Use the Application Accelerator Visual Studio Code extension
This topic describes how to use the Application Accelerator Visual Studio Code extension to explore and generate projects from the defined accelerators in Tanzu Application Platform (commonly known as TAP) using VS Code.
Dependencies
-
To use the VS Code extension to explore and generate projects, the extension must either:
-
Have access the Tanzu Developer Portal URL. For information about how to retrieve the Tanzu Developer Portal URL, see Retrieving the URL for the Tanzu Developer Portal.
-
Alternatively, you can use the local engine server to explore and generate projects locally without requiring access to Tanzu Developer Portal. For more information, see Use a local Application Accelerator engine server.
-
-
(Optional) To use Git repository provisioning during project creation in the VS Code extension, you must enable GitHub repository creation in the Application Accelerator plug-in. For more information, see Create an Application Accelerator Git repository during project creation.
Install the extension
Use the following steps to install the Application Accelerator Visual Studio Code extension:
- Open Visual Studio Code.
- Open the command palette and enter
Extensions. - Click Extensions: Install Extensions.
- The Extensions view opens on the left side of your screen. In the search box, enter
Tanzu. - Click Tanzu App Accelerator.
- Click Install.
Configure the extension
Before using the extension, you must configure it as follows:
-
Go to VS Code settings and click Code > Preferences > Settings > Extensions > Tanzu App Accelerator.
-
Configure the extension to either use Tanzu Developer Portal or the local engine server:
-
For Tanzu Developer Portal:
In the Tanzu Application Platform Gui Url text box, add your Tanzu Developer Portal URL. For example,
https://tap-gui.myclusterdomain.myorg.com.To get the fully-qualified domain name, if you have access to the Tanzu Application Platform cluster that is running Tanzu Developer Portal, run:
kubectl get httpproxy tap-gui -n tap-gui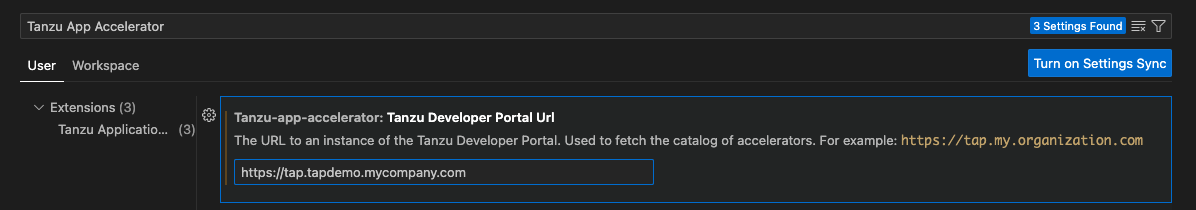
-
For the local engine server:
To use the local engine server to explore and generate projects based on local files without requiring access to Tanzu Developer Portal, follow the instructions in Use a local Application Accelerator engine server.
-
Use the extension
You can use the VS Code extension to generate a project and to export your accelerator configuration.
Generate a project
To use the VS Code extension to generate a project:
-
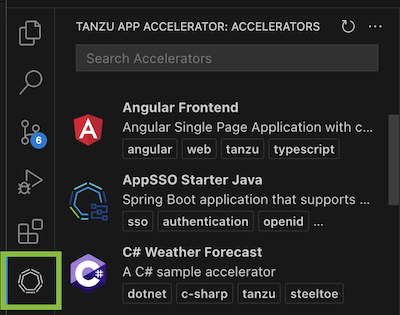
Click the Tanzu Application Accelerator extension icon in the Activity Bar to explore the defined accelerators.
-
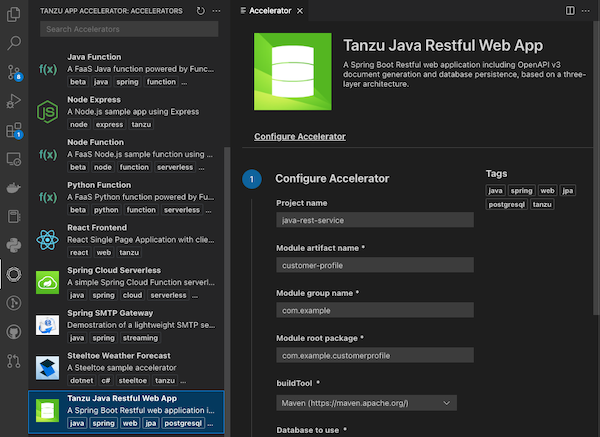
Choose any of the defined accelerators, fill in the options under Configure Accelerator, and click Next.
