This topic describes how to use Velero to backup and restore a stateful application with ingress and a static IP address.
Overview
This topic describes how to use Velero to backup and restore a stateful application with ingress and a static IP address.
The application we are going to use to demonstrate this scenario is the Cafe stateless app. Kubernetes ingress provides a layer 7 load balancer. In this case the IP address must be static.
To demonstrate backing up and restoring a stateful application:
- Create a Network Profile
- Deploy the Coffee-Tea App
- Back Up the Coffee-Tea App Using Namespace
- Restore the Coffee-Tea App
- Review Conclusions
Prerequisites
Before starting your Velero demonstraion, you need to:
- Have a TKGI Kubernetes cluster with static IP set from a floating IP pool.
- Minio, Velero, and Restic have been installed. For more information, see Installing Velero and Restic.
-
Download the Coffee-Tea app YAML files to a local known directory:
coffee-rc.ymltea-rc.ymlcoffee-svc.ymltea-svc.ymlcafe-ingress-http.yml
-
If testing locally, ensure the following entry is present in the
/etc/hostsof the computer accessing the Coffee-Tea app:/etc/hosts 10.199.41.111 cafe.example.com
Create a Network Profile
To create and apply a network profile for DNS lookup of the Kubernetes API server and the fixed IP address:
-
Create a network profile using the following template:
{ "name": "dns-lookup-api-ingress", "description": "Network Profile for DNS Lookup - API and INGRESS", "parameters": { "fip_pool_ids": [ "970e09f1-6f28-4457-b069-5c40d145f4e3" ], "dns_lookup_mode": "API_INGRESS", "ingress_prefix": "INGRESS-SUBDOMAIN" } }Where
INGRESS-SUBDOMAINis the ingress subdomain prefix.
Because DNS mode is set toAPI_INGRESS, TKGI creates the cluster with ingress_prefix.hostname as the Kubernetes control plane FQDN. TKGI confirms that the ingress subdomain can be resolved as a subdomain prefix on the host before creating new clusters. -
Apply the network profile to your Kubernetes cluster using
tkgi update-cluster. For more information, see Assign a Network Profile to an Existing Cluster in Using Network Profiles.
Deploy the Coffee-Tea App
To deploy the example Coffee-Tea App:
-
To create the Namespace for the application:
