App Autoscaler with VMware Tanzu Application Service for VMs (TAS for VMs) scales your apps and control costs of running them.
App Autoscaler overview
App Autoscaler is a TAS for VMs Marketplace service that scales apps in your environment based on app performance metrics or a schedule. This controls the cost of running apps while maintaining app performance.
To use App Autoscaler:
- Configure scaling rules that adjust app instance counts based on metrics thresholds
- Modify the maximum and minimum number of instances for an app, either manually or following a schedule
- Configure scaling factors so that the app scales more quickly. Use caution when setting the scaling factors by which to scale your applications up or down.
For example, you might configure App Autoscaler to scale down the number of instances for an app over the weekend. You can configure App Autoscaler to scale up the number of instances for an app when the value of the CPU Usage metric increases above a custom threshold.
About app Autoscaler scaling rules
This section describes how the app Autoscaler decides when to scale an app up or down.
It also provides information about the Custom App Metrics, Custom App Metric Ratios, and default metrics that you can use when you create scaling rules for an app in App Autoscaler.
How App Autoscaler decides when to scale
Every 35-seconds, App Autoscaler makes a decision about whether to scale up, scale down, or keep the same number of instances.
To make a scaling decision, App Autoscaler averages the values of a metric for the most recent 120-seconds.
Configure App Autoscaler in Configuring TAS for VMs.
App Autoscaler scales as follows:
- Increment the instances by the app’s scale up factor when any metric exceeds its maximum threshold.
- Decrement the instances by the app’s scale down factor when all metrics fall below their minimum thresholds.
- Keep the same number of instances when app metrics do not exceed thresholds.
The following diagram provides an example of how App Autoscaler makes scaling decisions:

As shown in the diagram, an app has a maximum threshold of 200-milliseconds and a minimum threshold of 80-milliseconds for an HTTP Request Latency metric. The scale up factor and scale down factor are not set in the scaling manifest, so the default value is one.
If HTTP Request Latency averages 220-milliseconds for 120-seconds, App Autoscaler scales the app up one instance.
If HTTP Request Latency then averages 70-milliseconds over the next 120-second window and the app’s other scaling metrics also fall below their minimum thresholds, App Autoscaler scales the app down one instance.
If the average value for HTTP Request Latency over a 120-second window falls below the maximum threshold of 200-milliseconds or the minimum threshold of 80-milliseconds, App Autoscaler maintains the same number of instances for the app.
You can set a maximum and minimum number of instances. For example, if an app exceeds the maximum threshold of selected metric, but the number of instances is already at the maximum number of instances, App Autoscaler does not scale up the app.
You can set a period of time after a scaling action within which no further scaling action may be taken to prevent scaling decisions for an app with a slow startup time. App Autoscaler refers to this concept as cooldown period. For example, when an app configured with a cooldown period of 5m is scaled by App Autoscaler, App Autoscaler will not consider the app for further scaling decisions until at least five minutes after that scaling event. This helps App Autoscaler avoid overscaling an app while a new instance is still starting up and producing metrics that would otherwise cause further scaling actions.
Default metrics for scaling rules
App Autoscaler includes several default metrics for which you might create scaling rules.
NoteVMware recommends that you define Custom App Metrics for scaling rules instead of using the default metrics. You can use Custom App Metrics to accurately monitor the performance of your apps based on your environment.
The following table lists the default metrics for App Autoscaler:
| Metric | Description | Note |
|---|---|---|
| CPU Processor Utilization | Average CPU percentage for all instances of the app. | App CPU utilization data might vary greatly based on the number of CPU cores on Diego Cells and app density. For more information, see Use CPU Entitlement Utilization as a scaling metric with App Autoscaler. |
| Container Memory Utilization | Average memory percentage across all instances of the app. | n/a |
| HTTP Request Throughput | Average number of HTTP requests per second across all of the app instances. | n/a |
| HTTP Request Latency | Average latency of apps response to HTTP requests. This does not include Gorouter processing time or other network latency. Average is calculated on the middle 99% or middle 95% of all HTTP requests. |
n/a |
| RabbitMQ Queue Depth | The queue length of the specified RabbitMQ queue. | n/a |
Custom App Metrics for scaling rules
VMware recommends that you define Custom App Metrics for App Autoscaler scaling rules. You can use Custom App Metrics to define the metrics that are the best indicators of app performance for your environment.
