Artifact Metadata Repository (AMR) data model and concepts
This topic tells you about data models used in the Artifact Metadata Repository (AMR).
Overview
The following diagram shows the data models used in the AMR to store artifact information and the relationship between them.
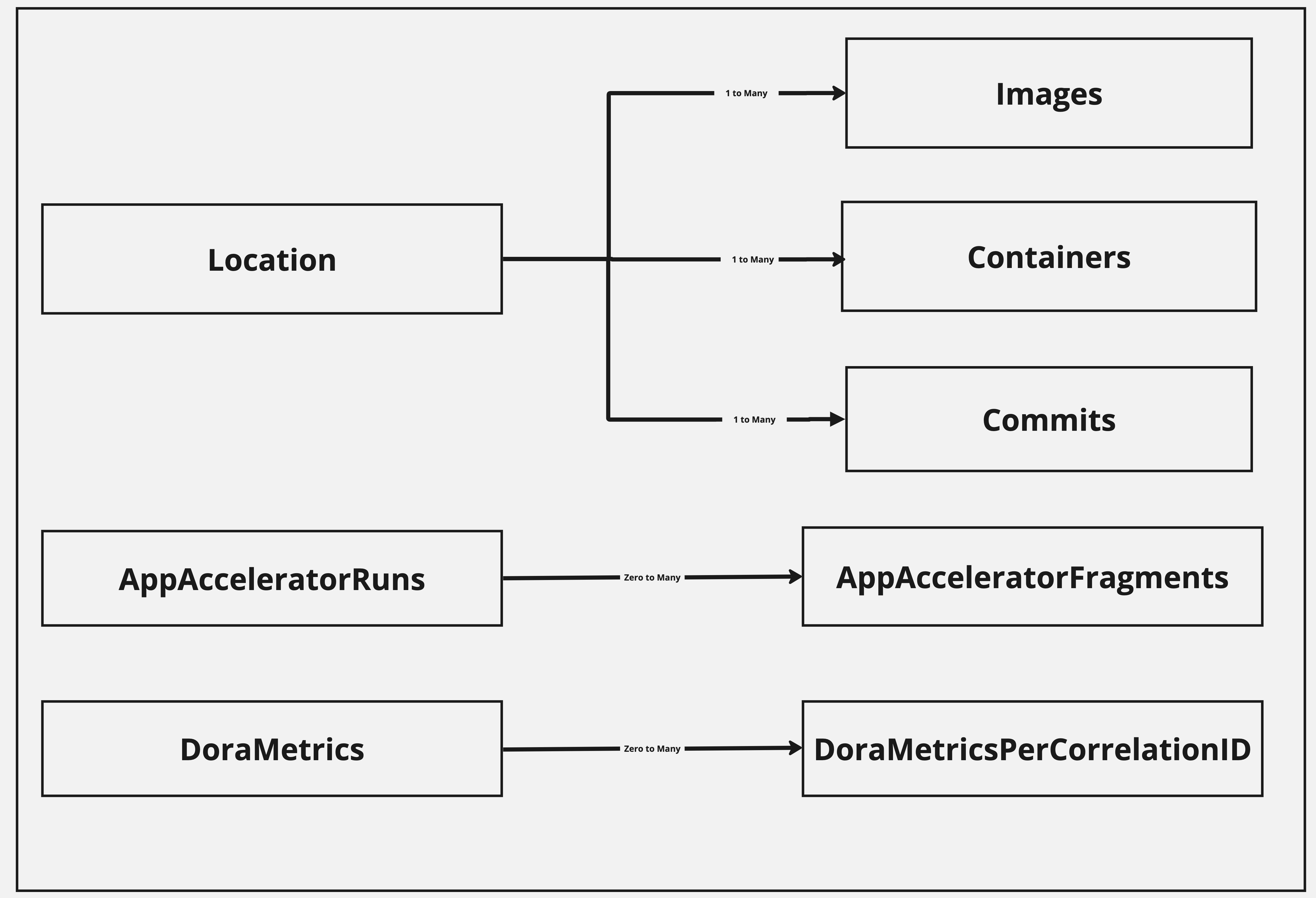
AMR data models
The following data models are stored in the AMR:
Locations(alpha)ContainersImagesCommitsAppAcceleratorRuns(alpha)AppAcceleratorFragments(alpha)DoraMetrics(alpha)DoraMetricsPerCorrelationID(alpha)
Locations (alpha)
The Locations data model stores data about the locations that Apps are deployed on, like clusters. It stores data using:
reference: unique reference to the location. It is automatically set to be thekube-systemnamespace UID by the AMR. You can’t configure this value.labels: labels of the location. You can add labels in thetap-values.yamlfile. See AMR Configuration.