kubectl create ns tea-coffeeFor example:
kubectl create ns tea-coffee
namespace/tea-coffee created
-
To deploy the Tea-Coffee app:
kubectl apply -f . -n tea-coffeeFor example:
kubectl apply -f . -n tea-coffee
ingress.extensions/cafe-ingress created
replicationcontroller/coffee-rc created
service/coffee-svc created
replicationcontroller/tea-rc created
service/tea-svc created
-
To verify the example app deployment:
kubectl get all -n tea-coffeeFor example:
kubectl get all -n tea-coffee
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/coffee-rc-8lrwn 1/1 Running 0 7m19s
pod/coffee-rc-kn65r 1/1 Running 0 7m19s
pod/tea-rc-fhhnz 1/1 Running 0 7m19s
pod/tea-rc-t59cs 1/1 Running 0 7m19sNAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicationcontroller/coffee-rc 2 2 2 7m19s
replicationcontroller/tea-rc 2 2 2 7m19sNAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/coffee-svc ClusterIP 10.100.200.22380/TCP 7m19s
service/tea-svc ClusterIP 10.100.200.22980/TCP 7m19s
-
To review the sample app’s ingress configuration:
kubectl get ingress -n tea-coffeeFor example:
kubectl get ingress -n tea-coffee
NAME HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
cafe-ingress cafe.example.com 10.199.41.111 80 8s
-
To review the sample app’s ingress configuration:
kubectl describe ingress cafe-ingress -n tea-coffeeFor example:
kubectl describe ingress cafe-ingress -n tea-coffee
Name: cafe-ingress
Namespace: tea-coffee
Address: 10.199.41.111
Default backend: default-http-backend:80 ()
Rules:
Host Path Backends
—- —- ——–
cafe.example.com
/tea tea-svc:80 (172.16.19.4:80,172.16.19.5:80)
/coffee coffee-svc:80 (172.16.19.2:80,172.16.19.3:80)
Annotations:
kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration: {“apiVersion”:“extensions/v1beta1”,“kind”:“Ingress”,“metadata”:{“annotations”:{},“name”:“cafe-ingress”,“namespace”:“tea-coffee”},“spec”:{“rules”:[{“host”:“cafe.example.com”,“http”:{“paths”:[{“backend”:{“serviceName”:“tea-svc”,“servicePort”:80},“path”:“/tea”},{“backend”:{“serviceName”:“coffee-svc”,“servicePort”:80},“path”:“/coffee”}]}}]}}ncp/internal_ip_for_policy: 100.64.208.63
Events:
-
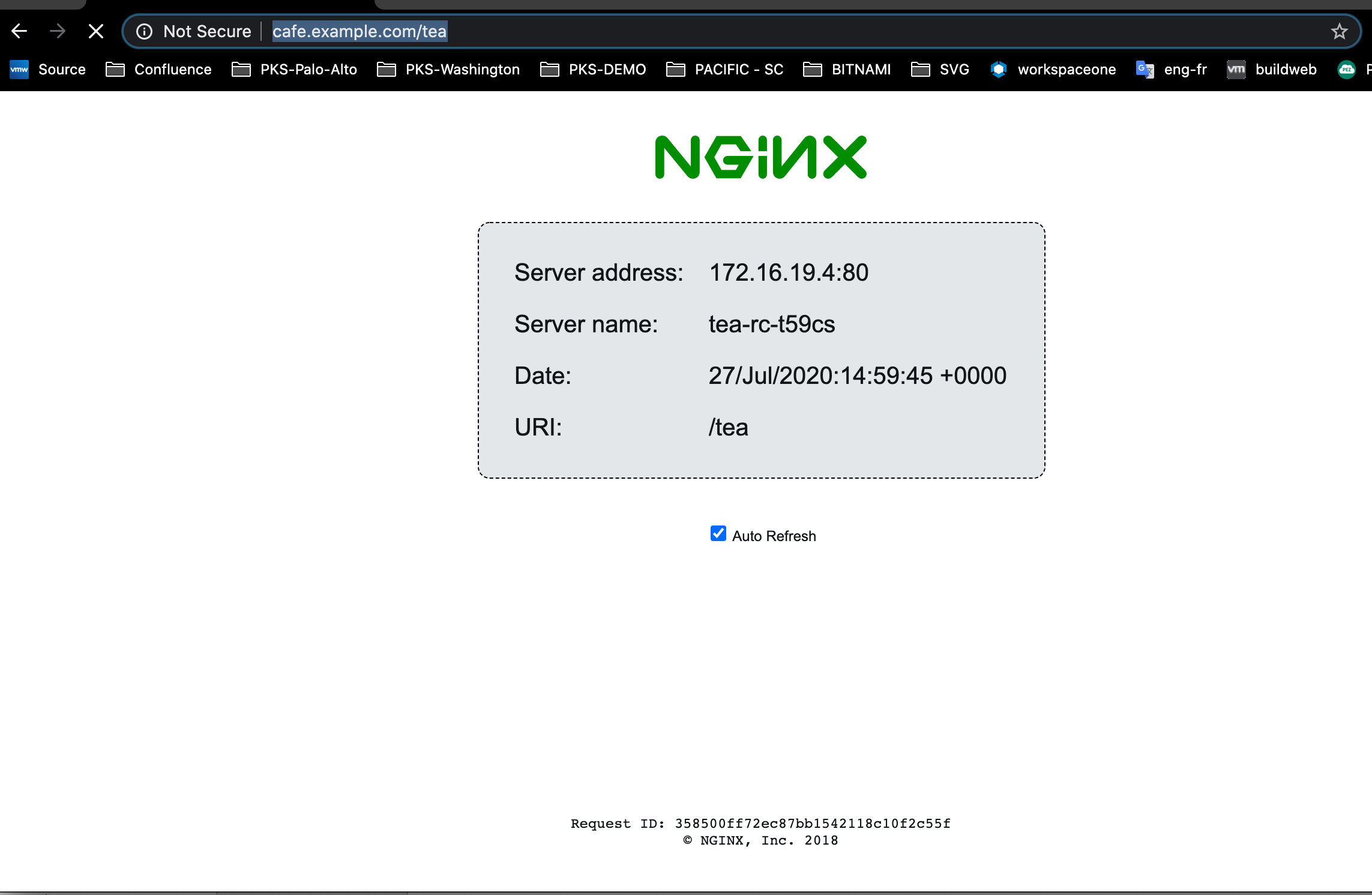
To access the Coffee-Tea app, connect to the Coffee-Tea app at
http://cafe.example.com/coffeeandhttp://cafe.example.com/tea.