You can configure apps to emit Custom App Metrics out of the Loggregator Firehose using Metric Registrar. For steps on how to configure your apps to emit Custom App Metrics with Metric Registrar, see Registering custom app metrics.
Custom App Metric Ratios
You can use the Comparison Metric text box in Apps Manager to define a scaling rule that divides one Custom App Metric by another.
When you add a scaling rule, the Metric text box is the dividend and the Comparison Metric text box is the divisor.
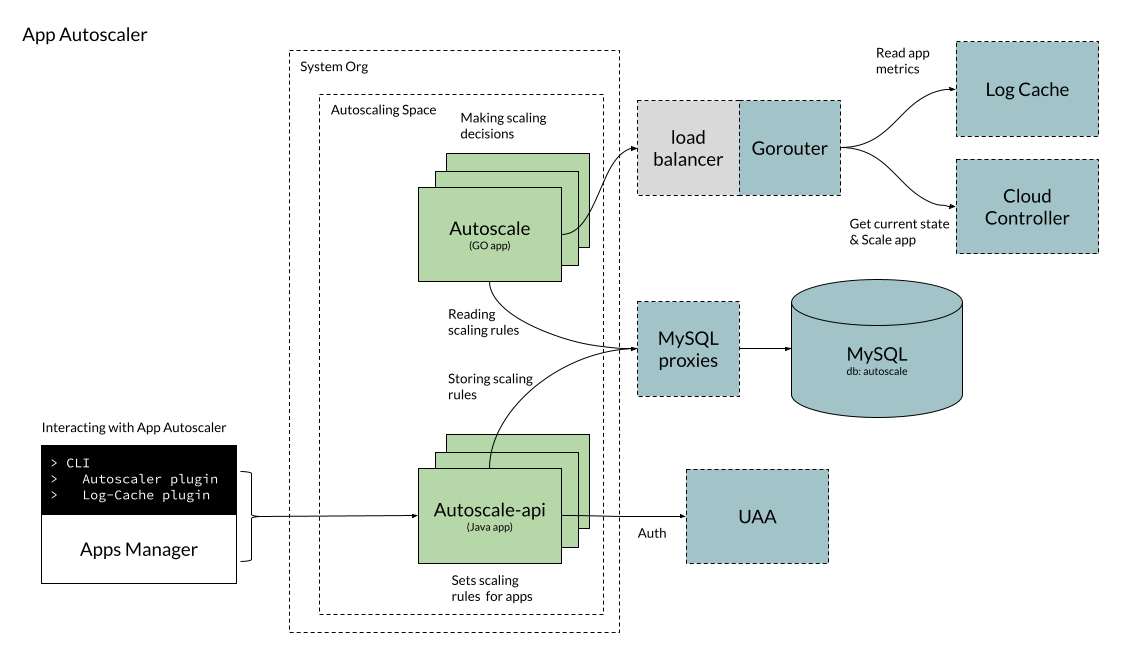
App Autoscaler architecture
The following diagram shows the components and architecture of App Autoscaler. It also shows how App Autoscaler components interact with VMware Tanzu Application Service for VMs (TAS for VMs) components to make app scaling decisions.
View a larger version of this image.
As demonstrated in the architecture diagram, App Autoscaler makes scaling decisions based on autoscaling rules that users configure by using either the Cloud Foundry Command Line Interface (cf CLI) or Apps Manager. The Autoscale API stores these autoscaling rules in a MySQL database.
At a predefined interval, known as the scaling interval, the App Autoscaler app reads the scaling rules and retrieves app metric data from the Loggregator Log Cache. Then, App Autoscaler makes a scaling decision and communicates with the Cloud Controller to scale the app, if necessary.
For more information about Loggregator Log Cache, see Loggregator architecture.
For more information about the Cloud Controller, see Cloud Controller.