This topic tells you about VMware Tanzu Application Service for VMs (TAS for VMs) and how it works with Tanzu Operations Manager.
Cloud platforms let anyone deploy network apps or services and make them available to the world in a few minutes. When an app becomes popular, the cloud scales it to handle more traffic, replacing build-out and migration efforts that once took months with a few keystrokes. Cloud platforms enable you to focus exclusively on your apps and data without worrying about underlying infrastructure.
The following diagram shows the layers of a typical technology stack, and compares the traditional IT model to the cloud platform model:
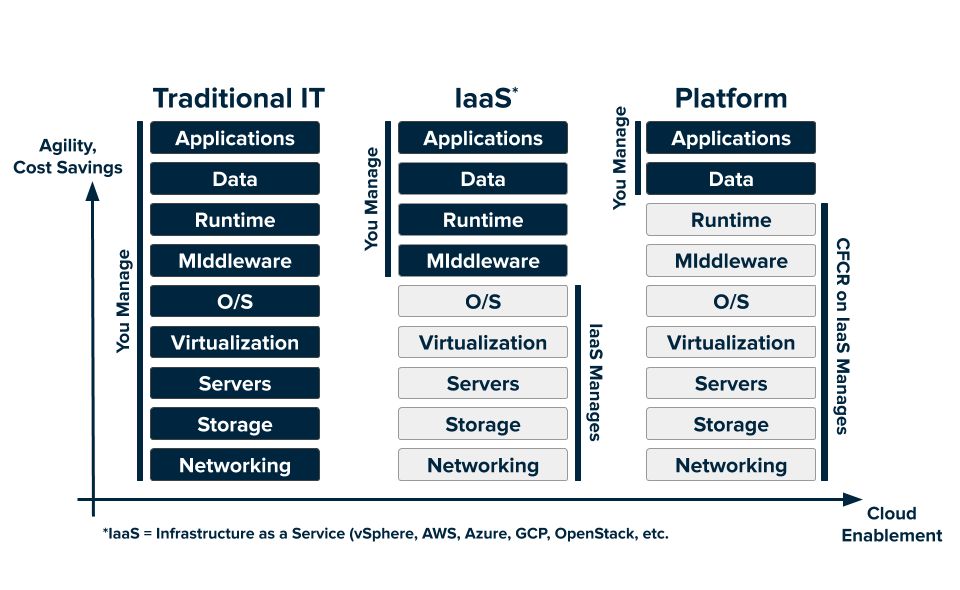
View a larger version of this diagram.
See the following sections in this topic:
About TAS for VMs
This section describes why TAS for VMs is an industry-standard cloud platform.
Not all cloud platforms are created equal. Some have limited language and framework support, lack key app services, or restrict deployment to a single cloud.
As an industry-standard cloud platform, TAS for VMs offers the following:
-
Open source code: The platform’s openness and extensibility prevent its users from being locked into a single framework, set of app services, or cloud. For more information, see the Cloud Foundry project on GitHub.
-
Deployment automation: Developers can deploy their apps to TAS for VMs using their existing tools and with zero modification to their code.
-
Flexible infrastructure: You can deploy TAS for VMs to run your apps on your own computing infrastructure, or deploy on an IaaS like vSphere, AWS, Azure, GCP, or OpenStack.
-
Commercial options: You can also use a PaaS deployed by a commercial TAS for VMs cloud provider. For more information, see Cloud Foundry Certified Platforms.
-
Community support: A broad community contributes to and supports TAS for VMs. See Welcome to the Cloud Foundry Community.
TAS for VMs is ideal for anyone interested in removing the cost and complexity of configuring infrastructure for their apps.
How TAS for VMs Works
To flexibly serve and scale apps online, TAS for VMs has subsystems that perform specialized functions. The following sections describe how some of these main subsystems work.
Load balancing
This section describes how TAS for VMs handles load balancing.
Clouds balance their processing loads over multiple machines, optimizing for efficiency and resilience against point failure. A TAS for VMs installation accomplishes this using the following components:
-
BOSH creates and deploys VMs on top of a physical computing infrastructure, and deploys and runs TAS for VMs on top of this cloud. To configure the deployment, BOSH follows a manifest document. For more information, see the BOSH documentation.
