testing purposes you only want to deploy or upgrade the nodes but avoiding the creation of the cluster you can set cluster.init to false.
Backup and restore
To back up and restore Valkey Cluster Helm chart deployments on Kubernetes, you need to back up the persistent volumes from the source deployment and attach them to a new deployment using Velero, a Kubernetes backup/restore tool.
These are the steps you will usually follow to back up and restore your Valkey Cluster database cluster data:
- Install Velero on the source and destination clusters.
- Use Velero to back up the PersistentVolumes (PVs) used by the deployment on the source cluster.
- Use Velero to restore the backed-up PVs on the destination cluster.
- Create a new deployment on the destination cluster with the same chart, deployment name, credentials and other parameters as the original. This new deployment will use the restored PVs and hence the original data.
NetworkPolicy
To enable network policy for Valkey, install a networking plugin that implements the Kubernetes NetworkPolicy spec, and set networkPolicy.enabled to true.
For Kubernetes v1.5 & v1.6, you must also turn on NetworkPolicy by setting the DefaultDeny namespace annotation. Note: this will enforce policy for all pods in the namespace:
kubectl annotate namespace default "net.beta.kubernetes.io/network-policy={\"ingress\":{\"isolation\":\"DefaultDeny\"}}"
With NetworkPolicy enabled, only pods with the generated client label will be able to connect to Valkey. This label will be displayed in the output after a successful install.
With networkPolicy.ingressNSMatchLabels pods from other namespaces can connect to valkey. Set networkPolicy.ingressNSPodMatchLabels to match pod labels in matched namespace. For example, for a namespace labeled valkey=external and pods in that namespace labeled valkey-client=true the fields should be set:
networkPolicy:
enabled: true
ingressNSMatchLabels:
valkey: external
ingressNSPodMatchLabels:
valkey-client: true
Setting Pod’s affinity
This chart allows you to set your custom affinity using the XXX.affinity paremeter(s). Find more information about Pod’s affinity in the kubernetes documentation.
As an alternative, you can use of the preset configurations for pod affinity, pod anti-affinity, and node affinity available at the bitnami/common chart. To do so, set the XXX.podAffinityPreset, XXX.podAntiAffinityPreset, or XXX.nodeAffinityPreset parameters.
Persistence
By default, the chart mounts a Persistent Volume at the /bitnami path. The volume is created using dynamic volume provisioning.
If persistence is disabled, an emptyDir volume is used. This is only recommended for testing environments because the required information included in the nodes.conf file is missing. This file contains the relationship between the nodes and the cluster. For example, if any node is down or faulty, when it starts again, it is a self-proclaimed master and also acts as an independent node outside the main cluster as it doesn’t have the necessary information to connect to it.
To reconnect the failed node, run the following:
See nodes.sh
$ cat /bitnami/valkey/data/nodes.sh
declare -A host_2_ip_array=([valkey-node-0]="192.168.192.6" [valkey-node-1]="192.168.192.2" [valkey-node-2]="192.168.192.4" [valkey-node-3]="192.168.192.5" [valkey-node-4]="192.168.192.3" [valkey-node-5]="192.168.192.7" )
Run valkey-cli and run CLUSTER MEET to any other node in the cluster. Now the node has connected to the main cluster.
