This topic describes the topologies supported for deploying VMware Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition (TKGI) with NSX.
NAT Topology
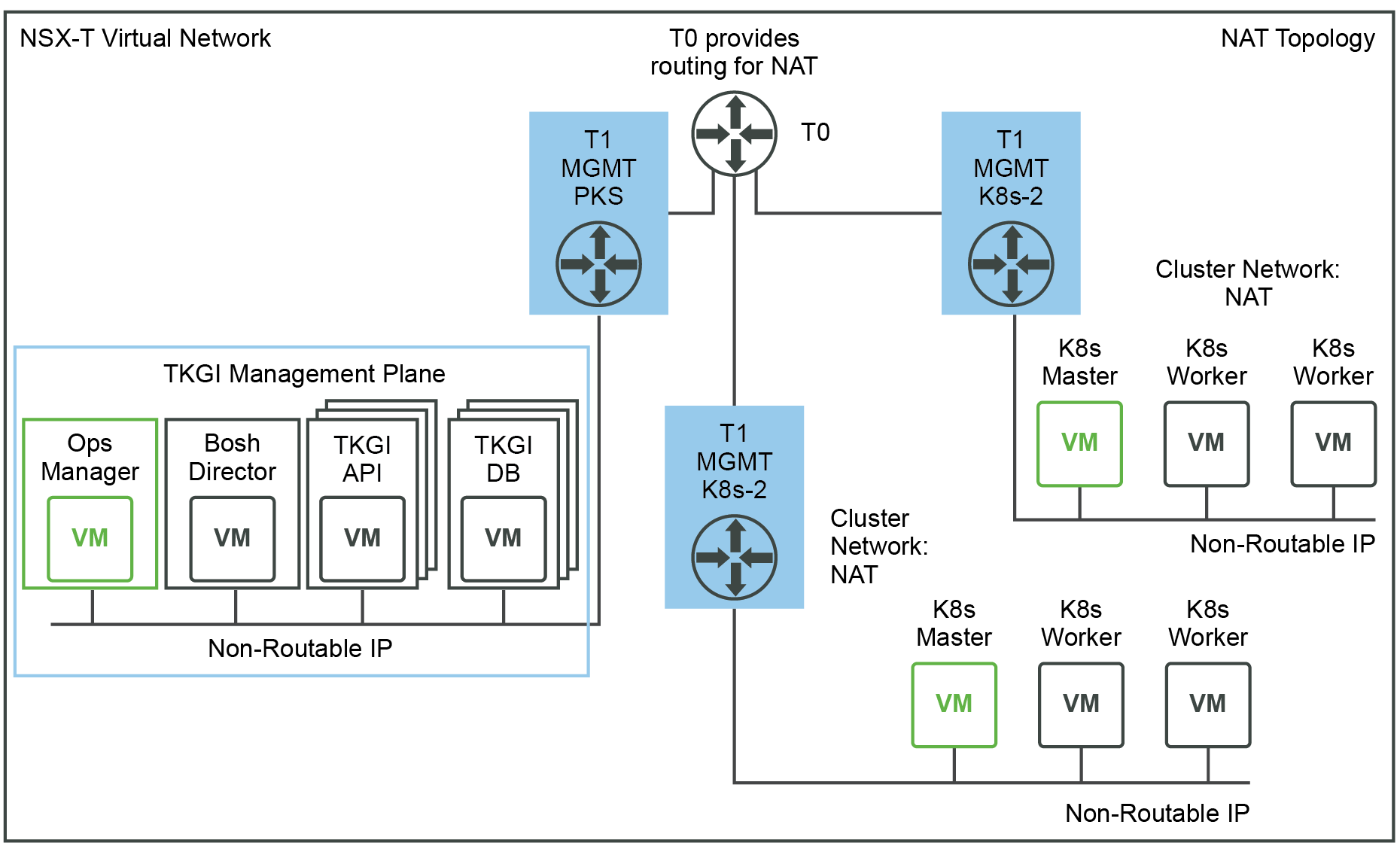
The following figure shows a Network Address Translation (NAT) deployment:
View a larger version of this image.
This topology has the following characteristics:
- TKGI Management Plane (Ops Manager, BOSH Director, and Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition VMs such as the TKGI API and TKGI Database VMs) components are all located on a logical switch that has undergone Network Address Translation on a T0.
- Kubernetes cluster control plane and worker nodes are located on a logical switch that has undergone Network Address Translation on a T0. This requires DNAT rules to allow access to Kubernetes APIs.
No-NAT Topology
A No-NAT topology uses a routable IP subnet for the TKGI Management network and for Kubernetes nodes.
There are two flavors of No-NAT topology: No-NAT with Virtual Switch or No-NAT with Logical Switch.