-
Cloud Controller runs the apps and other processes on the cloud’s VMs, balancing demand and managing app lifecycles. For more information, see Cloud Controller.
-
The Gorouter routes incoming traffic from the world to the VMs that are running the apps that the traffic demands, usually working with a customer-provided load balancer. For more information, see TAS for VMs Routing Architecture.
Running apps
This section describes the VMs that run your apps in TAS for VMs and how the platform packages your apps to run on these VMs.
VMs in TAS for VMs
TAS for VMs designates the following types of VMs:
- Component VMs make up the platform’s infrastructure.
- Host VMs host your apps for the outside world.
Within TAS for VMs, the Diego system distributes the hosted app load over all of the host VMs, and keeps it running and balanced through demand surges, outages, or other changes. Diego accomplishes this through an auction algorithm.
For more information, see Diego Components and Architecture.
Distributing apps
To meet demand, multiple host VMs run duplicate instances of the same app. This means that apps must be portable. TAS for VMs distributes app source code to VMs with everything the VMs need to compile and run the apps locally.
TAS for VMs includes the following with your app’s source code:
- Stack: the operating system the app runs on.
- Buildpack: contains all languages, libraries, and services that the app uses.
Before sending an app to a VM, the Cloud Controller stages it for delivery by combining the stack, buildpack, and source code into a droplet that the VM can unpack, compile, and run. For simple, standalone apps with no dynamic pointers, the droplet can contain a pre-compiled executable instead of source code, language, and libraries.
For more information, see:
Organizing users and workspaces
This section describes how TAS for VMs organizes users and workspaces.
TAS for VMs manages user accounts through two User Account and Authentication (UAA) servers, which support access control as OAuth2 services and can store user information internally, or connect to external user stores through LDAP or SAML.
For more information, see User Account and Authentication (UAA) Server.
The following table describes what the two UAA servers do:
| Server | Purpose |
|---|---|
| First UAA server |
|
| Second UAA server |
|
For more information, see Orgs, Spaces, Roles, and Permissions.
Storing resources
The following table describes where TAS for VMs stores resources:
| Resource | Storage Location |
|---|---|
|
GitHub |
|
Internal or external blobstore |
|
MySQL |
Communicating with components
This section describes how TAS for VMs components communicate with one another.
TAS for VMs components communicate in the following ways:
- By sending messages internally using HTTP and HTTPS protocols
- By sending NATS messages to each other directly
BOSH Director co-locates a BOSH DNS server on every deployed VM. All VMs keep up-to-date DNS records for all the other VMs in the same foundation. This enables service discovery between VMs.
BOSH DNS allows deployments to continue communicating with VMs even when the VMs’ IP addresses change. It also provides client-side load balancing by randomly selecting a healthy VM when multiple VMs are available.
For more information about BOSH DNS, see Native DNS Support in the BOSH documentation.
Monitoring and Analyzing
This section describes logging in TAS for VMs.
TAS for VMs generates system logs from TAS for VMs components and app logs from hosted apps. As TAS for VMs runs, its component and host VMs generate logs and metrics. TAS for VMs apps also typically generate logs.
The following table describes where TAS for VMs sends logs:
| Log Type | Destination |
|---|---|
| TAS for VMs component logs | Rsyslog agents |
| TAS for VMs component metrics | Loggregator |
| App logs | Loggregator |
Component logs stream from rsyslog agents, and the cloud operator can configure them to stream out to a syslog drain.
The Loggregator system aggregates the component metrics and app logs into a structured, usable form, the Firehose. You can use all of the output of the Firehose, or direct the output to specific uses, such as monitoring system internals, triggering alerts, or analyzing user behavior, by applying nozzles.
For more information, see Loggregator Architecture.
Using services
This section describes how you can use services with your apps on TAS for VMs.
Typical apps depend on free or metered services such as databases or third-party APIs. To incorporate these into an app:
-
Write a Service Broker: This component manages the life cycle of the service. The Service Broker uses the Service Broker API to advertise a catalog of service offerings to TAS for VMs apps.
-
Provision the Service Instance: Create an instance of the service offering by sending a provision request to the Service Broker API.
-
Enable apps to access the Service Instance: Configure the TAS for VMs app to make calls to the Service Instance using the Service Broker API.
For more information, see Services.