$ REDISCLI_AUTH=bitnami valkey-cli
127.0.0.1:6379> cluster meet 192.168.192.7 6379
OK
Parameters
Global parameters
| Name | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
global.imageRegistry |
Global Docker image registry | "" |
global.imagePullSecrets |
Global Docker registry secret names as an array | [] |
global.defaultStorageClass |
Global default StorageClass for Persistent Volume(s) | "" |
global.storageClass |
DEPRECATED: use global.defaultStorageClass instead | "" |
global.valkey.password |
Valkey password (overrides password) |
"" |
global.compatibility.openshift.adaptSecurityContext |
Adapt the securityContext sections of the deployment to make them compatible with Openshift restricted-v2 SCC: remove runAsUser, runAsGroup and fsGroup and let the platform use their allowed default IDs. Possible values: auto (apply if the detected running cluster is Openshift), force (perform the adaptation always), disabled (do not perform adaptation) | auto |
Valkey Cluster Common parameters
| Name | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
nameOverride |
String to partially override common.names.fullname template (will maintain the release name) | "" |
fullnameOverride |
String to fully override common.names.fullname template | "" |
clusterDomain |
Kubernetes Cluster Domain | cluster.local |
commonAnnotations |
Annotations to add to all deployed objects | {} |
commonLabels |
Labels to add to all deployed objects | {} |
extraDeploy |
Array of extra objects to deploy with the release (evaluated as a template) | [] |
diagnosticMode.enabled |
Enable diagnostic mode (all probes will be disabled and the command will be overridden) | false |
diagnosticMode.command |
Command to override all containers in the deployment | ["sleep"] |
diagnosticMode.args |
Args to override all containers in the deployment | ["infinity"] |
image.registry |
Valkey cluster image registry | REGISTRY_NAME |
image.repository |
Valkey cluster image repository | REPOSITORY_NAME/valkey-cluster |
image.digest |
Valkey cluster image digest in the way sha256:aa…. Please note this parameter, if set, will override the tag | "" |
image.pullPolicy |
Valkey cluster image pull policy | IfNotPresent |
image.pullSecrets |
Specify docker-registry secret names as an array | [] |
image.debug |
Enable image debug mode | false |
networkPolicy.enabled |
Enable creation of NetworkPolicy resources | true |
networkPolicy.allowExternal |
The Policy model to apply | true |
networkPolicy.allowExternalEgress |
Allow the pod to access any range of port and all destinations. | true |
networkPolicy.extraIngress |
Add extra ingress rules to the NetworkPolicy | [] |
networkPolicy.extraEgress |
Add extra ingress rules to the NetworkPolicy | [] |
networkPolicy.ingressNSMatchLabels |
Labels to match to allow traffic from other namespaces | {} |
networkPolicy.ingressNSPodMatchLabels |
Pod labels to match to allow traffic from other namespaces | {} |
serviceAccount.create |
Specifies whether a ServiceAccount should be created | true |
serviceAccount.name |
The name of the ServiceAccount to create | "" |
serviceAccount.annotations |
Annotations for Cassandra Service Account | {} |
serviceAccount.automountServiceAccountToken |
Automount API credentials for a service account. | false |
rbac.create |
Specifies whether RBAC resources should be created | false |
rbac.role.rules |
Rules to create. It follows the role specification | [] |
podSecurityContext.enabled |
Enable Valkey pod Security Context | true |
podSecurityContext.fsGroupChangePolicy |
Set filesystem group change policy | Always |
podSecurityContext.supplementalGroups |
Set filesystem extra groups | [] |
podSecurityContext.fsGroup |
Group ID for the pods | 1001 |
podSecurityContext.sysctls |
Set namespaced sysctls for the pods | [] |
podDisruptionBudget |
DEPRECATED please use pdb instead | {} |
pdb.create |
Created a PodDisruptionBudget | true |
pdb.minAvailable |
Min number of pods that must still be available after the eviction. | "" |
pdb.maxUnavailable |
Max number of pods that can be unavailable after the eviction. | "" |
containerSecurityContext.enabled |
Enabled containers’ Security Context | true |
containerSecurityContext.seLinuxOptions |
Set SELinux options in container | nil |
containerSecurityContext.runAsUser |
Set containers’ Security Context runAsUser | 1001 |
containerSecurityContext.runAsGroup |
Set containers’ Security Context runAsGroup | 1001 |
containerSecurityContext.runAsNonRoot |
Set container’s Security Context runAsNonRoot | true |
containerSecurityContext.privileged |
