Install Contour for Ingress Control
This topic explains how to deploy Contour into a workload cluster in Tanzu Kubernetes Grid.
Contour is a Kubernetes ingress controller that uses the Envoy edge and service proxy. Tanzu Kubernetes Grid includes signed binaries for Contour and Envoy, which you can deploy into workload clusters to provide ingress control services in those clusters.
You deploy Contour and Envoy directly into workload clusters. Deploying Contour is a prerequisite if you want to deploy the Prometheus, Grafana, and Harbor packages.
For general information about ingress control, see Ingress Controllers in the Kubernetes documentation.
Prerequisites
- A bootstrap machine with the following installed:
- Tanzu CLI, Tanzu CLI plugins, and
kubectl, as described in Install the Tanzu CLI and Kubernetes CLI for Use with a vSphere with Tanzu Supervisor or Install the Tanzu CLI and Kubernetes CLI for Use with Standalone Management Clusters. - yq v4.5 or later.
- Tanzu CLI, Tanzu CLI plugins, and
- You have deployed at least one workload cluster. For instructions, see Creating Workload Clusters.
ImportantIn this release of Tanzu Kubernetes Grid, the provided implementation of Contour and Envoy assumes that you use self-signed certificates.
Prepare the Workload Cluster for Contour Deployment
To prepare the cluster:
-
Get the
admincredentials of the workload cluster into which you want to deploy Contour. For example:tanzu cluster kubeconfig get my-cluster --adminIn the example above,
my-clusteris the name of the cluster. -
Set the context of
kubectlto the cluster. For example:kubectl config use-context my-cluster-admin@my-cluster -
If the cluster does not have a package repository with the Contour package installed, such as the
tanzu-standardrepository, install one:tanzu package repository add PACKAGE-REPO-NAME --url PACKAGE-REPO-ENDPOINT --namespace tkg-systemWhere:
PACKAGE-REPO-NAMEis the name of the package repository, such astanzu-standardor the name of a private image registry configured withADDITIONAL_IMAGE_REGISTRYvariables.-
PACKAGE-REPO-ENDPOINTis the URL of the package repository.- For this release, the
tanzu-standardURL isprojects.registry.vmware.com/tkg/packages/standard/repo:v2023.10.16. See List Package Repositories to obtain this value from the Tanzu CLI, or in Tanzu Mission Control see the Addons > Repositories list in the Cluster pane.
- For this release, the
-
If you have not already done so, install cert-manager in the cluster. For instructions, see Install cert-manager for Certificate Management.
-
Proceed to Deploy Contour into the Workload Cluster below.
Deploy Contour into the Workload Cluster
After you have set up the cluster, you must first create the configuration file that is used when you install the Contour package and then install the package.
-
Create a configuration file for the Contour package by retrieving the default configuration of the package:
tanzu package available get contour.tanzu.vmware.com/PACKAGE-VERSION --default-values-file-output FILE-PATHWhere
PACKAGE-VERSIONis the version of the Contour package that you want to install andFILE-PATHis the location to which you want to save the configuration file, for example,contour-data-values.yaml. -
Configure the following in the
contour-data-values.yamlfile:- vSphere
-
This file configures the Contour package on vSphere.
--- infrastructure_provider: vsphere namespace: tanzu-system-ingress contour: configFileContents: {} useProxyProtocol: false replicas: 2 pspNames: "vmware-system-restricted" logLevel: info envoy: service: type: NodePort annotations: {} externalTrafficPolicy: Cluster disableWait: false hostPorts: enable: true http: 80 https: 443 hostNetwork: false terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 300 logLevel: info certificates: duration: 8760h renewBefore: 360h - AWS
-
This file configures the Contour package on vSphere.
--- infrastructure_provider: aws namespace: tanzu-system-ingress contour: configFileContents: {} useProxyProtocol: false replicas: 2 pspNames: "vmware-system-restricted" logLevel: info envoy: service: type: LoadBalancer annotations: {} externalTrafficPolicy: Cluster aws: LBType: classic disableWait: false hostPorts: enable: true http: 80 https: 443 hostNetwork: false terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 300 logLevel: info certificates: duration: 8760h renewBefore: 360h - Azure
-
This file configures the Contour package on Azure.