Containers
The Containers data model includes information about a container, like runtime information about an image. The Observer sends this information to the Cloud Event Handler. Each entry represents the state of the container when an event occurred, such as when a container runs or stops. This lets you see the history of your containers.
Each Container data entry stores information about the associated deployment location, details about the state, and what image was used. You can only associate a Containers entry with one Locations entry. You can point multiple Containers entries to the same Locations entry.
Images
The Images data model includes information about image which acts as a template for containers. The Observer sends this information to the Cloud Event Handler to store newly generated images.
Each Image data entry stores information about the associated deployment location. You can only associate an Images entry with one Locations entry. You can point multiple Images entries to the same Locations entry.
Commits
The Commits data model includes information about a snapshot of the changes made to a project’s files. The Observer sends this information to the Cloud Event Handler to store new commits.
Each Commit data entry stores information about the deployment location, details about the state, and what commit sha or tag were used. You can only associate a Commits entry with one Locations entry. You can point multiple Commits entries to the same Locations entry.
AppAcceleratorRuns (alpha)
The AppAcceleratorRuns data model represents new projects running from Git repositories. An accelerator.yaml file in the repository declares input options for the accelerator. This file contains instructions for processing the files when you generate a new project. Observer sends this information to the CloudEvent Handler to store AppAcceleratorRuns.
Each AppAcceleratorRun data entry has a unique guid. The guid includes information about the Git repository including, AppAcceleratorRepoURL, AppAcceleratorRevision, and AppAcceleratorSubpath. You can point multiple AppAcceleratorFragments entries to the same AppAcceleratorRun entry. You can also associate an AppAcceleratorRun with one AppAcceleratorSource, also known as Commit.
AppAcceleratorFragments (alpha)
The AppAcceleratorFragments Accelerator fragments are reusable accelerator components that can provide options, files, or transforms. You can import accelerators using an import entry. An InvokeFragment transform references the transforms from the fragment in the accelerator that declares the import. The AppAcceleratorFragments data model represents the information of a fragment in the accelerator app. The Observer sends this information to the Cloud Event Handler to store AppAcceleratorFragments.
Each AppAcceleratorFragment data entry stores information about source Git repository: AppAcceleratorFragmentSourceRepoURL, AppAcceleratorFragmentSourceRevision, and AppAcceleratorFragmentSourceSubpath. You can associate an AppAcceleratorFragment to an AppAcceleratorRun. You can point a AppAcceleratorFragmentSource (also known as Commit) to one AppAcceleratorFragment.
DoraMetrics (alpha)
The DoraMetrics data model represents the DORA Metric information. The Observer sends this information to the CloudEvent Handler to store DoraMetrics.
AggregatedLeadTime is a velocity metric that describes the median amount of time in seconds for a commit to deploy to an environment. AggregatedDeployments describes how frequently a team releases to production in a time range. You can point multiple DoraMetricsPerCorrelationID to one DoraMertric.
DoraMetricsPerCorrelationID (alpha)
The DoraMetricsPerCorrelationID data model represents the information of DORA Metric for a Correlation ID. The Correlation ID groups the all the artifacts together. The Observer sends this information to the CloudEvent Handler to store DoraMetricsPerCorrelationID.