Set container’s Security Context privileged | false |
containerSecurityContext.readOnlyRootFilesystem |
Set container’s Security Context readOnlyRootFilesystem | true |
containerSecurityContext.allowPrivilegeEscalation |
Set container’s Security Context allowPrivilegeEscalation | false |
containerSecurityContext.capabilities.drop |
List of capabilities to be dropped | ["ALL"] |
containerSecurityContext.seccompProfile.type |
Set container’s Security Context seccomp profile | RuntimeDefault |
usePassword |
Use password authentication | true |
password |
Valkey password (ignored if existingSecret set) | "" |
existingSecret |
Name of existing secret object (for password authentication) | "" |
existingSecretPasswordKey |
Name of key containing password to be retrieved from the existing secret | "" |
usePasswordFile |
Mount passwords as files instead of environment variables | false |
tls.enabled |
Enable TLS support for replication traffic | false |
tls.authClients |
Require clients to authenticate or not | true |
tls.autoGenerated |
Generate automatically self-signed TLS certificates | false |
tls.existingSecret |
The name of the existing secret that contains the TLS certificates | "" |
tls.certificatesSecret |
DEPRECATED. Use tls.existingSecret instead | "" |
tls.certFilename |
Certificate filename | "" |
tls.certKeyFilename |
Certificate key filename | "" |
tls.certCAFilename |
CA Certificate filename | "" |
tls.dhParamsFilename |
File containing DH params (in order to support DH based ciphers) | "" |
service.ports.valkey |
Kubernetes Valkey service port | 6379 |
service.nodePorts.valkey |
Node port for Valkey | "" |
service.extraPorts |
Extra ports to expose in the service (normally used with the sidecar value) |
[] |
service.annotations |
Provide any additional annotations which may be required. | {} |
service.labels |
Additional labels for valkey service | {} |
service.type |
Service type for default valkey service | ClusterIP |
service.clusterIP |
Service Cluster IP | "" |
service.loadBalancerIP |
Load balancer IP if service.type is LoadBalancer |
"" |
service.loadBalancerSourceRanges |
Service Load Balancer sources | [] |
service.externalTrafficPolicy |
Service external traffic policy | Cluster |
service.sessionAffinity |
Session Affinity for Kubernetes service, can be “None” or “ClientIP” | None |
service.sessionAffinityConfig |
Additional settings for the sessionAffinity | {} |
service.headless.annotations |
Annotations for the headless service. | {} |
persistence.enabled |
Enable persistence on Valkey | true |
persistence.path |
Path to mount the volume at, to use other images Valkey images. | /bitnami/valkey/data |
persistence.subPath |
The subdirectory of the volume to mount to, useful in dev environments and one PV for multiple services | "" |
persistence.storageClass |
Storage class of backing PVC | "" |
persistence.annotations |
Persistent Volume Claim annotations | {} |
persistence.labels |
Persistent Volume Claim labels | {} |
persistence.accessModes |
Persistent Volume Access Modes | ["ReadWriteOnce"] |
persistence.size |
Size of data volume | 8Gi |
persistence.matchLabels |
Persistent Volume selectors | {} |
persistence.matchExpressions |
matchExpressions Persistent Volume selectors | {} |
persistentVolumeClaimRetentionPolicy.enabled |
Controls if and how PVCs are deleted during the lifecycle of a StatefulSet | false |
persistentVolumeClaimRetentionPolicy.whenScaled |
Volume retention behavior when the replica count of the StatefulSet is reduced | Retain |
persistentVolumeClaimRetentionPolicy.whenDeleted |
Volume retention behavior that applies when the StatefulSet is deleted | Retain |
volumePermissions.enabled |
Enable init container that changes volume permissions in the registry (for cases where the default k8s runAsUser and fsUser values do not work) |
false |
volumePermissions.image.registry |
Init container volume-permissions image registry | REGISTRY_NAME |
volumePermissions.image.repository |
Init container volume-permissions image repository | REPOSITORY_NAME/os-shell |
volumePermissions.image.digest |
Init container volume-permissions image digest in the way sha256:aa…. Please note this parameter, if set, will override the tag | "" |
volumePermissions.image.pullPolicy |
Init container volume-permissions image pull policy | IfNotPresent |
volumePermissions.image.pullSecrets |
Specify docker-registry secret names as an array | [] |
volumePermissions.containerSecurityContext.enabled |
Enable Containers’ Security Context | true |
volumePermissions.containerSecurityContext.seLinuxOptions |
