Key Concepts for API Auto Registration
This topic explains key concepts you use with API Auto Registration.
API Auto Registration architecture
You can use the full potential of API Auto Registration by using a distributed environment, as shown in the following diagrams:
-
The workloads that expose APIs through the supply chains cause generated
APIDescriptors. This triggers API Auto Registration’s Kubernetes controller to generate and register API entities in Tanzu Developer Portal.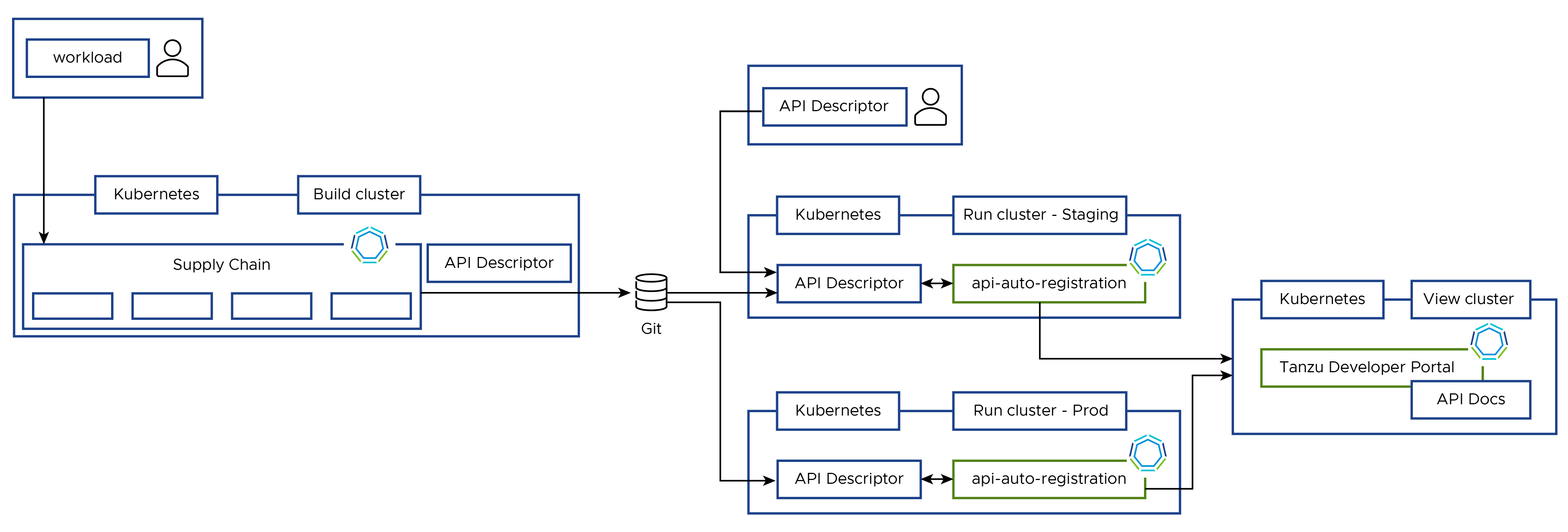
-
Aggregate one or more
CuratedAPIDescriptorinto a curated API by usingAPIDescriptors. Optionally, this can trigger Spring Cloud Gateway routing resource generation for the referenced APIs.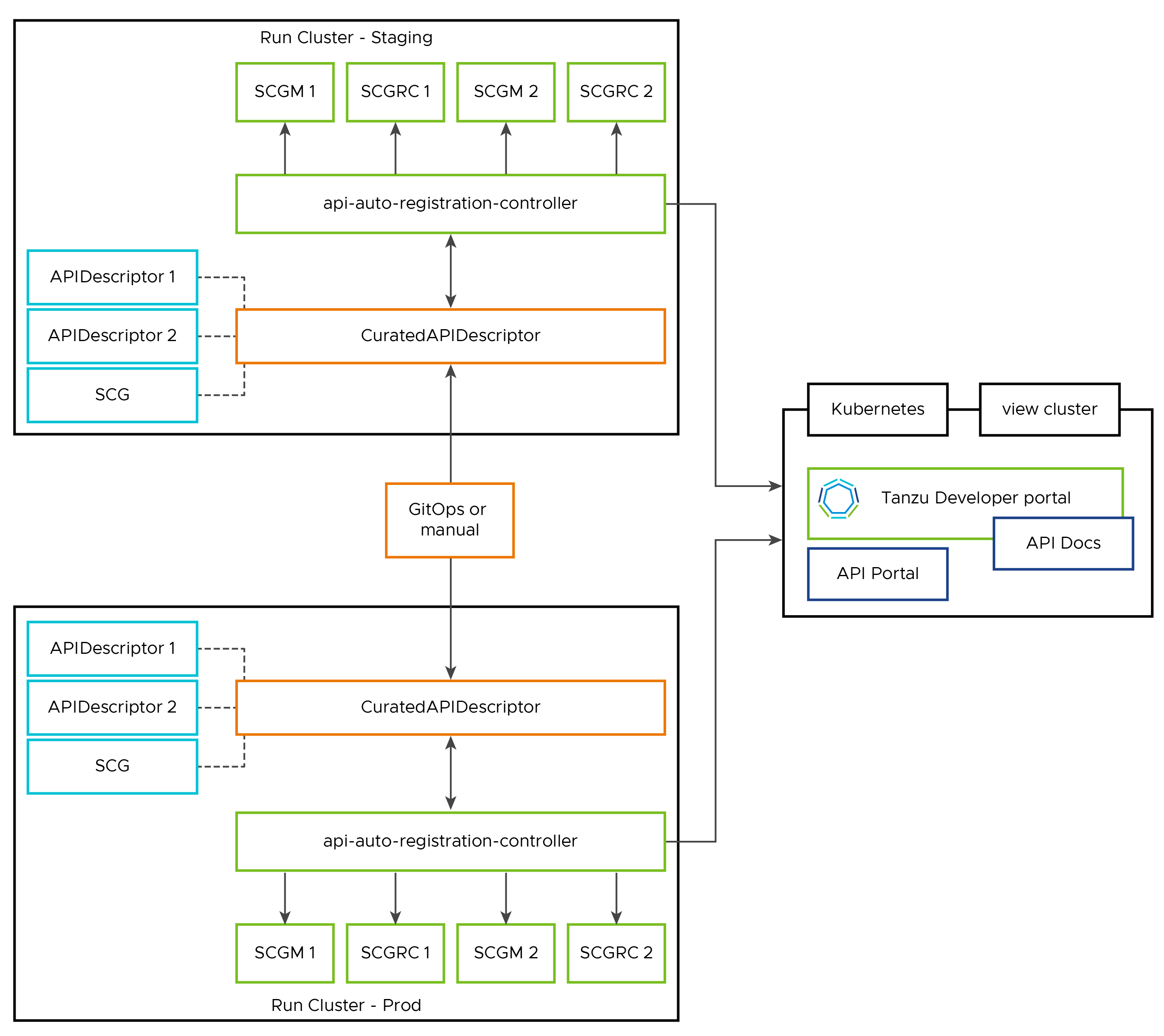
APIDescriptor custom resource explained
To initiate API registration, the supply chain must create the custom resource of type APIDescriptor automatically or through other processes. The information from this custom resource constructs an API entity in Tanzu Developer Portal.
This custom resource exposes the following text boxes:
apiVersion: apis.apps.tanzu.vmware.com/v1alpha1
kind: APIDescriptor
metadata:
name: # name of your APIDescriptor
namespace: # optional: namespace of your APIDescriptor
spec:
type: # type of the API spec. oneOf(openapi, grpc, asyncapi, graphql)
description: # description for the API exposed
system: # system that the API is part of
owner: # person/team that owns the API
location:
apiSpec:
path: # sub-path where the API spec is available (previously `location.path`)
url: # optional: static absolute base URL for the API spec
server: # base URL object where the API spec is available. oneOf(url, ref) (previously `location.baseURL`)
url: # optional: static absolute base URL for the API server
ref: # optional: object ref to oneOf(HTTPProxy, Knative Service, Ingress)
apiVersion:
kind:
name:
namespace:
The text boxes cause specific behavior in Tanzu Developer Portal:
- The system and owner are copied to the API entity. You might have to separately create and add the System and Group kind to the catalog.