No-NAT with Virtual Switch (VSS/VDS) Topology
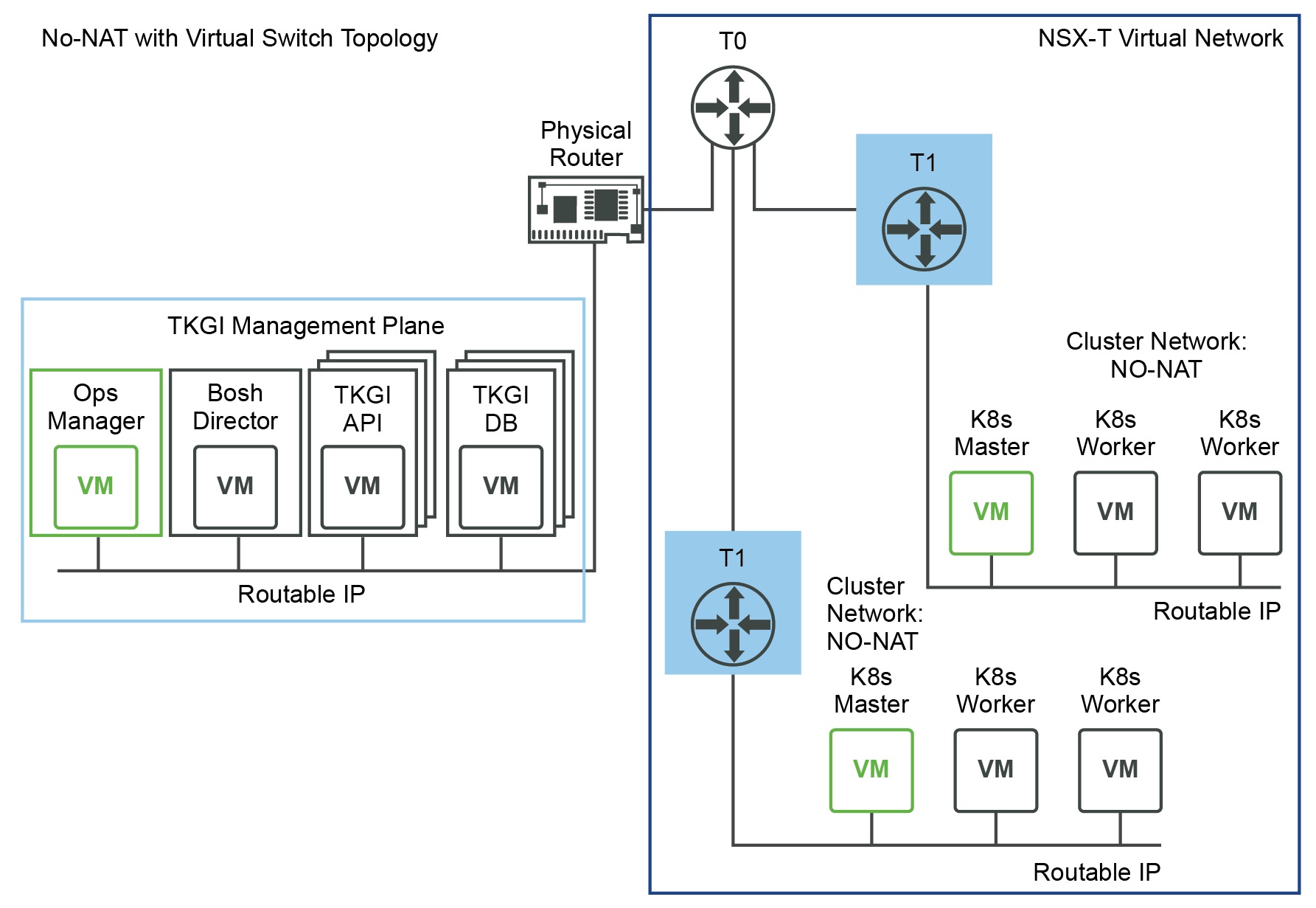
The following figure shows a No-NAT with Virtual Switch (VSS/VDS) deployment:
View a larger version of this image.
This topology has the following characteristics:
- TKGI Management Plane (Ops Manager, BOSH Director, and Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition VMs such as the TKGI API and TKGI Database VMs) components are using corporate routable IP addresses.
- Kubernetes cluster control plane and worker nodes are using corporate routable IP addresses.
- The TKGI Management Plane is deployed outside of the NSX network and the Kubernetes clusters are deployed and managed within the NSX network. Since BOSH needs routable access to the Kubernetes Nodes to monitor and manage them, the Kubernetes Nodes need routable access.
- (Optional) You can use multiple vCenter Servers to separate management plane components.
Consider the following caveats before using multiple vCenter Servers:- This configuration is only supported through Ops Manager.