-
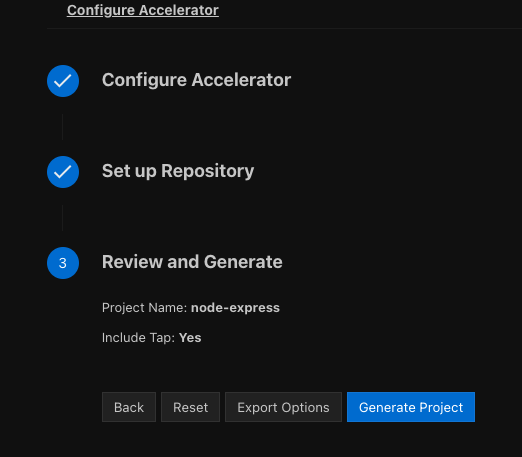
Review your settings and click Generate Project.
Export accelerator configuration options
For faster iteration while writing accelerators, you can export the accelerator options you set under Configure Accelerators to a JSON file. You can use this file to generate your project again from the CLI.
To export your options using the VS Code extension:
-
Select the accelerator that you want to use.
-
On the under Configure Accelerators page, use the form to configure the accelerator with your options and click Next.
-
On the Review and Generate page, export the options you configured by clicking Export Options before clicking Generating Project.
-
Choose a location to save the JSON file.
Use the language server provided by the local server
If you are using the local engine server, it includes a language server that enables you to use VS Code features such as syntax highlighting and code folding.
To enable these features, you must start the local server. For instructions, see Use a local Application Accelerator engine server. After you have enabled the local server, these features are available while editing an accelerator.axl file in VS Code.
Retrieve the URL for the Tanzu Developer Portal
If you have access to the Tanzu Application Platform cluster that is running Tanzu Developer Portal, run the following command to determine the fully-qualified domain name:
kubectl get httpproxy tap-gui -n tap-gui
Example output:
NAME FQDN TLS SECRET STATUS STATUS DESCRIPTION
tap-gui tap-gui.tap.tapdemo.myorg.com tap-gui-cert valid Valid HTTPProxy
Download and install self-signed certificates from the Tanzu Developer Portal
To enable the Application Accelerator extension for VS Code to communicate with a Tanzu Developer Portal instance that is secured using TLS, you must download and install the certificates locally.
Prerequisites
yq is required to process the YAML output.
Procedure
-
Find the name of the Tanzu Developer Portal certificate. The name of the certificate might look different to the following example.
kubectl get secret -n cert-managerNAME TYPE DATA AGE canonical-registry-secret kubernetes.io/dockerconfigjson 1 18d cert-manager-webhook-ca Opaque 3 18d postgres-operator-ca-certificate kubernetes.io/tls 3 18d tanzu-sql-with-mysql-operator-ca-certificate kubernetes.io/tls 3 18d tap-ingress-selfsigned-root-ca kubernetes.io/tls 3 18d <------- This is the certificate that is needed -
Download the certificate:
kubectl get secret -n cert-manager tap-ingress-selfsigned-root-ca -o yaml | yq '.data."ca.crt"' | base64 -d > ca.crt -
Install the certificate on your local system and fully restart any applications that uses the certificate. After restarting, the application uses the certificate to communicate with the endpoints using TLS. For more information, see Installing a root CA certificate in the trust store in the Ubuntu documentation.
- macOS
-
Run:
sudo security add-trusted-cert -d -r trustRoot -k /Library/Keychains/System.keychain ca.crt - Windows
-
Complete the following steps:
- Use Windows Explorer to navigate to the directory where the certificate was downloaded and click on the certificate.
- In the Certificate window, click Install Certificate….
- Change the Store Location from Current User to Local Machine. Click Next.
- Select Place all certificates in the following store, click Browse, and select Trusted Root Certification Authorities
- Click Finish.
- A pop-up window stating The import was successful. is displayed.