Authentication and authorization
This topic tells you how to authenticate and authorize the Artifact Metadata Repository (AMR).
Overview
Authentication and authorization includes:
- High-level design
- Kubernetes service account automatic configuration
- Configuring a user-defined Kubernetes service account
- A CloudEvent user-defined service account
- Configuring AMR Observer with the CloudEvent Handler service account access token
High-level design
The AMR deploys the following Kubernetes services which expose HTTP endpoints:
- CloudEvent-handler
- GraphQL
Both CloudEvent-handler and GraphQL are in the same cluster. In a multicluster Tanzu Application Platform deployment, they are in the View cluster and the clients can be from any cluster. This topic shows the client in the build cluster in these examples.
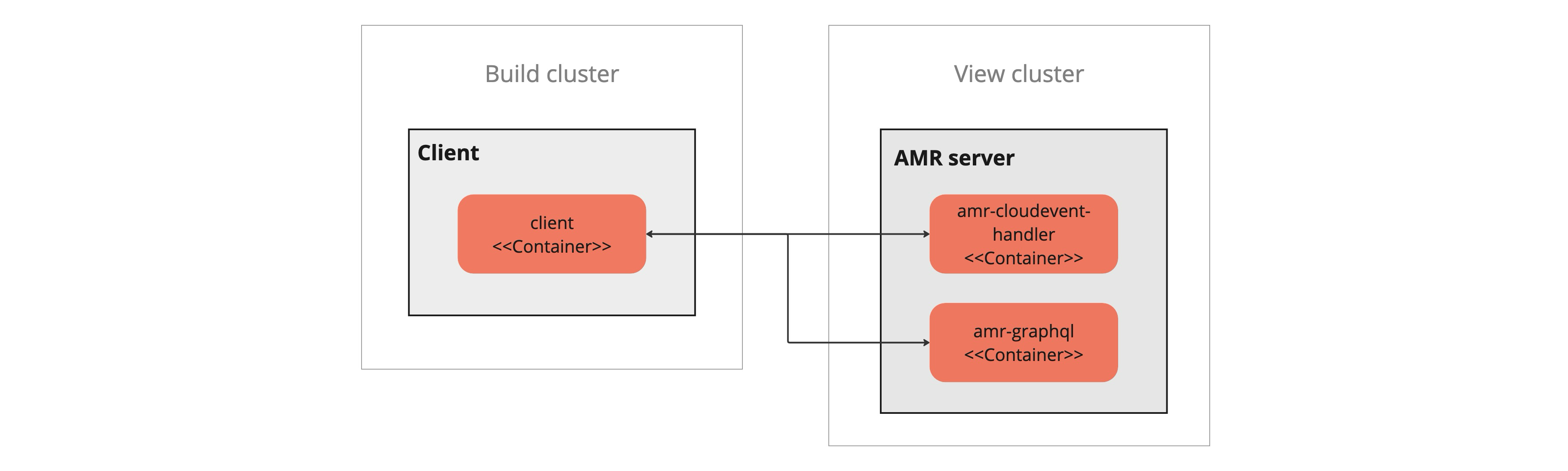
The client sends requests to either service depending on their current task. cloudevent-handler ingests events from the client and stores it in a database. The GraphQL server answers queries from the client and returns data from the database.
Other than those points, cloudevent-handler and the GraphQL server are treated the same in this design. They both use the same authentication and authorization solution. This topic simplifies the explanation by only showing cloudevent-handler.
Kubernetes role-based access control (RBAC)
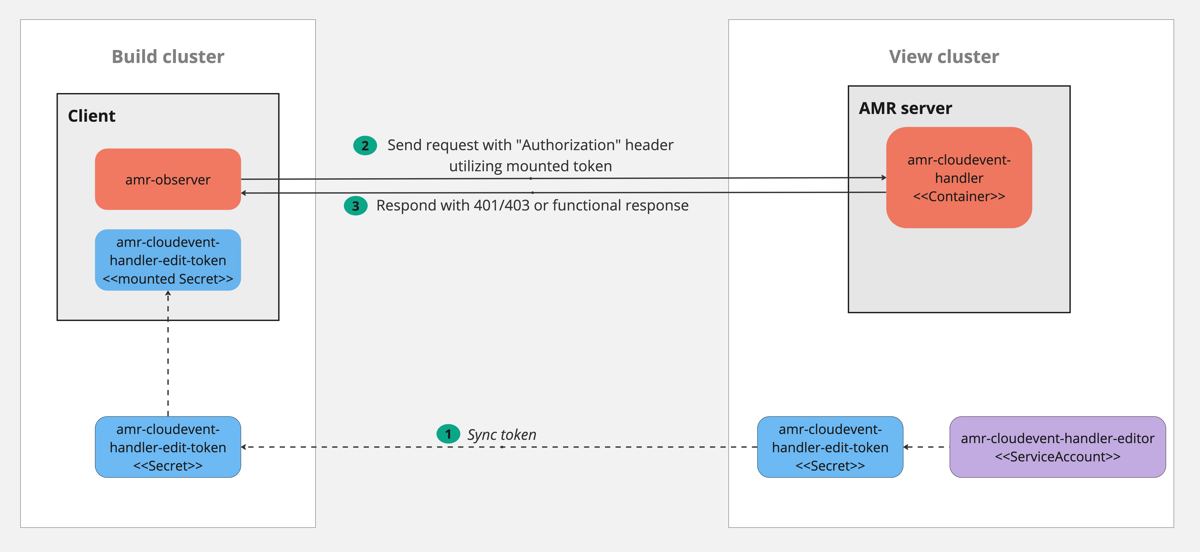
The server implements support for authentication by using Kubernetes RBAC. This includes requiring the client to send a token from a Kubernetes service account token bound to a Kubernetes role.
-
The administrator creates a service account,
RoleorClusterRole, and role binding in the cluster wherecloudevent-handleris deployed in the View cluster. The role declares what permissions the client has:-
For AMR Observer, the supported permissions are
update, the resource*, and the groupcloudevents.amr.apps.tanzu.vmware.com. NoresourceNamesare supported. That translates to “write for all resources” for the CloudEvents API. -
For the GraphQL service, the supported permissions are
get, the resource*, and the groupgraphql.amr.apps.tanzu.vmware.com. NoresourceNamesare supported. That translates to “read all” from the GraphQL API.
-
-
The administrator copies the service account token and puts it in the client cluster where the client container can read it. For example, the client can get the token mounted as a Kubernetes secret.
- The client sends a request to AMR, and puts the service account token in the HTTP header
Authorization: Bearer <token>. cloudevent-handlerreads the token and conducts aTokenReview.cloudevent-handlerdoes aSubjectAccessReviewusing the user information returned fromTokenReviewand the resource information as described earlier.- According to the Kubernetes RBAC system,
SubjectAccessReviewsearches for anyRoleorClusterRoleassociations by using bindings to find a match between the assigned roles to the specific service account and the requested resource information.