- Tanzu Developer Portal uses the namespace for the API entity where the APIDescriptor CR is applied. This causes the API entity’s name, system, and owner to all be in that namespace.
- To explicitly use a system or owner in a different namespace, you can specify that in the
system: my-namespace/my-other-systemorowner: my-namespace/my-other-teamtext boxes. - If the system or owner you are trying to link doesn’t have a namespace specified, you can qualify them with the
defaultnamespace. For example,system: default/my-default-system
Important
spec.location.pathis deprecated in favor ofspec.location.apiSpec.path, andspec.location.baseURLis deprecated in favor ofspec.location.server. This change supports having a different API server location from the specification’s location. These deprecated fields will be removed in Tanzu Application Platform 1.8.
With an absolute URL
To create an APIDescriptor with a static server.url, you must apply the following YAML to your cluster.
apiVersion: apis.apps.tanzu.vmware.com/v1alpha1
kind: APIDescriptor
metadata:
name: sample-absolute-url
spec:
type: openapi
description: A set of API endpoints to manage the resources within the petclinic app.
system: spring-petclinic
owner: team-petclinic
location:
apiSpec:
path: "/v3/api-docs.yaml"
server:
url: https://myservice.mynamespace.svc.cluster.local:6789
With an object ref
You can use an object reference, instead of hard coding the URL, to point to a HTTPProxy, Knative Service, or Ingress. VMware does not support referencing Kubernetes Service with Object Ref. To point to your Kubernetes Service directly, you can use the static URL with cluster DNS address. For example, https://myservice.mynamespace.svc.cluster.local:6789.
With an HTTPPRoxy object ref
This section includes an example YAML that points to an HTTPProxy from which the controller extracts the .spec.virtualhost.fqdn as the baseURL.
apiVersion: apis.apps.tanzu.vmware.com/v1alpha1
kind: APIDescriptor
metadata:
name: sample-contour-ref
spec:
type: openapi
description: A set of API endpoints to manage the resources within the petclinic app.
system: spring-petclinic
owner: team-petclinic
location:
apiSpec:
path: "/test/openapi"
server:
ref:
apiVersion: projectcontour.io/v1
kind: HTTPProxy
name: my-httpproxy
namespace: my-namespace # optional
With a Knative service object ref
To use a Knative Service, your controller reads the status.url as the baseURL. For example:
# all other fields similar to the above example
server:
ref:
apiVersion: serving.knative.dev/v1
kind: Service
name: my-knative-service
namespace: my-namespace # optional
With an ingress object ref
To use an Ingress instead, your controller reads the URL from the jsonPath specified. When jsonPath is left empty, your controller reads the "{.spec.rules[0].host}" as the URL. For example:
# all other fields similar to the above example
server:
ref:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
name: my-ingress
jsonPath: "{.spec.rules[1].host}"
namespace: my-namespace # optional
APIDescriptor status fields
When API Auto Registration processes an APIDescriptor, it adds several fields describing the progress to the status. Including conditions, which provides information useful for troubleshooting. For information about the conditions, see Troubleshoot API Auto Registration.
In addition to conditions, the status contains other useful fields showing the resolved API’s details. The following is a list of these fields with a brief explanation of what they contain.
status:
registeredEntityURL: # Url of the corresponding API Entity in Tanzu Developer Portal
registeredTapUID: # Unique identifier for the corresponding API Entity in Tanzu Developer Portal
resolvedAPIServerURL: # Url to the API runtime server
resolvedAPISpecURL: # Url used to retrieve the full API Spec by Api Auto Registration
resolvedAPISpec: # Full API Spec as retrieved by Api Auto Registration
resolvedAPISpecHash: # Hash value of the `resolvedAPISpec`. This field can be used to see whether the spec has been updated or not.
apiSpecLastUpdateTime: # Timestamp representing the server time when API Spec was last updated. It is not guaranteed to be set in happens-before order across separate operations. It is represented in RFC3339 form and is in UTC.
CuratedAPIDescriptor custom resource explained
To curate one or more Workload OpenAPI specifications into a single aggregated API, create a custom resource of type CuratedAPIDescriptor. The information from this custom resource references a list of APIDescriptors and how path-based routing aggregates them.