For example: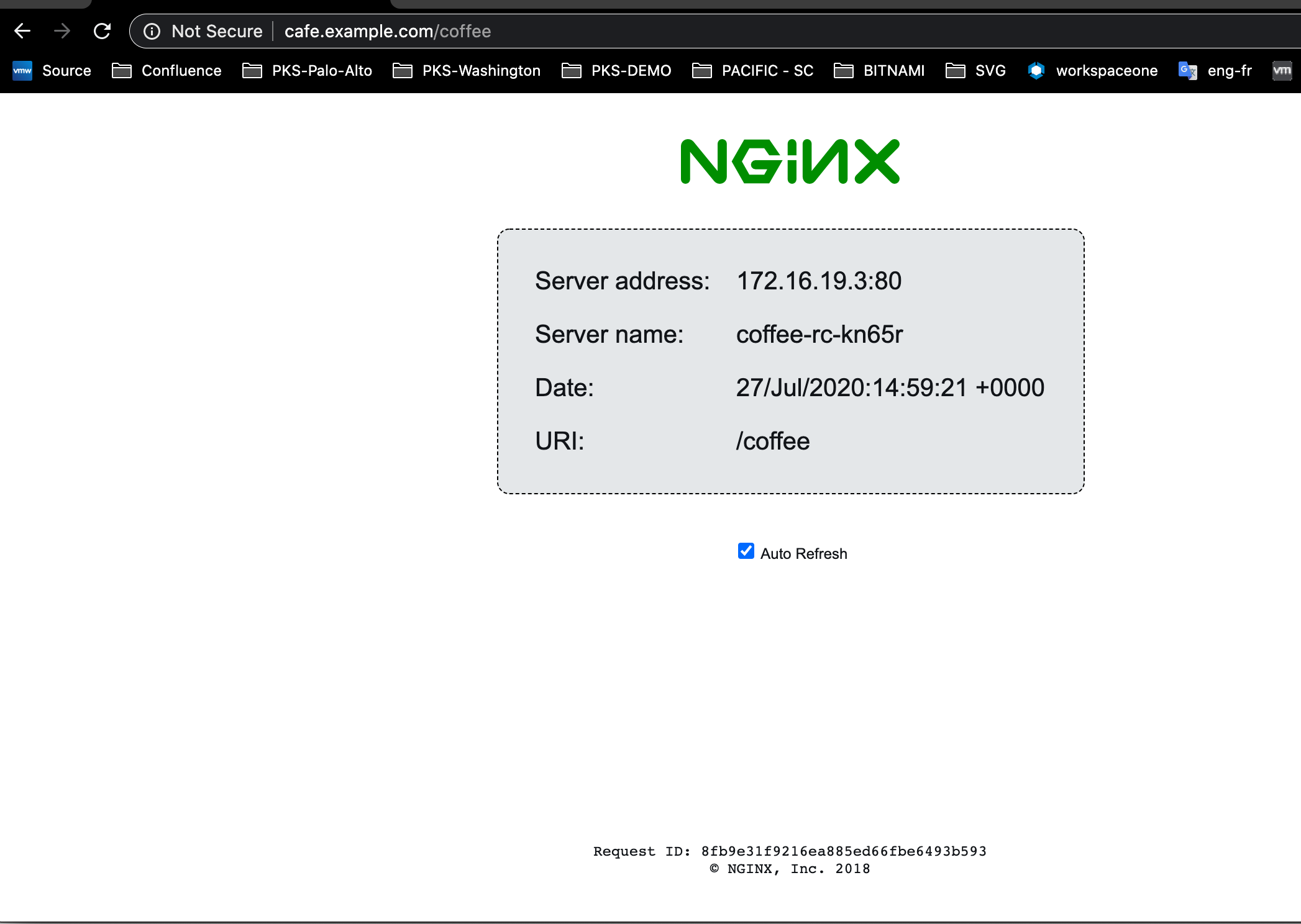
Back Up the Coffee-Tea App Using Namespace
To back up the Coffee-Tea App using the sample apps’s tea-coffee-backup namespace:
-
Use the Velero
backupcommand:velero backup create tea-coffee-backup --include-namespaces tea-coffeeFor example:
velero backup create tea-coffee-backup –include-namespaces tea-coffee
Backup request “tea-coffee-backup” submitted successfully.
Runvelero backup describe tea-coffee-backuporvelero backup logs tea-coffee-backupfor more details.