How TAS for VMs Differs from Open Source Cloud Foundry
Open-source software provides the basis for TAS for VMs, which is the VMware distribution of Cloud Foundry Application Runtime software for hosting apps. VMware offers additional commercial features, enterprise services, support, documentation, certificates, and other value-adds.The following diagram shows open source Cloud Foundry components in blue and commercial features available with TAS for VMs in green: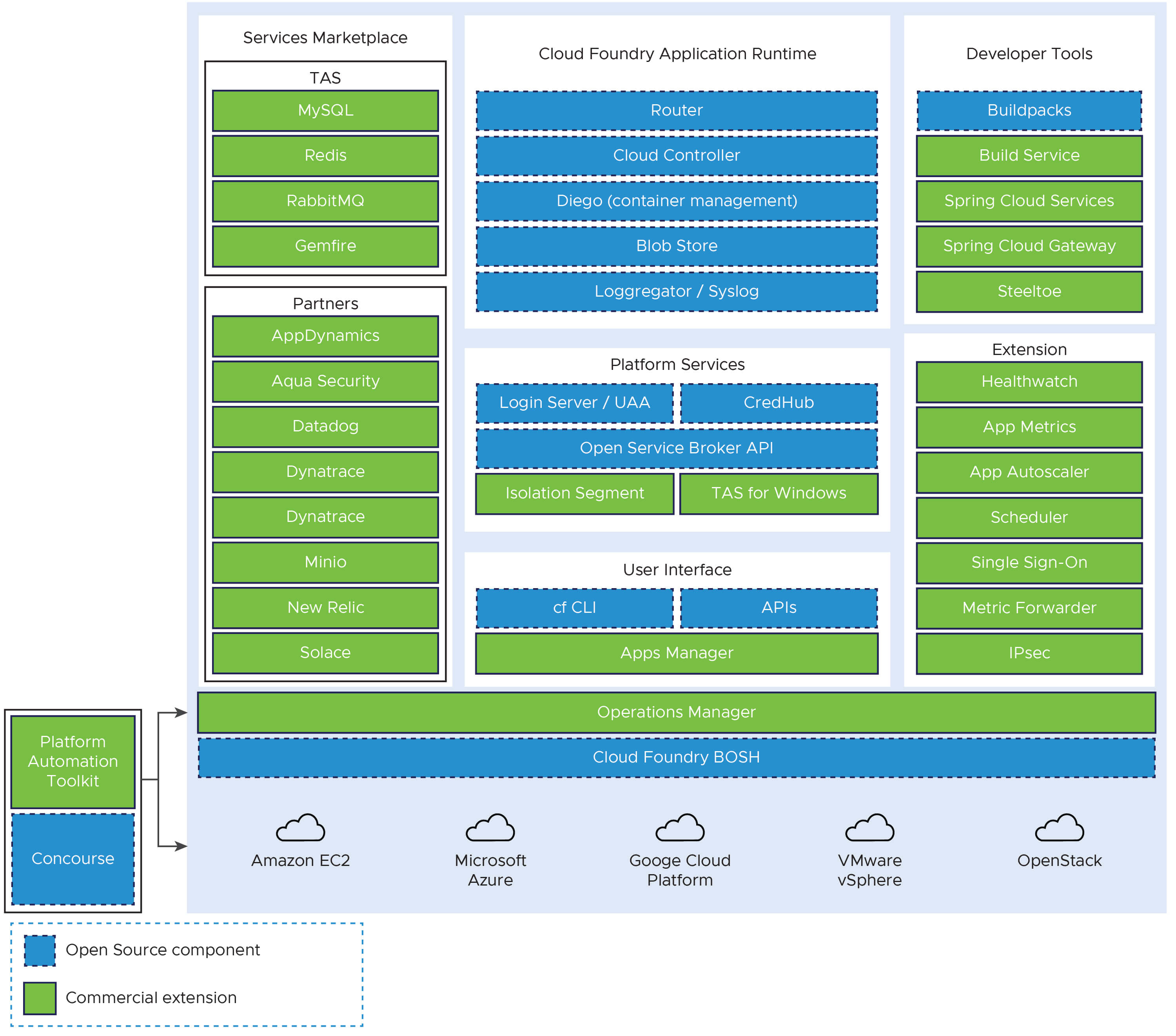
View a larger version of this diagram.