- Workload clusters must all use the same vCenter Server.
No-NAT with Logical Switch (NSX) Topology
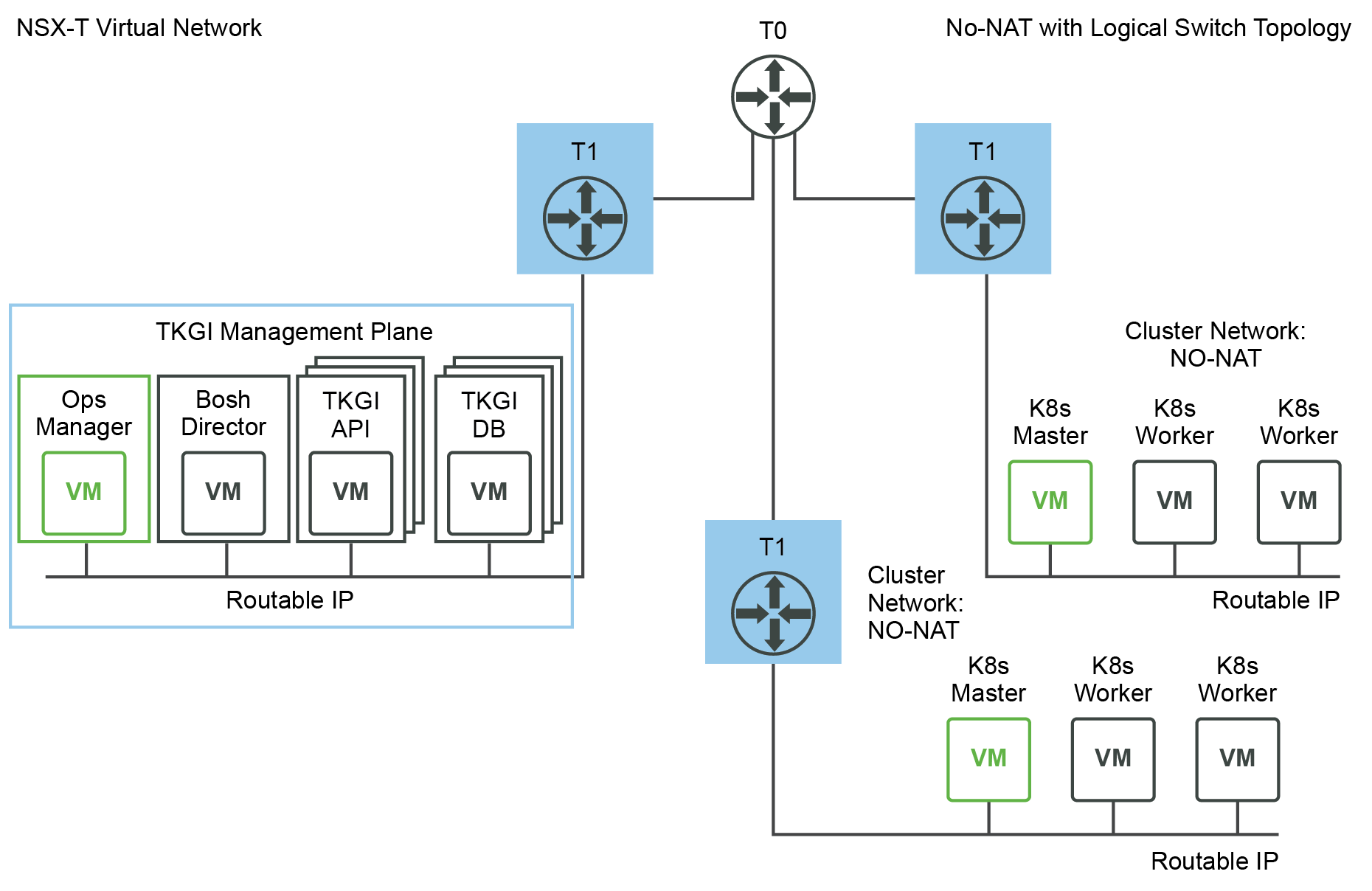
The following figure shows a No-NAT with Logical Switch (NSX) deployment:
View a larger version of this image.
This topology has the following characteristics:
- TKGI Management Plane (Ops Manager, BOSH Director, and Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition VMs such as the TKGI API and TKGI Database VMs) components are using corporate routable IP addresses.
- Kubernetes cluster control plane and worker nodes are using corporate routable IP addresses.
- The TKGI Management Plane is deployed inside of the NSX network. Both the TKGI Management Plane components (VMs) and the Kubernetes Nodes use corporate routable IP addresses.
Hybrid Topology
With a hybrid topology, the TKGI Management Network is on a routable subnet, while the Kubernetes Nodes Network uses a non-routable subnet (NAT mode is checked in the TKGI tile).
