This topic describes what an availability zone (AZ) is in vSphere, and gives an example of how you might scale an app across AZs.
VMware defines an AZ as an operator-assigned, functionally independent segment of network infrastructure. In cases of partial infrastructure failure, a tile distributes and balances all instances of running apps across remaining AZs. Strategic use of AZs contributes to the fault tolerance and high availability of a tile deployment.
vSphere supports distributing deployments across multiple AZs. For more information, see Step 4: Create Availability Zones in Configuring BOSH Director on vSphere.
VMware recommends that customers use three AZs to operate a highly available tile deployment.
Example scenario: Balancing across AZs during failure
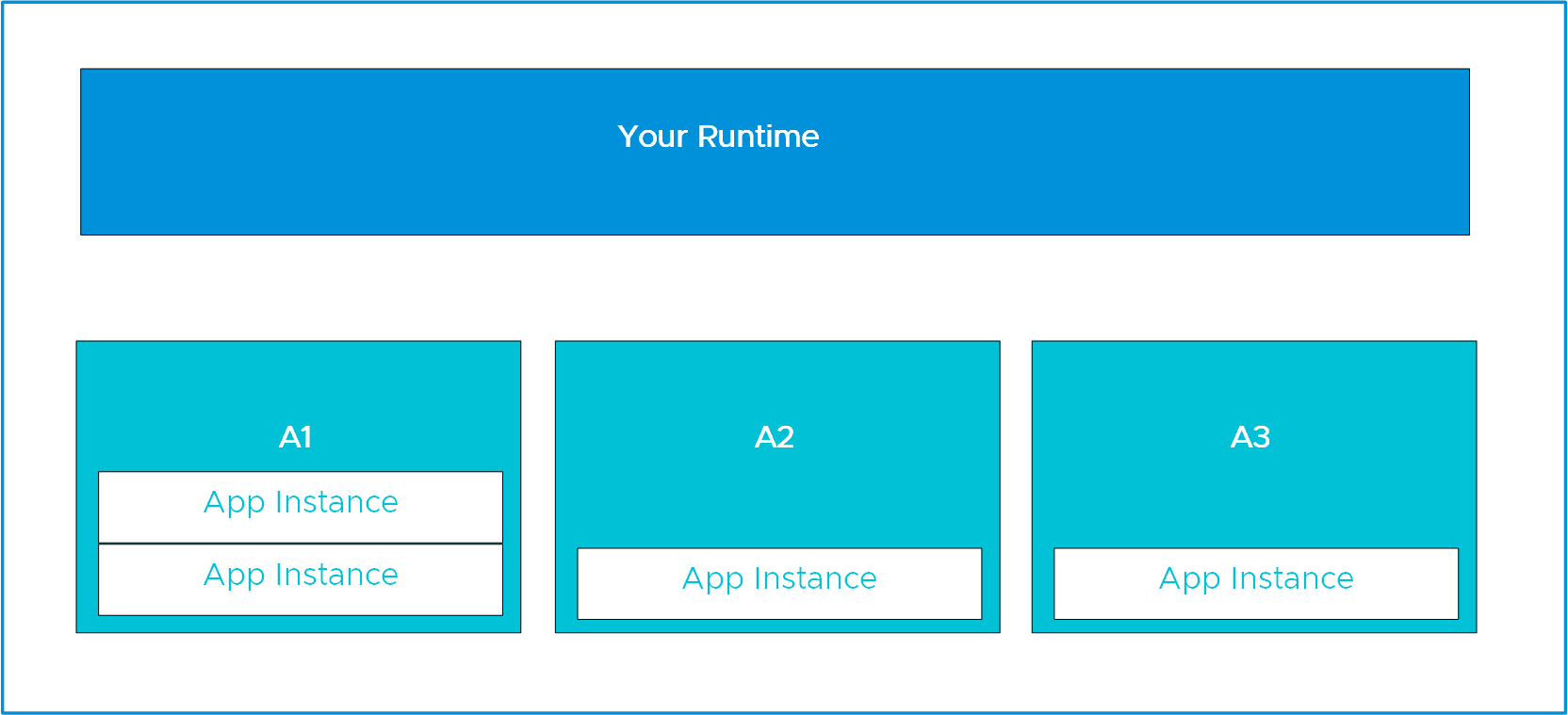
You can scale an app to four instances in a tile environment distributed across three AZs: A1, A2, and A3. The environment allocates the instances according to the Diego Auction. For more information about the Diego Auction, see How Diego balances app processes in Cloud Foundry.