Set SELinux options in container | nil |
volumePermissions.containerSecurityContext.runAsUser |
User ID for the containers. | 0 |
volumePermissions.containerSecurityContext.privileged |
Run container as privileged | false |
volumePermissions.resourcesPreset |
Set container resources according to one common preset (allowed values: none, nano, micro, small, medium, large, xlarge, 2xlarge). This is ignored if volumePermissions.resources is set (volumePermissions.resources is recommended for production). | nano |
volumePermissions.resources |
Set container requests and limits for different resources like CPU or memory (essential for production workloads) | {} |
Valkey statefulset parameters
| Name | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
valkey.command |
Valkey entrypoint string. The command valkey-server is executed if this is not provided |
[] |
valkey.args |
Arguments for the provided command if needed | [] |
valkey.updateStrategy.type |
Argo Workflows statefulset strategy type | RollingUpdate |
valkey.updateStrategy.rollingUpdate.partition |
Partition update strategy | 0 |
valkey.podManagementPolicy |
Statefulset Pod management policy, it needs to be Parallel to be able to complete the cluster join | Parallel |
valkey.automountServiceAccountToken |
Mount Service Account token in pod | false |
valkey.hostAliases |
Deployment pod host aliases | [] |
valkey.hostNetwork |
Host networking requested for this pod. Use the host’s network namespace. | false |
valkey.useAOFPersistence |
Whether to use AOF Persistence mode or not | yes |
valkey.containerPorts.valkey |
Valkey port | 6379 |
valkey.containerPorts.bus |
The busPort should be obtained adding 10000 to the valkeyPort. By default: 10000 + 6379 = 16379 | 16379 |
valkey.lifecycleHooks |
LifecycleHook to set additional configuration before or after startup. Evaluated as a template | {} |
valkey.extraVolumes |
Extra volumes to add to the deployment | [] |
valkey.extraVolumeMounts |
Extra volume mounts to add to the container | [] |
valkey.customLivenessProbe |
Override default liveness probe | {} |
valkey.customReadinessProbe |
Override default readiness probe | {} |
valkey.customStartupProbe |
Custom startupProbe that overrides the default one | {} |
valkey.initContainers |
Extra init containers to add to the deployment | [] |
valkey.sidecars |
Extra sidecar containers to add to the deployment | [] |
valkey.podLabels |
Additional labels for Valkey pod | {} |
valkey.priorityClassName |
Valkey Master pod priorityClassName | "" |
valkey.defaultConfigOverride |
Optional default Valkey configuration for the nodes | "" |
valkey.configmap |
Additional Valkey configuration for the nodes | "" |
valkey.extraEnvVars |
An array to add extra environment variables | [] |
valkey.extraEnvVarsCM |
ConfigMap with extra environment variables | "" |
valkey.extraEnvVarsSecret |
Secret with extra environment variables | "" |
valkey.podAnnotations |
Valkey additional annotations | {} |
valkey.resourcesPreset |
Set container resources according to one common preset (allowed values: none, nano, micro, small, medium, large, xlarge, 2xlarge). This is ignored if valkey.resources is set (valkey.resources is recommended for production). | nano |
valkey.resources |
Set container requests and limits for different resources like CPU or memory (essential for production workloads) | {} |
valkey.schedulerName |
Use an alternate scheduler, e.g. “stork”. | "" |
valkey.shareProcessNamespace |
Enable shared process namespace in a pod. | false |
valkey.livenessProbe.enabled |
Enable livenessProbe | true |
valkey.livenessProbe.initialDelaySeconds |
Initial delay seconds for livenessProbe | 5 |
valkey.livenessProbe.periodSeconds |
Period seconds for livenessProbe | 5 |
valkey.livenessProbe.timeoutSeconds |
Timeout seconds for livenessProbe | 5 |
valkey.livenessProbe.failureThreshold |
Failure threshold for livenessProbe | 5 |
valkey.livenessProbe.successThreshold |
Success threshold for livenessProbe | 1 |
valkey.readinessProbe.enabled |
Enable readinessProbe | true |
valkey.readinessProbe.initialDelaySeconds |
Initial delay seconds for readinessProbe | 5 |
valkey.readinessProbe.periodSeconds |
Period seconds for readinessProbe | 5 |
valkey.readinessProbe.timeoutSeconds |
Timeout seconds for readinessProbe | 1 |
valkey.readinessProbe.failureThreshold |
Failure threshold for readinessProbe | 5 |
valkey.readinessProbe.successThreshold |
Success threshold for readinessProbe | 1 |
valkey.startupProbe.enabled |
Enable startupProbe | false |
valkey.startupProbe.path |
Path to check for startupProbe | / |
valkey.startupProbe.initialDelaySeconds |
Initial delay seconds for startupProbe | 300 |
valkey.startupProbe.periodSeconds |
Period seconds for startupProbe | 10 |
valkey.startupProbe.timeoutSeconds |
Timeout seconds for startupProbe | 5 |
valkey.startupProbe.failureThreshold |
Failure threshold for startupProbe | 6 |
valkey.startupProbe.successThreshold |
Success threshold for startupProbe | 1 |
valkey.podAffinityPreset |
Valkey pod affinity preset. Ignored if valkey.affinity is set. Allowed values: soft or hard |
"" |
valkey.podAntiAffinityPreset |
Valkey pod anti-affinity preset. Ignored if valkey.affinity is set. Allowed values: soft or hard |
soft |
valkey.nodeAffinityPreset.type |
Valkey node affinity preset type. Ignored if valkey.affinity is set. Allowed values: soft or hard |
"" |
valkey.nodeAffinityPreset.key |
Valkey node label key to match Ignored if valkey.affinity is set. |
"" |
valkey.nodeAffinityPreset.values |
Valkey node label values to match. Ignored if valkey.affinity is set. |
[] |
valkey.affinity |
Affinity settings for Valkey pod assignment | {} |
valkey.nodeSelector |
Node labels for Valkey pods assignment | {} |
valkey.tolerations |
Tolerations for Valkey pods assignment | [] |
valkey.topologySpreadConstraints |
Pod topology spread constraints for Valkey pod | [] |
Cluster update job parameters
| Name | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
updateJob.activeDeadlineSeconds |
Number of seconds the Job to create the cluster will be waiting for the Nodes to be ready. | 600 |
updateJob.command |
Container command (using container default if not set) | [] |
updateJob.args |
Container args (using container default if not set) | [] |
updateJob.automountServiceAccountToken |
Mount Service Account token in pod | false |
updateJob.hostAliases |
Deployment pod host aliases | [] |
updateJob.helmHook |
Job Helm hook | post-upgrade |
updateJob.annotations |
Job annotations | {} |
updateJob.podAnnotations |
Job pod annotations | {} |
updateJob.podLabels |
Pod extra labels | {} |
updateJob.extraEnvVars |
An array to add extra environment variables | [] |
updateJob.extraEnvVarsCM |
ConfigMap containing extra environment variables | "" |
updateJob.extraEnvVarsSecret |
Secret containing extra environment variables | "" |
updateJob.extraVolumes |
Extra volumes to add to the deployment | [] |
updateJob.extraVolumeMounts |
Extra volume mounts to add to the container | [] |
updateJob.initContainers |
Extra init containers to add to the deployment | [] |
updateJob.podAffinityPreset |
Update job pod affinity preset. Ignored if updateJob.affinity is set. Allowed values: soft or hard |
"" |
updateJob.podAntiAffinityPreset |
Update job pod anti-affinity preset. Ignored if updateJob.affinity is set. Allowed values: soft or hard |
soft |
updateJob.nodeAffinityPreset.type |
Update job node affinity preset type. Ignored if updateJob.affinity is set. Allowed values: soft or hard |
"" |
updateJob.nodeAffinityPreset.key |
Update job node label key to match Ignored if updateJob.affinity is set. |
"" |
updateJob.nodeAffinityPreset.values |
Update job node label values to match. Ignored if updateJob.affinity is set. |
[] |
updateJob.affinity |
Affinity for update job pods assignment | {} |
updateJob.nodeSelector |
Node labels for update job pods assignment | {} |
updateJob.tolerations |
Tolerations for update job pods assignment | [] |
updateJob.priorityClassName |
Priority class name | "" |
updateJob.resourcesPreset |
Set container resources according to one common preset (allowed values: none, nano, micro, small, medium, large, xlarge, 2xlarge). This is ignored if updateJob.resources is set (updateJob.resources is recommended for production). | nano |
updateJob.resources |
Set container requests and limits for different resources like CPU or memory (essential for production workloads) | {} |
Cluster management parameters
| Name | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
cluster.init |
Enable the initialization of the Valkey Cluster | true |
cluster.nodes |
The number of master nodes should always be >= 3, otherwise cluster creation will fail | 6 |
cluster.replicas |
Number of replicas for every master in the cluster | 1 |
cluster.externalAccess.enabled |
Enable access to the Valkey | false |
cluster.externalAccess.hostMode |
Set cluster preferred endpoint type as hostname | false |
cluster.externalAccess.service.disableLoadBalancerIP |
Disable use of Service.spec.loadBalancerIP |
false |
cluster.externalAccess.service.loadBalancerIPAnnotaion |
Name of annotation to specify fixed IP for service in. Disables Service.spec.loadBalancerIP if not empty |
"" |
cluster.externalAccess.service.type |
Type for the services used to expose every Pod | LoadBalancer |
cluster.externalAccess.service.port |
Port for the services used to expose every Pod | 6379 |
cluster.externalAccess.service.loadBalancerIP |
Array of load balancer IPs for each Valkey node. Length must be the same as cluster.nodes | [] |
cluster.externalAccess.service.loadBalancerSourceRanges |
Service Load Balancer sources | [] |
cluster.externalAccess.service.annotations |
Annotations to add to the services used to expose every Pod of the Valkey Cluster | {} |
cluster.update.addNodes |
Boolean to specify if you want to add nodes after the upgrade | false |
cluster.update.currentNumberOfNodes |
Number of currently deployed Valkey nodes | 6 |
cluster.update.currentNumberOfReplicas |
Number of currently deployed Valkey replicas | 1 |
cluster.update.newExternalIPs |
External IPs obtained from the services for the new nodes to add to the cluster | [] |
Metrics sidecar parameters
| Name | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
metrics.enabled |
Start a side-car prometheus exporter | false |
metrics.image.registry |
Valkey exporter image registry | REGISTRY_NAME |
metrics.image.repository |
Valkey exporter image name | REPOSITORY_NAME/redis-exporter |
metrics.image.digest |
Valkey exporter image digest in the way sha256:aa…. Please note this parameter, if set, will override the tag | "" |
metrics.image.pullPolicy |
Valkey exporter image pull policy | IfNotPresent |
metrics.image.pullSecrets |
Specify docker-registry secret names as an array | [] |
metrics.resourcesPreset |
Set container resources according to one common preset (allowed values: none, nano, micro, small, medium, large, xlarge, 2xlarge). This is ignored if metrics.resources is set (metrics.resources is recommended for production). | nano |
metrics.resources |
Set container requests and limits for different resources like CPU or memory (essential for production workloads) | {} |
metrics.extraArgs |
Extra arguments for the binary; possible values here | {} |
metrics.extraEnvVars |
Array with extra environment variables to add to Valkey exporter | [] |
metrics.containerPorts.http |
Metrics HTTP container port | 9121 |
metrics.podAnnotations |
Additional annotations for Metrics exporter pod | {} |
metrics.podLabels |
Additional labels for Metrics exporter pod | {} |
metrics.containerSecurityContext.enabled |
Enabled containers’ Security Context | true |
metrics.containerSecurityContext.seLinuxOptions |
Set SELinux options in container | nil |
metrics.containerSecurityContext.runAsUser |
Set containers’ Security Context runAsUser | 1001 |
metrics.containerSecurityContext.runAsGroup |
Set containers’ Security Context runAsGroup | 1001 |
metrics.containerSecurityContext.runAsNonRoot |
Set container’s Security Context runAsNonRoot | true |
metrics.containerSecurityContext.privileged |
Set container’s Security Context privileged | false |
metrics.containerSecurityContext.readOnlyRootFilesystem |
Set container’s Security Context readOnlyRootFilesystem | true |
metrics.containerSecurityContext.allowPrivilegeEscalation |
Set container’s Security Context allowPrivilegeEscalation | false |
metrics.containerSecurityContext.capabilities.drop |
List of capabilities to be dropped | ["ALL"] |
metrics.containerSecurityContext.seccompProfile.type |
Set container’s Security Context seccomp profile | RuntimeDefault |
metrics.serviceMonitor.enabled |
If true, creates a Prometheus Operator ServiceMonitor (also requires metrics.enabled to be true) |
false |
metrics.serviceMonitor.namespace |
Optional namespace which Prometheus is running in | "" |
metrics.serviceMonitor.interval |
How frequently to scrape metrics (use by default, falling back to Prometheus’ default) | "" |
metrics.serviceMonitor.scrapeTimeout |
Timeout after which the scrape is ended | "" |
metrics.serviceMonitor.selector |
Prometheus instance selector labels | {} |
metrics.serviceMonitor.labels |
ServiceMonitor extra labels | {} |
metrics.serviceMonitor.annotations |
ServiceMonitor annotations | {} |
metrics.serviceMonitor.jobLabel |
The name of the label on the target service to use as the job name in prometheus. | "" |
metrics.serviceMonitor.relabelings |
RelabelConfigs to apply to samples before scraping | [] |
metrics.serviceMonitor.metricRelabelings |
MetricRelabelConfigs to apply to samples before ingestion | [] |
metrics.prometheusRule.enabled |
Set this to true to create prometheusRules for Prometheus operator | false |