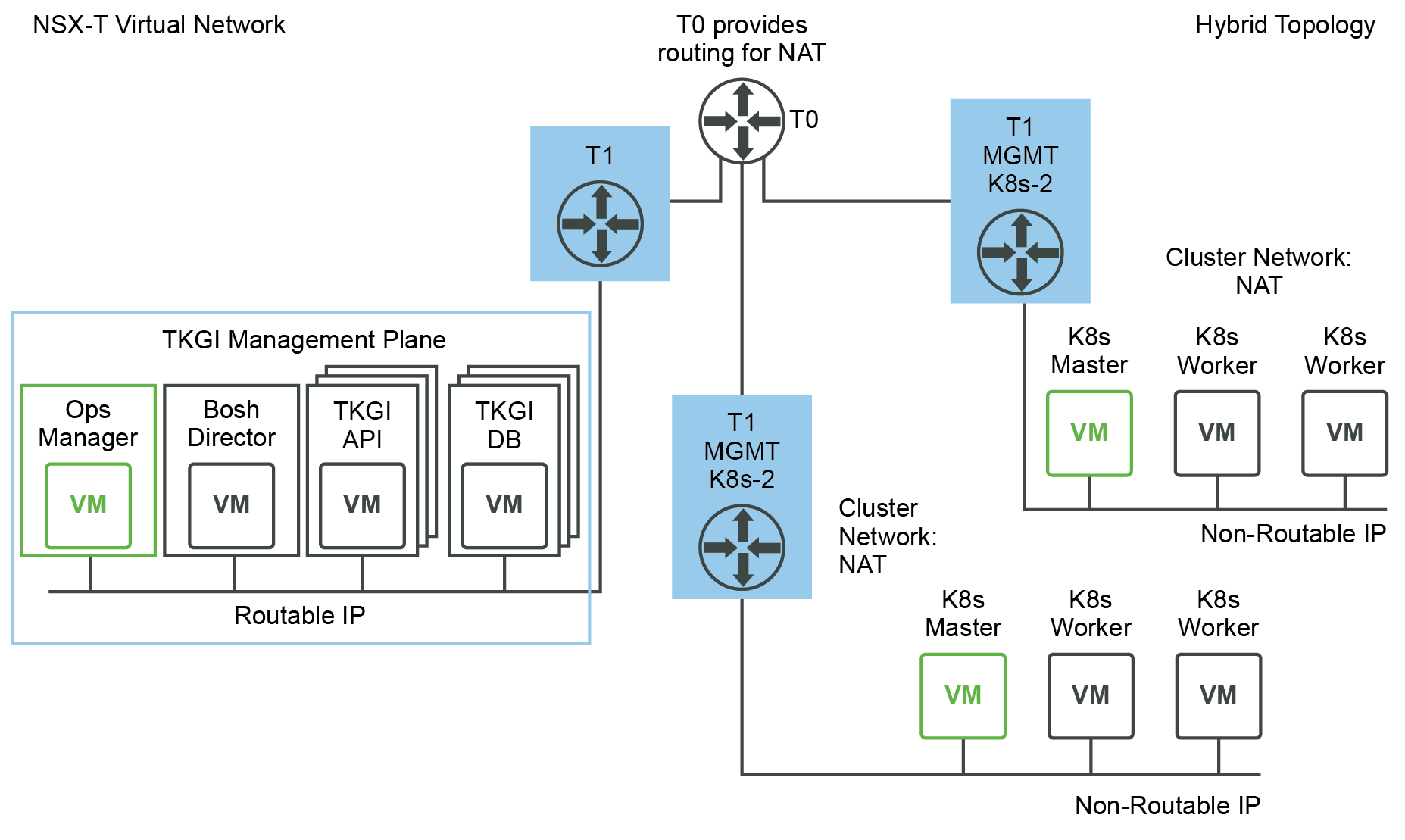
The following figure shows a hybrid topology deployment:
View a larger version of this image.
This topology has the following characteristics:
- TKGI Management Plane (Ops Manager, BOSH Director, and Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition VMs such as the TKGI API and TKGI Database VMs) components are using corporate routable IP addresses.
- Kubernetes cluster control plane and worker nodes are located on a logical switch that has undergone Network Address Translation on a T0. This requires DNAT rules to allow access to Kubernetes APIs.
vSAN Stretched Cluster Topologies
A vSAN Stretched Cluster topology runs across two sites to support highly resilient workloads. vSAN Stretched Cluster topologies include:
- Topology 1: Dedicated vSphere clusters
- Topology 2: Fully collapsed vSphere clusters
For more information about vSAN Stretched Cluster topologies for TKGI, see Solution Guide for Enabling Highly Resilient Kubernetes Workloads Using vSAN Stretched Clusters.