This topic describes the topologies supported for deploying VMware Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition (TKGI) with NSX.
NAT Topology
The following figure shows a Network Address Translation (NAT) deployment:
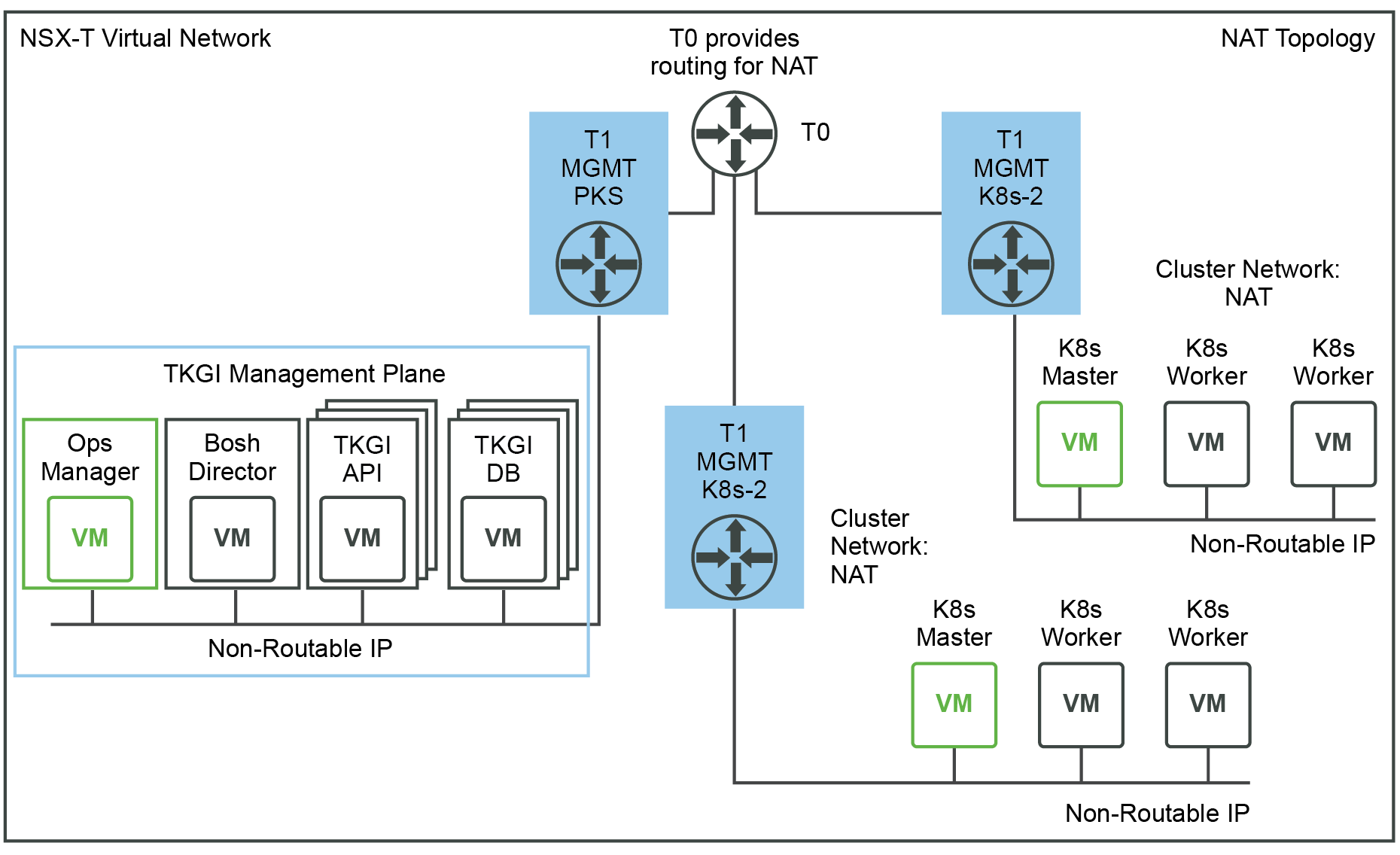
View a larger version of this image.
This topology has the following characteristics:
- TKGI Management Plane (Ops Manager, BOSH Director, and Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition VMs such as the TKGI API and TKGI Database VMs) components are all located on a logical switch that has undergone Network Address Translation on a T0.
- Kubernetes cluster control plane and worker nodes are located on a logical switch that has undergone Network Address Translation on a T0. This requires DNAT rules to allow access to Kubernetes APIs.
No-NAT Topology
A No-NAT topology uses a routable IP subnet for the TKGI Management network and for Kubernetes nodes.
There are two flavors of No-NAT topology: No-NAT with Virtual Switch or No-NAT with Logical Switch.
No-NAT with Virtual Switch (VSS/VDS) Topology
The following figure shows a No-NAT with Virtual Switch (VSS/VDS) deployment:

View a larger version of this image.
This topology has the following characteristics:
- TKGI Management Plane (Ops Manager, BOSH Director, and Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition VMs such as the TKGI API and TKGI Database VMs) components are using corporate routable IP addresses.
- Kubernetes cluster control plane and worker nodes are using corporate routable IP addresses.
- The TKGI Management Plane is deployed outside of the NSX-T network and the Kubernetes clusters are deployed and managed within the NSX-T network. Since BOSH needs routable access to the Kubernetes Nodes to monitor and manage them, the Kubernetes Nodes need routable access.
- (Optional) You can use multiple vCenter Servers to separate management plane components.
Consider the following caveats before using multiple vCenter Servers:- This configuration is only supported through Ops Manager.
