This topic describes how to use Velero to back up and restore a stateful application with a load balancer service with a static IP address.
Overview
This topic describes how to use Velero to back up and restore a Kubernetes stateful application with a service of type load balancer that uses a static IP address.
The application used to demonstrate Velero back up and restore with fixed IP is the WordPress stateful app. By design WordPress stores in its data structure the original IP address that was used during its initial launch. To successfully restore from backup a WordPress app, the service of type load balancer must be deployed with a fixed IP address. This ensures the same IP will be used when a Velero restore is performed.
Prerequisites
Install and configure Minio and Velero.
Download the WordPress app YAML files to a local known directory:
- mysql-deployment.yaml
- wordpress-deployment.yaml
Configure WordPress YAML Files
Edit the wordpress-deployment.yaml to include the static IP for the load balancer (loadBalancerIP: IP). In this example, the IP address used is taken from the NSX floating IP pool that is resourced for TKGI.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: wordpress
labels:
app: wordpress
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
selector:
app: wordpress
tier: frontend
type: LoadBalancer
loadBalancerIP: 10.199.41.110
Create the kustomization.yaml file`:
secretGenerator:
- name: mysql-pass
literals:
- password=YOUR-PASSWORD
resources:
- mysql-deployment.yaml
- wordpress-deployment.yaml
Where YOUR-PASSWORD is your password.
Create the default storage class YAML default-sc.yaml:
kind: StorageClass
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: default-sc
annotations:
storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class: "true"
provisioner: kubernetes.io/vsphere-volume
parameters:
diskformat: thin
Apply the storage class YAML file:
kubectl apply -f 0-default-sc.yaml
storageclass.storage.k8s.io/default-sc created
Verify the storage class:
kubectl get sc
NAME PROVISIONER RECLAIMPOLICY VOLUMEBINDINGMODE ALLOWVOLUMEEXPANSION AGE
default-sc (default) kubernetes.io/vsphere-volume Delete Immediate false 3m38s
Deploy WordPress App
Create WordPress namespace:
kubectl create ns wordpress-lbstaticip
namespace/wordpress-lbstaticip created
Deploy the WordPress app:
kubectl apply -k . -n wordpress-lbstaticip
secret/mysql-pass-c57bb4t7mf created
service/wordpress-mysql created
service/wordpress created
deployment.apps/wordpress-mysql created
deployment.apps/wordpress created
persistentvolumeclaim/mysql-pv-claim created
persistentvolumeclaim/wp-pv-claim created
Verify WordPress app deployment:
kubectl get all -n wordpress-lbstaticip
kubectl get pvc,pv -n wordpress-lbstaticip
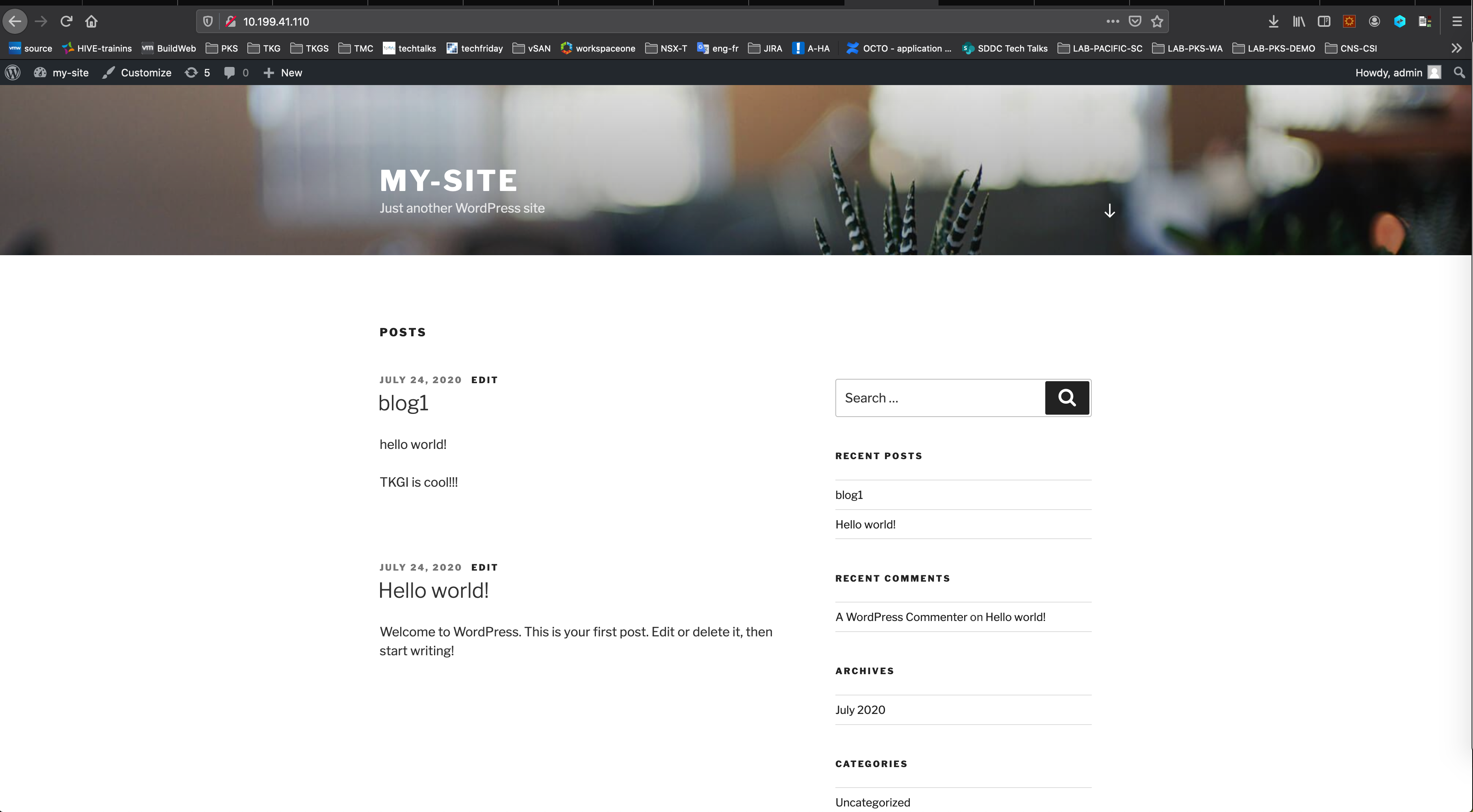
Access the WordPress app at http://10.199.41.110/. Use the static IP you set for the load balancer.
Create a user and log in.
Create blog post.
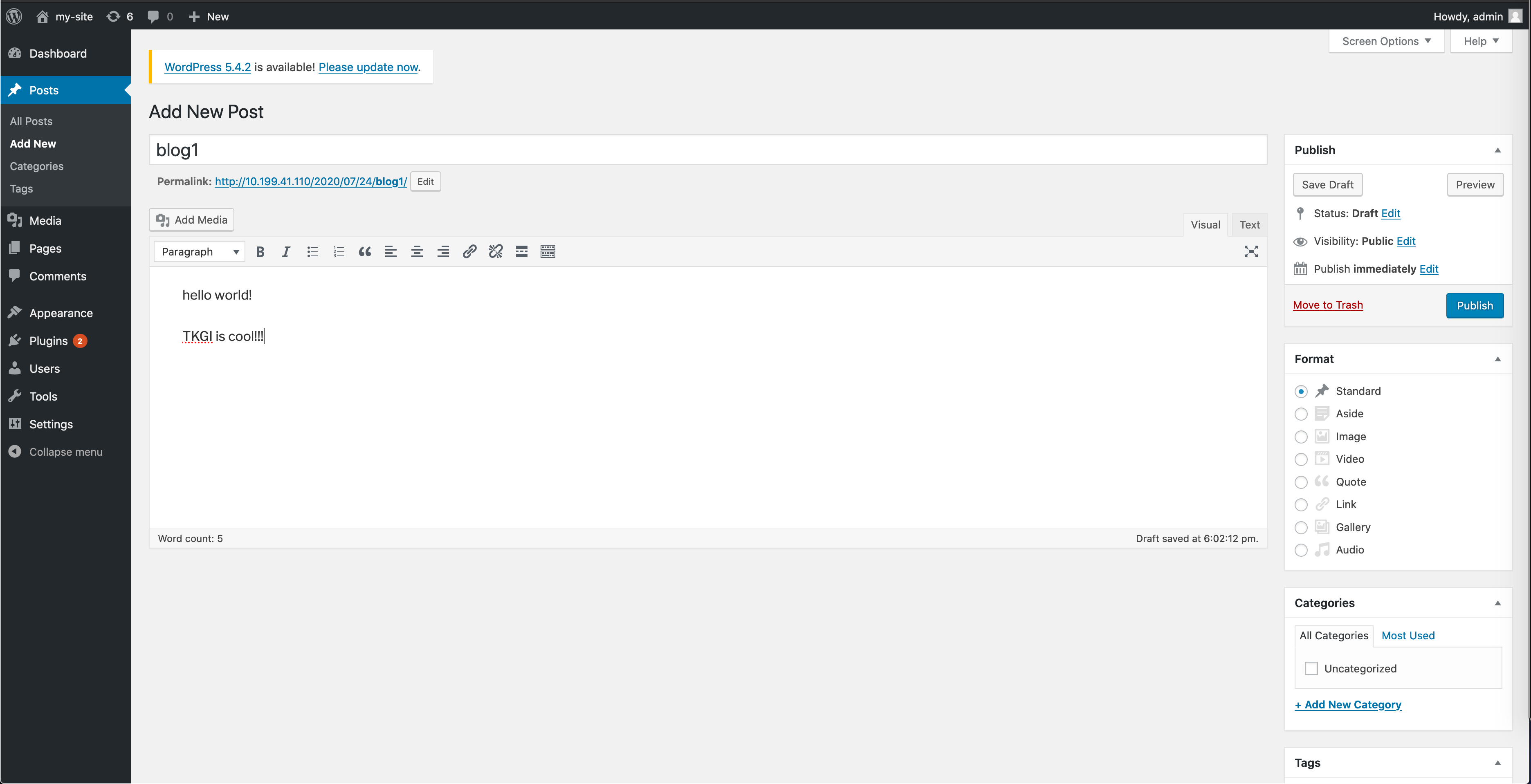
Publish the blog.
Back Up the WordPress App Using Namespace
Because the WordPress app is stateful, add annotations for the stateful pods with the volume name.
From wordpress-deployment.yaml, the volume name is wordpress-persistent-storage.
From mysql-deployment.yaml the volume name is mysql-persistent-storage.
Get the pod names:
kubectl get pod -n wordpress-lbstaticip
Annotate the pods:
kubectl -n wordpress-lbstaticip annotate pod/wordpress-675699f695-f5zdl backup.velero.io/backup-volumes=wordpress-persistent-storage
pod/wordpress-675699f695-f5zdl annotated
kubectl -n wordpress-lbstaticip annotate pod/wordpress-mysql-69dcc4fc49-zpjrd backup.velero.io/backup-volumes=mysql-persistent-storage
pod/wordpress-mysql-69dcc4fc49-zpjrd annotated
Verify the annotations:
kubectl -n wordpress-lbstaticip describe pod wordpress-675699f695-f5zdl | grep Annotations
Annotations: backup.velero.io/backup-volumes: wordpress-persistent-storage
kubectl -n wordpress-lbstaticip describe pod wordpress-mysql-69dcc4fc49-zpjrd | grep Annotations
Annotations: backup.velero.io/backup-volumes: mysql-persistent-storage
Perform the Velero back up:
velero backup create wordpress-lbstaticip-backup --include-namespaces wordpress-lbstaticip
Backup request "wordpress-lbstaticip-backup" submitted successfully.
Run `velero backup describe wordpress-lbstaticip-backup` or `velero backup logs wordpress-lbstaticip-backup` for more details.
Verify the backup that was created.
velero backup get
NAME STATUS ERRORS WARNINGS CREATED EXPIRES STORAGE LOCATION SELECTOR
wordpress-lbstaticip-backup Completed 0 0 2020-07-24 11:35:46 -0700 PDT 29d default <none>
Verify backup details:
velero backup describe wordpress-lbstaticip-backup --details
Use Velero Kubernetes CustomResourceDefinition (CRD) commands to further verify the backup:
kubectl get crd
kubectl get backups.velero.io -n velero
kubectl describe backups.velero.io wordpress-lbstaticip-backup -n velero
Restore the WordPress App
To test the restoration of the WordPress app, delete it.
Delete the namespace:
kubectl delete ns wordpress-lbstaticip
namespace "wordpress-lbstaticip" deleted
Verify namespace deletion:
kubectl get ns
kubectl get pvc,pv --all-namespaces
Make sure the storage class used by the application is still present:
kubectl get sc
Restore the WordPress app:
velero restore create --from-backup wordpress-lbstaticip-backup
Restore request "wordpress-lbstaticip-backup-20200724114046" submitted successfully.
Run `velero restore describe wordpress-lbstaticip-backup-20200724114046` or `velero restore logs wordpress-lbstaticip-backup-20200724114046` for more details.
Verify that the WordPress app is restored:
velero restore get
NAME BACKUP STATUS ERRORS WARNINGS CREATED SELECTOR
wordpress-lbstaticip-backup-20200724114046 wordpress-lbstaticip-backup Completed 0 0 2020-07-24 11:40:46
Verify restoration details:
velero restore describe wordpress-lbstaticip-backup-20200724114046
Name: wordpress-lbstaticip-backup-20200724114046
Namespace: velero
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Phase: Completed
Backup: wordpress-lbstaticip-backup
Namespaces:
Included: all namespaces found in the backup
Excluded: <none>
Resources:
Included: *
Excluded: nodes, events, events.events.k8s.io, backups.velero.io, restores.velero.io, resticrepositories.velero.io
Cluster-scoped: auto
Namespace mappings: <none>
Label selector: <none>
Restore PVs: auto
Node-Agent Restores (specify --details for more information):
Completed: 2
Verify the WordPress namespace:
kubectl get ns
NAME STATUS AGE
default Active 16d
kube-node-lease Active 16d
kube-public Active 16d
kube-system Active 16d
pks-system Active 16d
velero Active 2d21h
wordpress-lbstaticip Active 68s
Check for all WordPress objects in the namespace:
kubectl get all -n wordpress-lbstaticip
Verify persistent volume for WordPress:
kubectl get pvc,pv -n wordpress-lbstaticip
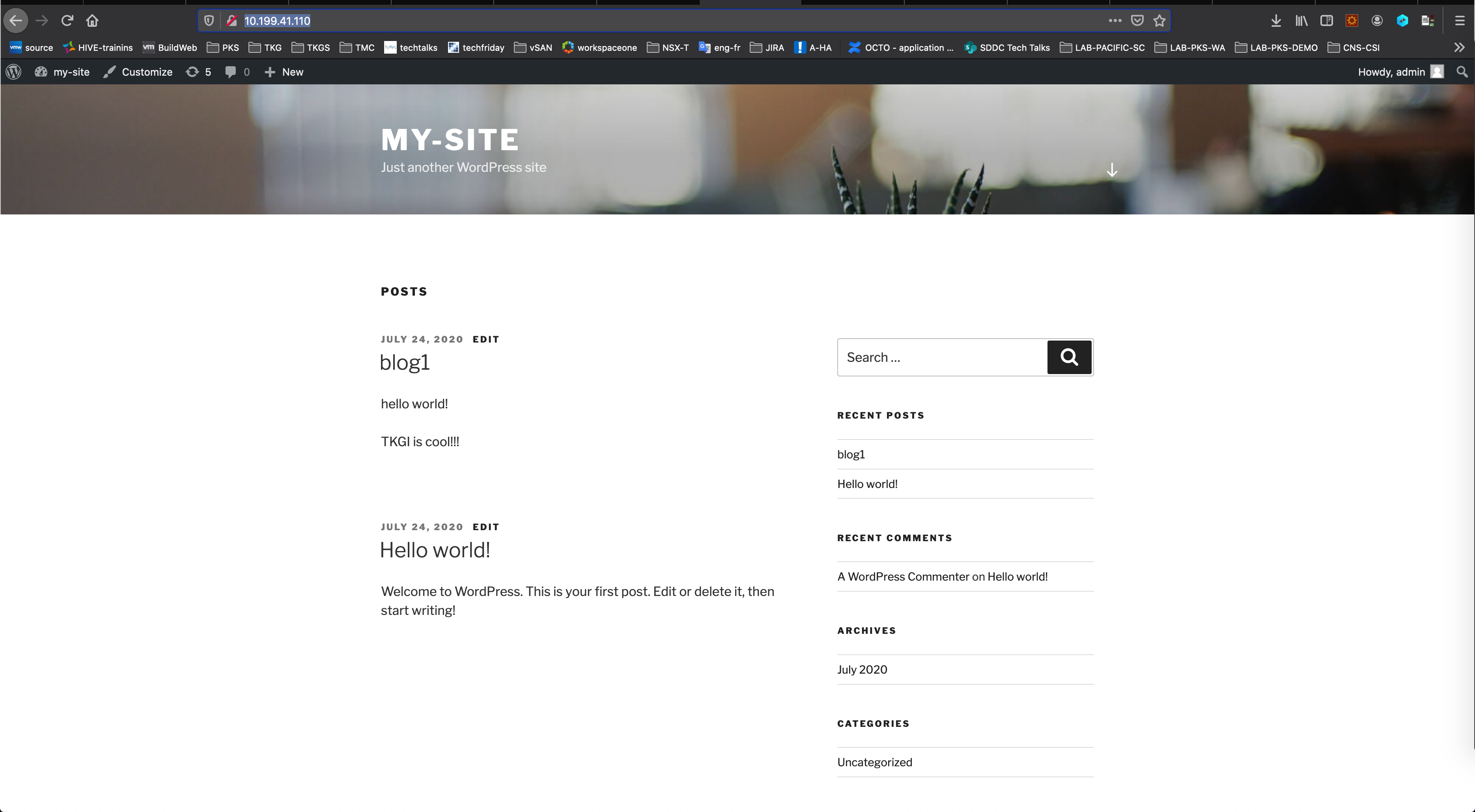
Access the WordPress blog at http://10.199.41.110/. Use the static IP you set for the load balancer.
Conclusions
Key takeaways from the Velero back up and restore operation for this type of application:
- Pod annotation is still required for Velero to back up a PV.
- The namespace
wordpress-lbstaticipwas automatically re-created. - The K8s SVC LB IP has been preserved as expected.