metrics.prometheusRule.additionalLabels |
Additional labels that can be used so prometheusRules will be discovered by Prometheus | {} |
metrics.prometheusRule.namespace |
namespace where prometheusRules resource should be created | "" |
metrics.prometheusRule.rules |
Create specified rules, check values for an example. | [] |
metrics.priorityClassName |
Metrics exporter pod priorityClassName | "" |
metrics.service.type |
Kubernetes Service type (valkey metrics) | ClusterIP |
metrics.service.loadBalancerIP |
Use serviceLoadBalancerIP to request a specific static IP, otherwise leave blank | "" |
metrics.service.annotations |
Annotations for the services to monitor. | {} |
metrics.service.labels |
Additional labels for the metrics service | {} |
metrics.service.ports.http |
Metrics HTTP service port | 9121 |
metrics.service.clusterIP |
Service Cluster IP | "" |
Sysctl Image parameters
| Name | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
sysctlImage.enabled |
Enable an init container to modify Kernel settings | false |
sysctlImage.command |
sysctlImage command to execute | [] |
sysctlImage.registry |
sysctlImage Init container registry | REGISTRY_NAME |
sysctlImage.repository |
sysctlImage Init container repository | REPOSITORY_NAME/os-shell |
sysctlImage.digest |
sysctlImage Init container digest in the way sha256:aa…. Please note this parameter, if set, will override the tag | "" |
sysctlImage.pullPolicy |
sysctlImage Init container pull policy | IfNotPresent |
sysctlImage.pullSecrets |
Specify docker-registry secret names as an array | [] |
sysctlImage.mountHostSys |
Mount the host /sys folder to /host-sys |
false |
sysctlImage.containerSecurityContext.enabled |
Enable Containers’ Security Context | true |
sysctlImage.containerSecurityContext.seLinuxOptions |
Set SELinux options in container | nil |
sysctlImage.containerSecurityContext.runAsUser |
User ID for the containers. | 0 |
sysctlImage.containerSecurityContext.privileged |
Run privileged as privileged | true |
sysctlImage.resourcesPreset |
Set container resources according to one common preset (allowed values: none, nano, micro, small, medium, large, xlarge, 2xlarge). This is ignored if sysctlImage.resources is set (sysctlImage.resources is recommended for production). | nano |
sysctlImage.resources |
Set container requests and limits for different resources like CPU or memory (essential for production workloads) | {} |
Specify each parameter using the --set key=value[,key=value] argument to helm install. For example,
helm install my-release \
--set password=secretpassword \
oci://REGISTRY_NAME/REPOSITORY_NAME/valkey-cluster
Note: You need to substitute the placeholders
REGISTRY_NAMEandREPOSITORY_NAMEwith a reference to your Helm chart registry and repository. For example, in the case of Bitnami, you need to useREGISTRY_NAME=registry-1.docker.ioandREPOSITORY_NAME=bitnamicharts.
The above command sets the Valkey server password to secretpassword.
NOTE: Once this chart is deployed, it is not possible to change the application’s access credentials, such as usernames or passwords, using Helm. To change these application credentials after deployment, delete any persistent volumes (PVs) used by the chart and re-deploy it, or use the application’s built-in administrative tools if available.
Alternatively, a YAML file that specifies the values for the parameters can be provided while installing the chart. For example,
helm install my-release -f values.yaml oci://REGISTRY_NAME/REPOSITORY_NAME/valkey-cluster
Note: You need to substitute the placeholders
REGISTRY_NAMEandREPOSITORY_NAMEwith a reference to your Helm chart registry and repository. For example, in the case of Bitnami, you need to useREGISTRY_NAME=registry-1.docker.ioandREPOSITORY_NAME=bitnamicharts. Tip: You can use the default values.yaml Note for minikube users: Current versions of minikube (v0.24.1 at the time of writing) provisionhostPathpersistent volumes that are only writable by root. Using chart defaults cause pod failure for the Valkey pod as it attempts to write to the/bitnamidirectory. See minikube issue 1990 for more information.
Troubleshooting
Find more information about how to deal with common errors related to Bitnami’s Helm charts in this troubleshooting guide.
License
Copyright © 2024 Broadcom. The term “Broadcom” refers to Broadcom Inc. and/or its subsidiaries.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the “License”); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an “AS IS” BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.