- Workload clusters must all use the same vCenter Server.
No-NAT with Logical Switch (NSX-T) Topology
The following figure shows a No-NAT with Logical Switch (NSX-T) deployment:

View a larger version of this image.
This topology has the following characteristics:
- TKGI Management Plane (Ops Manager, BOSH Director, and Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition VMs such as the TKGI API and TKGI Database VMs) components are using corporate routable IP addresses.
- Kubernetes cluster control plane and worker nodes are using corporate routable IP addresses.
- The TKGI Management Plane is deployed inside of the NSX-T network. Both the TKGI Management Plane components (VMs) and the Kubernetes Nodes use corporate routable IP addresses.
Hybrid Topology
With a hybrid topology, the TKGI Management Network is on a routable subnet, while the Kubernetes Nodes Network uses a non-routable subnet (NAT mode is checked in the TKGI tile).
The following figure shows a hybrid topology deployment:
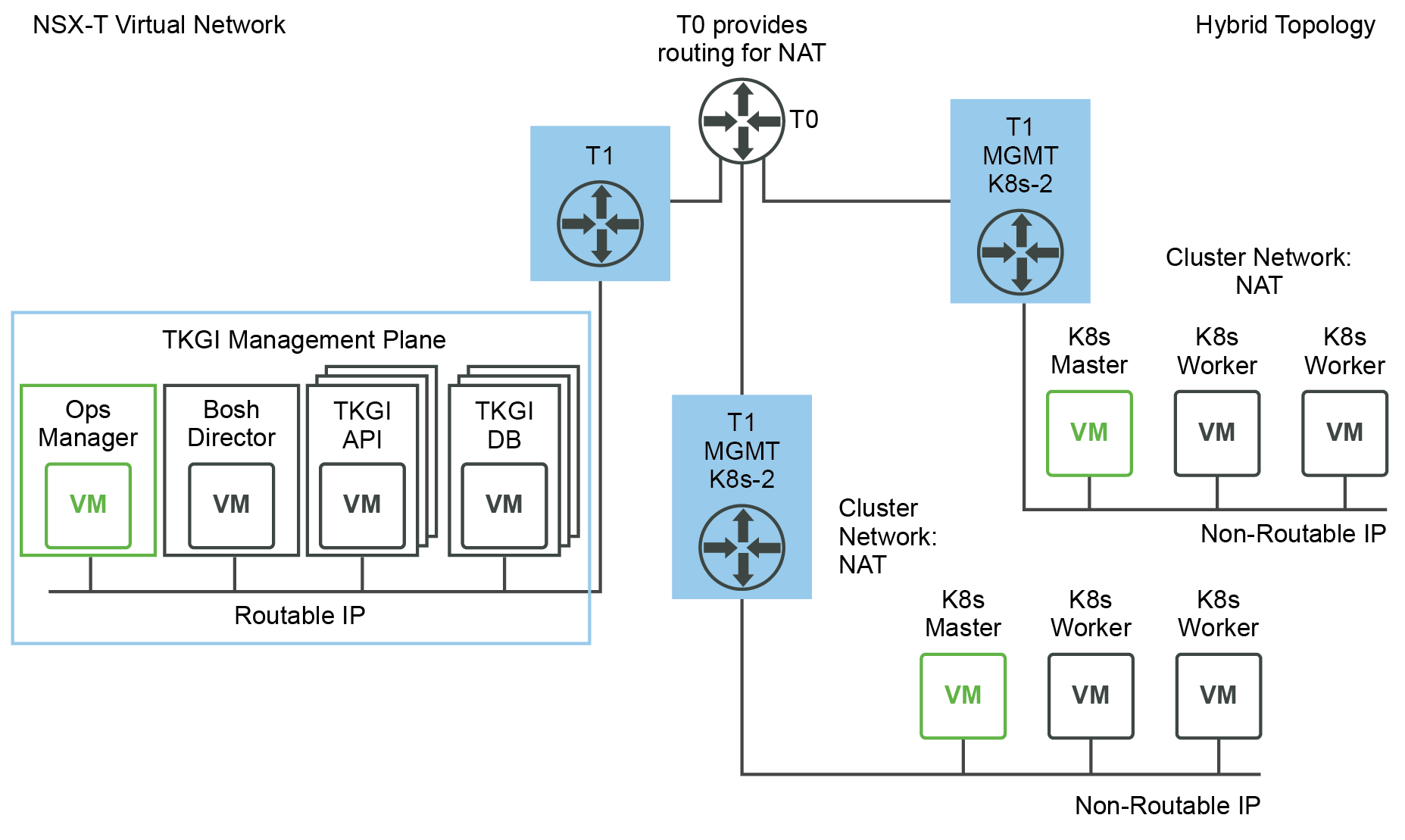
View a larger version of this image.
This topology has the following characteristics:
- TKGI Management Plane (Ops Manager, BOSH Director, and Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition VMs such as the TKGI API and TKGI Database VMs) components are using corporate routable IP addresses.
- Kubernetes cluster control plane and worker nodes are located on a logical switch that has undergone Network Address Translation on a T0. This requires DNAT rules to allow access to Kubernetes APIs.
vSAN Stretched Cluster Topologies
A vSAN Stretched Cluster topology runs across two sites to support highly resilient workloads. vSAN Stretched Cluster topologies include:
- Topology 1: Dedicated vSphere clusters
- Topology 2: Fully collapsed vSphere clusters
For more information about vSAN Stretched Cluster topologies for TKGI, see Solution Guide for Enabling Highly Resilient Kubernetes Workloads Using vSAN Stretched Clusters.