--- infrastructure_provider: azure namespace: tanzu-system-ingress contour: configFileContents: {} useProxyProtocol: false replicas: 2 pspNames: "vmware-system-restricted" logLevel: info envoy: service: type: LoadBalancer annotations: {} externalTrafficPolicy: Cluster disableWait: false hostPorts: enable: true http: 80 https: 443 hostNetwork: false terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 300 logLevel: info certificates: duration: 8760h renewBefore: 360h
-
If you are installing Contour to a workload cluster created by a vSphere with Tanzu Supervisor, do one of the following:
-
Without
hostPorts:If
hostPortsare not needed for the Envoy daemonset, editcontour-data-values.yamlto setenvoy.hostPorts.enabletofalse:contour-data-values.yaml envoy: hostPorts: enable: false -
With
hostPorts:If
hostPortsare needed, create aClusterRoleBindingthat gives the Envoy service account access to thetkg-system-privilegedPSP:kubectl create clusterrolebinding envoy-tkg-admin-privileged-binding --clusterrole=psp:vmware-system-privileged --serviceaccount=tanzu-system-ingress:envoy
-
-
If you are installing Contour to a vSphere cluster that uses NSX ALB as a load balancer service provider, modify the
contour-default-values.yamlfile to setenvoy.service.typetoLoadBalancer:[...] envoy: service: type: LoadBalancer -
If you are installing Contour to an internet-restricted AWS environment, modify the
contour-data-values.yamlfile to add the following annotation to the Envoy service:infrastructure_provider: aws [...] envoy: service: annotations: service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-internal: "true" -
(Optional) Modify the
contour-data-values.yamlfile if needed. The Optional Configuration section documents the values that you can customize in thecontour-data-values.yamlfile and how they can be used to modify the default behavior of Contour in your target cluster. For example, the Contour package deploys two Contour replicas by default, but the number of replicas is configurable. You set this number in thecontour.replicasvalue incontour-data-values.yaml. In most cases, you do not need to modify thecontour-data-values.yamlfile.You can also retrieve these values by running the below command against your target cluster:
tanzu package available get contour.tanzu.vmware.com/AVAILABLE-VERSION --values-schemaWhere
AVAILABLE-VERSIONis the version of the Contour package. The--values-schemaflag retrieves thevaluesSchemasection from thePackageAPI resource for the Contour package. You can set the output format,--output, for the values schema toyaml,json, ortable. For more information, see Packages in Install and Manage Packages.For example:
tanzu package available get contour.tanzu.vmware.com/1.25.4+vmware.1-tkg.1 --values-schema -
If your
contour-data-values.yamlfile contains comments, remove them:yq -i eval '... comments=""' contour-data-values.yaml -
Install the Contour package:
-
Retrieve the name of the available package:
tanzu package available list -A -
Retrieve the version of the available package:
tanzu package available list contour.tanzu.vmware.com -A -
Install the package:
tanzu package install contour \ --package contour.tanzu.vmware.com \ --version AVAILABLE-PACKAGE-VERSION \ --values-file contour-data-values.yaml \ --namespace TARGET-NAMESPACEWhere:
-
TARGET-NAMESPACEis the namespace in which you want to install the Contour package. For example, themy-packagesortanzu-cli-managed-packagesnamespace.- If the
--namespaceflag is not specified, the Tanzu CLI uses thedefaultnamespace. The Contour and Envoy pods and any other resources associated with the Contour component are created in thetanzu-system-ingressnamespace; do not install the Contour package into this namespace. - The specified namespace must already exist, for example from running
kubectl create namespace my-packages.
- If the
-
AVAILABLE-PACKAGE-VERSIONis the version that you retrieved above.
For example:
tanzu package install contour \ --package contour.tanzu.vmware.com \ --version 1.25.4+vmware.1-tkg.1 \ --values-file contour-data-values.yaml \ --namespace my-packages -
-
-
Confirm that the
contourpackage has been installed:tanzu package installed list -AFor example:
tanzu package installed list -A - Retrieving installed packages... NAME PACKAGE-NAME PACKAGE-VERSION STATUS NAMESPACE cert-manager cert-manager.tanzu.vmware.com 1.10.1+vmware.1-tkg.1 Reconcile succeeded my-packages contour contour.tanzu.vmware.com 1.25.4+vmware.1-tkg.1 Reconcile succeeded my-packages antrea antrea.tanzu.vmware.com Reconcile succeeded tkg-system [...]To see more details about the package, you can also run:
tanzu package installed get contour --namespace PACKAGE-NAMESPACEWhere
PACKAGE-NAMESPACEis the namespace in which thecontourpackage is installed.For example:
tanzu package installed get contour --namespace my-packages \ Retrieving installation details for contour... NAME: contour PACKAGE-NAME: contour.tanzu.vmware.com PACKAGE-VERSION: 1.25.4+vmware.1-tkg.1 STATUS: Reconcile succeeded CONDITIONS: [{ReconcileSucceeded True }] USEFUL-ERROR-MESSAGE: -
Confirm that the
contourapp has been successfully reconciled in yourPACKAGE-NAMESPACE:kubectl get apps -AFor example:
NAMESPACE NAME DESCRIPTION SINCE-DEPLOY AGE my-packages cert-manager Reconcile succeeded 78s 3h5m my-packages contour Reconcile succeeded 57s 6m3s tkg-system antrea Reconcile succeeded 45s 3h18m [...]If the status is not
Reconcile Succeeded, view the full status details of thecontourapp. Viewing the full status can help you troubleshoot the problem.kubectl get app contour --namespace PACKAGE-NAMESPACE -o yamlWhere
PACKAGE-NAMESPACEis the namespace in which you installed the package. If troubleshooting does not help you solve the problem, you must uninstall the package before installing it again:tanzu package installed delete contour --namespace PACKAGE-NAMESPACE -
Confirm that Contour and Envoy pods are running in the
tanzu-system-ingressnamespace:kubectl get pods -AFor example:
kubectl get pods -A NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE [...] tanzu-system-ingress contour-5dc6fc667c-c4w8k 1/1 Running 0 14m tanzu-system-ingress contour-5dc6fc667c-jnqwn 1/1 Running 0 14m tanzu-system-ingress envoy-mgfll 2/2 Running 0 14m [...] -
If you deployed Contour to AWS or Azure, confirm that a load balancer has been created for the Envoy service:
kubectl get svc envoy -n tanzu-system-ingress -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].hostname}'On AWS, the loadbalancer has a name similar to
aabaaad4dfc8e4a808a70a7cbf7d9249-1201421080.us-west-2.elb.amazonaws.com. On Azure, it will be an IP address similar to20.54.226.44.
Access the Envoy Administration Interface Remotely
After you have deployed Contour into a cluster, you can use the embedded Envoy administration interface to retrieve data about your deployments.
For information about the Envoy administration interface, see Administration Interface in the Envoy documentation.
-
Obtain the name of the Envoy pod:
ENVOY_POD=$(kubectl -n tanzu-system-ingress get pod -l app=envoy -o name | head -1) -
Forward the Envoy pod to port 9001 on your bootstrap machine:
kubectl -n tanzu-system-ingress port-forward $ENVOY_POD 9001 -
From your bootstrap machine, retrieve information from your Contour deployment by sending
curlqueries to the Envoy administration endpoints listed in Accessing the Envoy Administration Interface. For example, use the/config_dumpendpoint to retrieve the currently loaded configuration:curl http://localhost:9001/config_dump
Visualize the Internal Contour Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG)
When you have started running workloads in your cluster, you can visualize the traffic information that Contour exposes in the form of a directed acyclic graph (DAG).
-
Install Graphviz if it is not already installed. This package provides the
dotcommand that creates the DAG image file. -
Obtain the name of a Contour pod:
CONTOUR_POD=$(kubectl -n tanzu-system-ingress get pod -l app=contour -o name | head -1) -
Forward port 6060 on the Contour pod:
kubectl -n tanzu-system-ingress port-forward $CONTOUR_POD 6060 -
Open a new terminal window and download and save the DAG as a
*.pngfile. The below command requires you to installdoton your system if it is not present already.curl localhost:6060/debug/dag | dot -T png > contour-dag.png -
Open
contour-dag.pngto view the graph.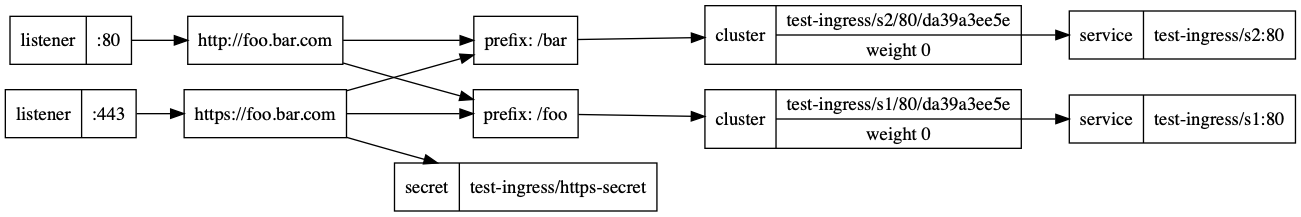
Optional Configuration
You can further customize your configuration by editing the default values in the Contour package configuration file.
The table below contains information about the values that you can customize in the contour-data-values.yaml file and how they can be used to modify the default behavior of Contour when deployed into a workload cluster.
If you reconfigure your Contour settings after the initial deployment, you must follow the steps in Update a Running Contour Deployment to apply the new configuration to the cluster.
| Config | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
infrastructure_provider |
vsphere |
The underlying target platform. Valid values are vsphere, aws, and azure. |
kubernetes_distribution |
none | The distribution of Kubernetes, used to determine if distribution-specific configurations need to be applied. Options are empty and openshift. If running on an Openshift cluster, this must be set to openshift. When set to openshift, a Role and RoleBinding are created to associate Contour’s controllers with the appropriate Openshift Security Context Constraint resource. |
kubernetes_version |
none | The version of Kubernetes being used, for enabling version-specific behaviors. Accept any valid major.minor.patch version of Kubernetes. This field is optional. Currently only has effect when kubernetes_distribution is set to openshift. |
namespace |
tanzu-system-ingress |
The namespace where Contour and Envoy pods run, distinct from where the packages are deployed. |
registry_secret_names |
["contour-reg-creds"] |
The names of the placeholder secrets that will contain registry credentials to pull the Contour and Envoy images. |
contour.configFileContents |
none | The YAML contents of the Contour config file. For more information, see Configuration File in the Contour documentation. |
contour.replicas |
2 |
How many Contour pod replicas to have. |
contour.useProxyProtocol |
false |
Whether to enable PROXY protocol for all Envoy listeners. |
contour.logLevel |
info |
The Contour log level. Valid values are info and debug. |
contour.pspNames |
vmware-system-restricted |
A comma-separated list of pod security policies (PSPs) to apply to the Contour pods. |
contour.resources.contour.limits.cpu |
none | CPU limit to apply to the contour container in the contour deployment. |
contour.resources.contour.limits.memory |
none | Memory limit to apply to the contour container in the contour deployment. |
contour.resources.contour.requests.cpu |
none | CPU request to apply to the contour container in the contour deployment. |
contour.resources.contour.requests.memory |
none | Memory request to apply to the contour container in the contour deployment. |
envoy.workload.type |
DaemonSet |
The type of Kubernetes workload Envoy is deployed as. Options are Deployment or DaemonSet. |
envoy.workload.replicas |
2 |
The number of Envoy replicas to deploy when envoy.workload.type is set to Deployment. |
envoy.workload.resources.envoy.limits.cpu |
none | CPU limit to apply to the envoy container in the envoy workload. |
envoy.workload.resources.envoy.limits.memory |
none | Memory limit to apply to the envoy container in the envoy workload. |
envoy.workload.resources.envoy.requests.cpu |
none | CPU request to apply to the envoy container in the envoy workload. |
envoy.workload.resources.envoy.requests.memory |
none | Memory request to apply to the envoy container in the envoy workload. |
envoy.workload.resources.shutdownManager.limits.cpu |
none | CPU limit to apply to the shutdown-manager container in the envoy workload. |
envoy.workload.resources.shutdownManager.limits.memory |
none | Memory limit to apply to the shutdown-manager container in the envoy workload. |
envoy.workload.resources.shutdownManager.requests.cpu |
none | CPU request to apply to the shutdown-manager container in the envoy workload. |
envoy.workload.resources.shutdownManager.limits.memory |
none | Memory request to apply to the shutdown-manager container in the envoy workload. |
envoy.service.type |
none | The type of Kubernetes service to provision for Envoy. Valid values are LoadBalancer, NodePort, and ClusterIP. If not specified, a NodePort service will be used for vsphere and a LoadBalancer for all other target platforms. |
envoy.service.loadBalancerIP |
none | The desired load balancer IP for Envoy service. This setting is ignored if envoy.service.type is not set to LoadBalancer |
envoy.service.externalTrafficPolicy |
Local |
The external traffic policy for the Envoy service. Valid values are Local and Cluster. |
envoy.service.annotations |
none | Annotations to set on the Envoy service. |
envoy.service.nodePorts.http |
none | If envoy.service.type == NodePort, the node port number to expose Envoy’s HTTP listener on. If not specified, a node port will be auto-assigned by Kubernetes. |
envoy.service.nodePorts.https |
none | If envoy.service.type == NodePort, the node port number to expose Envoy’s HTTPS listener on. If not specified, a node port will be auto-assigned by Kubernetes. |
envoy.service.aws.LBType |
classic |
If infrastructure_provider == aws, the type of AWS load balancer to use. Valid values are classic and nlb. If not using aws, this value is ignored. |
envoy.hostPorts.enable |
false |
Whether to enable host ports for the Envoy pods. If false, envoy.hostPorts.http and envoy.hostPorts.https are ignored. |
envoy.hostPorts.http |
80 |
If envoy.hostPorts.enable == true, the host port number to expose Envoy’s HTTP listener on. |
envoy.hostPorts.https |
443 |
If envoy.hostPorts.enable == true, the host port number to expose Envoy’s HTTPS listener on. |
envoy.hostNetwork |
false |
Whether to enable host networking for the Envoy pods. |
envoy.terminationGracePeriodSeconds |
300 |
The termination grace period, in seconds, for the Envoy pods. |
envoy.logLevel |
info |
The Envoy log level. Valid values are trace, debug, info, warn, error, critical, and off. |
envoy.pspNames |
none | A comma-separated list of pod security policies (PSPs) to apply to the Envoy pods. |
certificates.duration |
8760h |
How long the certificates for securing communication between Contour and Envoy should be valid for. |
certificates.renewBefore |
360h |
How long before expiration the certificates for securing communication between Contour and Envoy should be renewed. |
Update a Running Contour Deployment
If you need to make changes to the configuration of the Contour package after deployment, follow the steps below to update your deployed Contour package:
-
Update the Contour configuration in the
contour-data-values.yamlfile. For example, you can change the number of Contour replicas by settingcontour.replicasto a new value. -
Update the installed package:
tanzu package installed update contour \ --version INSTALLED-PACKAGE-VERSION \ --values-file contour-data-values.yaml \ --namespace INSTALLED-PACKAGE-NAMESPACEWhere:
INSTALLED-PACKAGE-VERSIONis the version of the installed Contour package.INSTALLED-PACKAGE-NAMESPACEis the namespace in which the Contour package is installed.
For example:
tanzu package installed update contour \ --version 1.25.4+vmware.1-tkg.1 \ --values-file contour-data-values.yaml \ --namespace my-packagesThe Contour package will be reconciled using the new value or values that you added. It can take up to five minutes for
kapp-controllerto apply the changes.For more information about the
tanzu package installed updatecommand, see Update a Package in Install and Manage Packages. You can use this command to update the version or the configuration of an installed package.