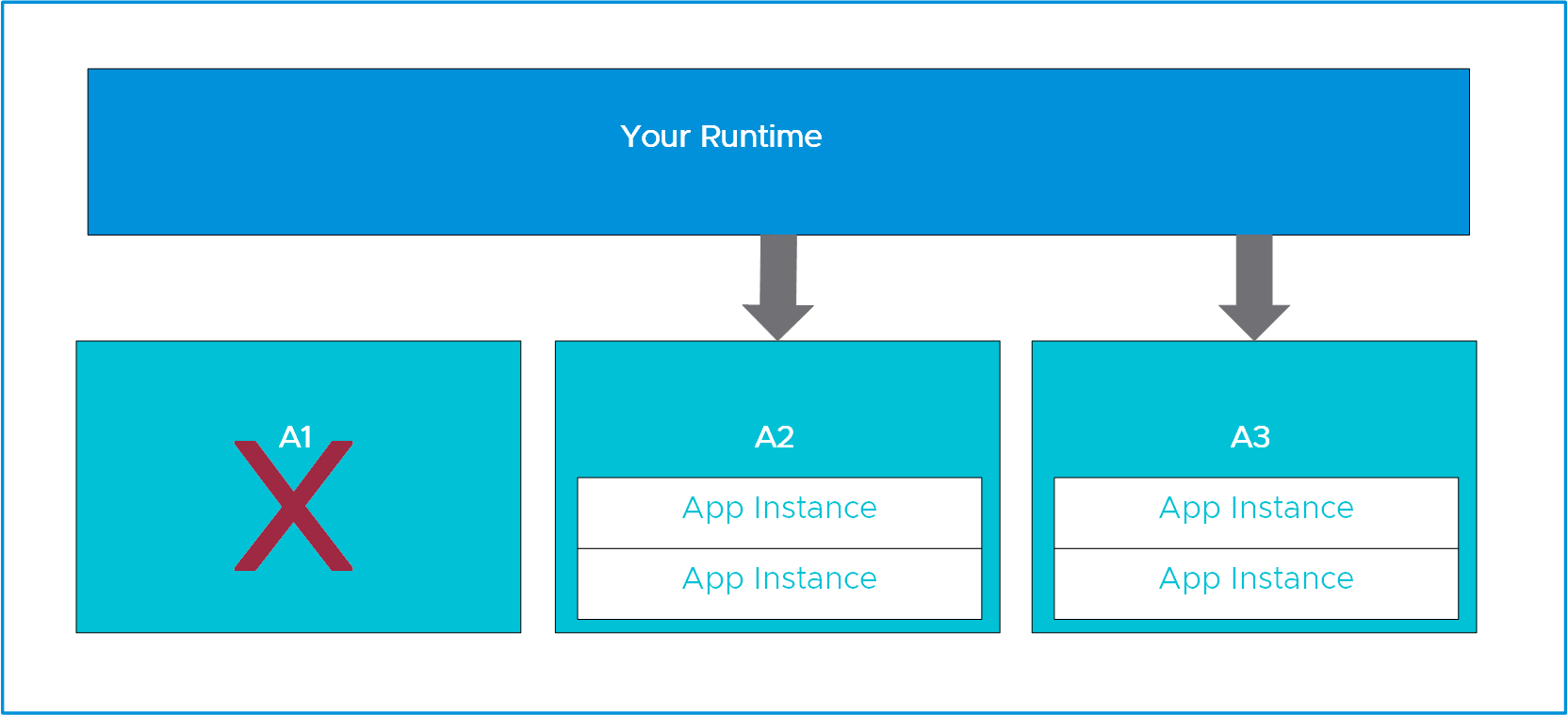
For this scenario, see the following diagram:
If A1 experiences a power outage or hardware failure, the two app instances running in A1 stops while the app instances in zones A2 and A3 continue to run.