If you specify a valid route provider, for example, spring-cloud-gateway for Spring Cloud Gateway for Kubernetes (SCG), the API Auto Registration controller finds the SpringCloudGateway resource and automatically creates the following routing resources for you to expose your curated APIs as:
- SpringCloudGatewayRouteConfig (SCGRC): a custom resource that describes all the API endpoints and optional routing modifiers to access the endpoints. This is generated from the resolved OpenAPI Specification of the APIDescriptor through SCG OpenAPI conversion service.
- SpringCloudGatewayMapping (SCGM): a custom resource that binds a SCGRC resource to a SCG resource.
This custom resource exposes the following text boxes:
apiVersion: apis.apps.tanzu.vmware.com/v1alpha1
kind: CuratedAPIDescriptor
metadata:
name: # name of your CuratedAPIDescriptor
namespace: # optional: namespace of your CuratedAPIDescriptor
annotations:
"apis.apps.tanzu.vmware.com/route-provider": "spring-cloud-gateway" # specify route provider
spec:
type: openapi # type of the API spec. oneOf(openapi, grpc, asyncapi, graphql)
title: # title of the curated API
description: # description of the curated API spec
documentation: # documentation for the curated API spec
groupId: # groupID of the curated API.
version: # version of the curated API
apiDescriptors:
- name: # name of a APIDescriptor to include in this curated API
namespace: # namespace of the APIDescriptor
pathPrefix: # Path prefix that the API endpoints from the linked APIDescriptor should have
routeConfig:
ssoEnabled: # whether to enable SSO on the gateway to perform authentication for users
tokenRelay: # whether to enable TokenRelay on the gateway to pass along the SSO ID token to the upstream service. This setting depends on `ssoEnabled`.
filters: # additional service lever filters to set on all the endpoints in this API
- ...
There are some key behaviors generated from the text boxes:
- The
apis.apps.tanzu.vmware.com/route-providerannotation specified how you want to provide routing to the curated API. VMware only supportsspring-cloud-gateway. groupIdis a concept that’s aligned with API portal to group APIs from different high-availability zones/locations or with differentversion.groupIdandversionidentify a matching gateway that route traffic for the curated APIrouteConfigsection specifies service level configuration you add when generating the routing resource for the API. For information about spring-cloud-gateway fields, see OpenAPI route conversion.- Prior to Spring Cloud Gateway (SCG) for Kubernetes v2.1.3, there is a known issue in the SCG OpenAPI Conversion Service to support adding token relay at the service level. The
tokenRelay: truesetting only works with SCG v2.1.3 and above. routeConfig.filterssection specifies service level filters for all the routes exposed in each API. You can add modifications to your endpoints, such asRateLimit=5,10sorRemoveRequestHeader=X-Request-Foo. For information about available filters, see SCG commercial filters.- Your controller automatically prepends each endpoint path with the
pathPrefixyou specified for each APIDescriptor, and adds theStripPrefixfilter to the end of the filter list to facilitate a successful path-based redirect. Additionally, you can add moreStripPrefixfilters to the service level filters to skip common paths in your specifications that are not in your service.
- Prior to Spring Cloud Gateway (SCG) for Kubernetes v2.1.3, there is a known issue in the SCG OpenAPI Conversion Service to support adding token relay at the service level. The
CuratedAPIDescriptor status fields
When processing an CuratedAPIDescriptor, several fields are added to the status. One of these is conditions, which provide information useful for troubleshooting. The conditions are explained in the Troubleshooting Guide.
In addition to conditions the status contains a couple of other useful fields. The following is a list of these fields with a brief explanation of what they contain.
status:
ResolvedBaseURL: # Base url to access the curated API. Empty if no route provider is configured.
ResolvedAPISpecURL: # Url to the generated aggregated API spec
AggregatedAPISpec: # Generated full API Spec as aggregated by Api Auto Registration
AggregatedAPISpecHash: # Hash of the aggregated API Spec. This field can be used to see whether the spec has been updated or not.
LastUpdateTime: # Timestamp representing the server time when API Spec was last updated. It is not guaranteed to be set in happens-before order across separate operations. It is represented in RFC3339 form and is in UTC.
MatchedGateway: # The Gateway resource the curated API is matched on. We currently only support SCG.