-
Verify the backup:
velero backup getFor example:
velero backup get
NAME STATUS ERRORS WARNINGS CREATED EXPIRES STORAGE LOCATION SELECTOR
tea-coffee-backup Completed 0 0 2020-07-27 09:16:02 -0700 PDT 29d default
-
Verify the backup by reviewing backup details:
velero backup describe tea-coffee-backup -
To verify the backup further:
-
Use the Velero CRD command:
kubectl get crd -
Review the status of the backup:
kubectl get backups.velero.io -n veleroFor example:
kubectl get backups.velero.io -n velero
NAME AGE
tea-coffee-backup 97s
-
Review the details of the backup:
kubectl describe backups.velero.io tea-coffee-backup -n velero
-
Restore the Coffee-Tea App
To restore the Coffee-Tea app from the backup using Velero:
-
To clear the original Coffee-Tea app from your cluster:
-
Delete the Coffee-Tea app namespace:
kubectl delete ns tea-coffeeFor example:
kubectl delete ns tea-coffee
namespace “tea-coffee” deleted
-
Verify that the Coffee-Tea app has been removed:
kubectl get ns
-
-
To restore the Coffee-Tea app from backup using Velero:
velero restore create --from-backup tea-coffee-backupFor example:
velero restore create –from-backup tea-coffee-backup
Restore request “tea-coffee-backup-20200727092014” submitted successfully.
Runvelero restore describe tea-coffee-backup-20200727092014orvelero restore logs tea-coffee-backup-20200727092014for more details.
-
To verify the Coffee-Tea app has been restored:
-
Review the Velero restoral history:
velero restore getFor example:
velero restore get
NAME BACKUP STATUS ERRORS WARNINGS CREATED SELECTOR
tea-coffee-backup-20200727092014 tea-coffee-backup Completed 0 0 2020-07-27 09:20:14 -0700 PDT
-
To review the Velero restoration:
velero restore describe tea-coffee-backup-20200727092014For example:
velero restore describe tea-coffee-backup-20200727092014
Name: tea-coffee-backup-20200727092014
Namespace: velero
Labels:
Annotations:Phase: Completed
Backup: tea-coffee-backup
Namespaces:
Included: all namespaces found in the backup
Excluded:Resources:
Included: *
Excluded: nodes, events, events.events.k8s.io, backups.velero.io, restores.velero.io, resticrepositories.velero.io
Cluster-scoped: autoNamespace mappings:
Label selector:
Restore PVs: auto
-
Confirm that the Coffee-Tea app’s
tea-coffeenamespace has been restored:kubectl get nsFor example:
kubectl get ns
NAME STATUS AGE
default Active 138m
kube-node-lease Active 138m
kube-public Active 138m
kube-system Active 138m
pks-system Active 121m
tea-coffee Active 56s
velero Active 9m24s
-
Verify that all app objects have been restored:
kubectl get all -n tea-coffeeFor example:
kubectl get all -n tea-coffee
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/coffee-rc-8lrwn 1/1 Running 0 89s
pod/coffee-rc-kn65r 1/1 Running 0 89s
pod/tea-rc-fhhnz 1/1 Running 0 89s
pod/tea-rc-t59cs 1/1 Running 0 89sNAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicationcontroller/coffee-rc 2 2 2 89s
replicationcontroller/tea-rc 2 2 2 89sNAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/coffee-svc ClusterIP 10.100.200.19780/TCP 89s
service/tea-svc ClusterIP 10.100.200.1780/TCP 89s
-
Review the Coffee-Tea app ingress:
kubectl get ingress -n tea-coffeeFor example:
kubectl get ingress -n tea-coffee
NAME HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
cafe-ingress cafe.example.com 10.199.41.111 80 112s
-
Review Coffee-Tea app ingress details:
kubectl describe ingress cafe-ingress -n tea-coffeeFor example:
kubectl describe ingress cafe-ingress -n tea-coffee
Name: cafe-ingress
Namespace: tea-coffee
Address: 10.199.41.111
Default backend: default-http-backend:80 ()
Rules:
Host Path Backends
—- —- ——–
cafe.example.com
/tea tea-svc:80 (172.16.19.2:80,172.16.19.3:80)
/coffee coffee-svc:80 (172.16.19.4:80,172.16.19.5:80)
Annotations:
kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration: {“apiVersion”:“extensions/v1beta1”,“kind”:“Ingress”,“metadata”:{“annotations”:{},“name”:“cafe-ingress”,“namespace”:“tea-coffee”},“spec”:{“rules”:[{“host”:“cafe.example.com”,“http”:{“paths”:[{“backend”:{“serviceName”:“tea-svc”,“servicePort”:80},“path”:“/tea”},{“backend”:{“serviceName”:“coffee-svc”,“servicePort”:80},“path”:“/coffee”}]}}]}}ncp/internal_ip_for_policy: 100.64.208.63
Events:
-
-
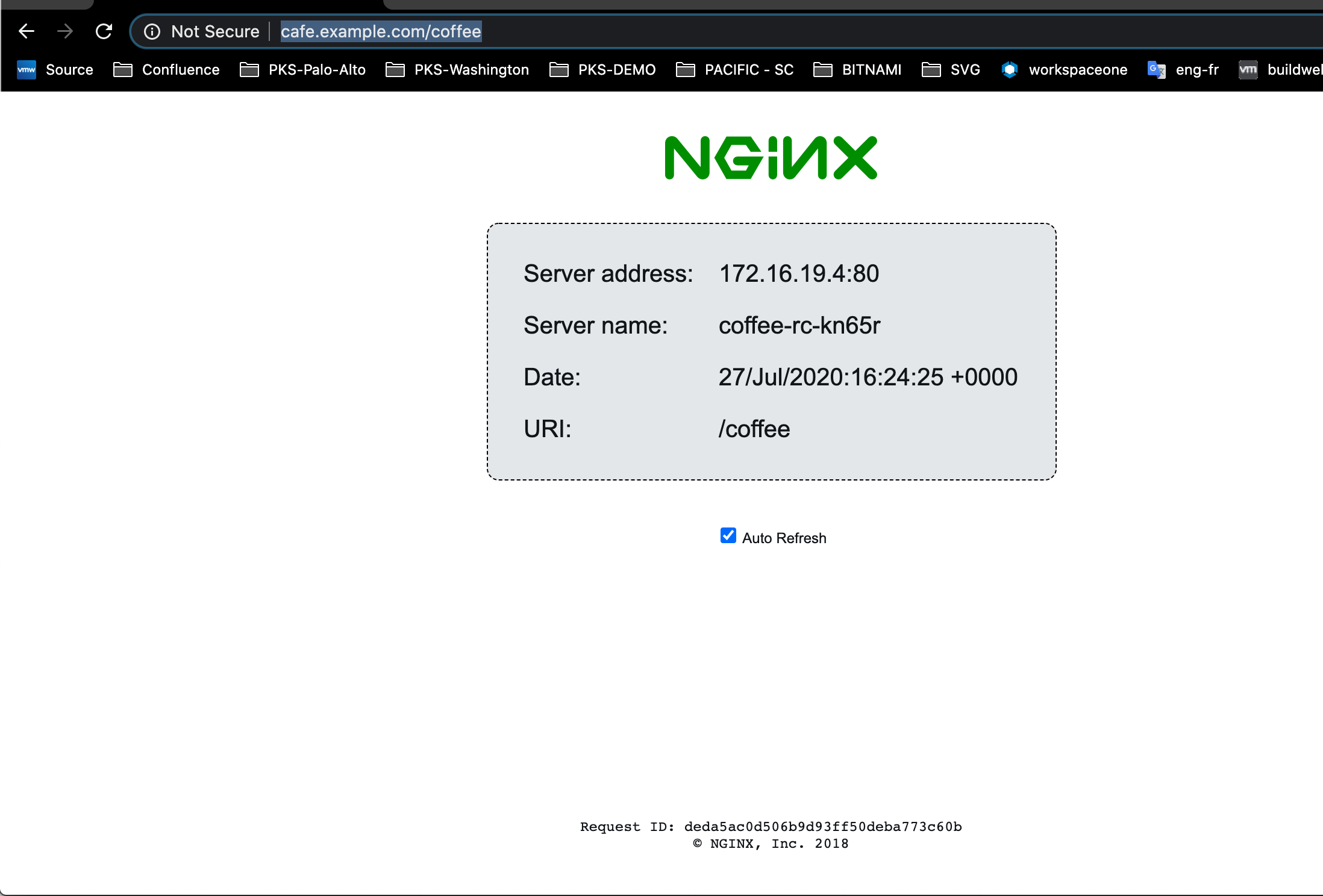
To access the restored Coffee-Tea app, connect to the Coffee-Tea app at
http://cafe.example.com/coffeeandhttp://cafe.example.com/tea.
For example:
Conclusions
Key takeaways from the Velero backup and restore operation for this type of application:
- The namespace ‘tea-coffee’ is automatically recreated by Velero
- The Kubernetes ingress IP is preserved (10.199.41.111)