See the following diagram:
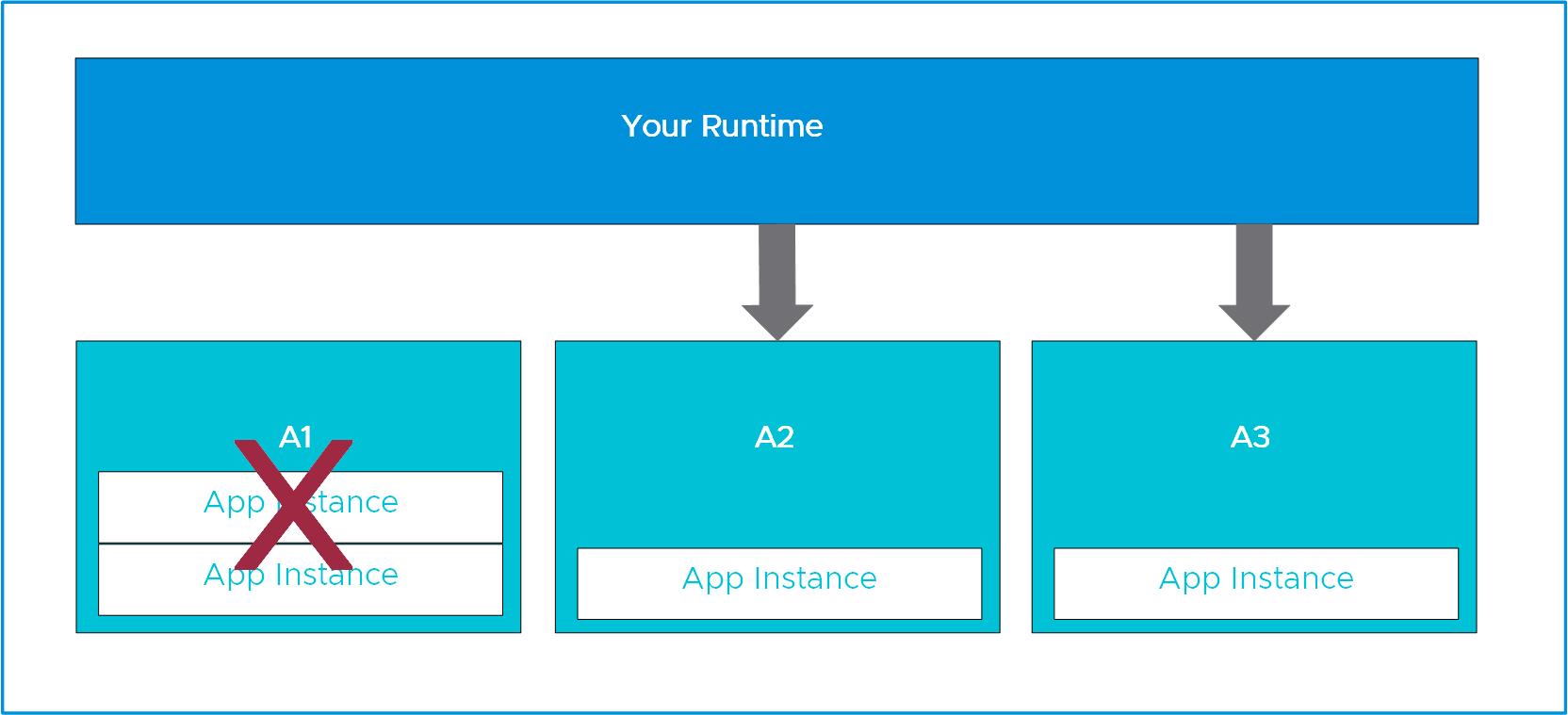
If A1 remains unavailable, the tile balances new instances of the app across the remaining AZs.
For this scenario, see the following diagram: