Artifact Metadata Repository architecture
This topic gives you an overview of the Artifact Metadata Repository (AMR) architecture.
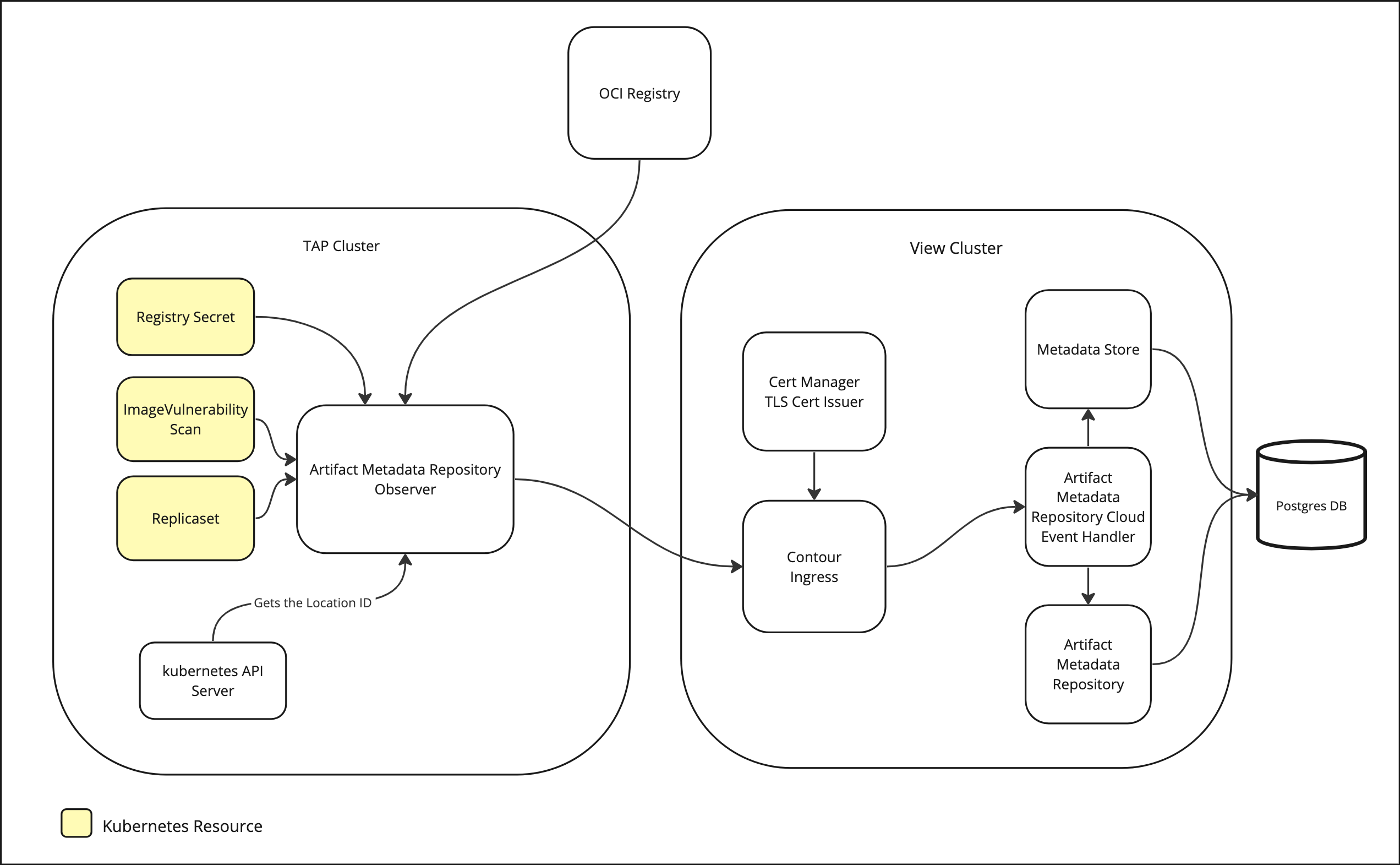
AMR Observer
The full, build, and run clusters include AMR Observer. AMR Observer communicates with the Kubernetes API Server to obtain the cluster’s location ID, which is the globally unique identifier (GUID) of the kube-system namespace.
After AMR Observer retrieves the location ID, AMR Observer emits a CloudEvent to AMR CloudEvent Handler, including any operator-defined metadata. This CloudEvent registers the location, and subsequent CloudEvents from that cluster use the same location reference in the source field. This mechanism helps AMR track artifacts with their associated location.
Watched resources
AMR Observer consists of managed controllers that watch resources. In Tanzu Application Platform v1.10, AMR Observer watches for:
| AMR Observer-supported Resources | Description |
|---|---|
| ImageVulnerabilityScans | app-scanning.apps.tanzu.vmware.com/v1alpha1 |
| Pods | v1 |
| GitRepository | source.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1 |
| OCIRepository | source.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1beta2 |
| ImageRepository | source.apps.tanzu.vmware.com/v1alpha1 |
| MavenArtifacts | source.apps.tanzu.vmware.com/v1alpha1 |
| Build | kpack.io/v1alpha2 |
| TaskRun | tekton.dev/v1beta1 |
ImageVulnerabilityScans
AMR Observer watches the ImageVulnerabilityScan Custom Resources for completed scans. When a scan finishes, AMR Observer uses the registry secret and the location information from the ImageVulnerabilityScan Custom Resources to fetch the Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) report.
After obtaining the SBOM report, AMR Observer wraps it in a CloudEvent and emits it to the AMR CloudEvent Handler. The AMR CloudEvent Handler persists this event in the Metadata Store.