Configure secret runtime environment variables
This topic tells you how to configure secret runtime environment variables on Tanzu Platform for Kubernetes.
You can configure non-secret environment variables at build-time.
You can also override environment variables later in the application lifecycle and during runtime by using secret environment variables. Secret environment variables enable you to provide environment-specific configuration, dynamically reconfigure an app, and handle sensitive values that are not permitted in source code.
The values for secret variables are stored as Kubernetes secrets. Modifying secret runtime environment variables restarts the app and applies the new values.
ImportantNon-secret environment variables are immutable at runtime and must not include sensitive data. You can override the value of an existing non-secret variable by configuring secret variables at runtime.
Before you begin
Run tanzu build and tanzu deploy to build a container app and deploy it into a Space.
Read and update environment variables
Read and update environment variables from any of the following:
- Tanzu Platform hub
- the Tanzu CLI
- Tanzu Platform hub GraphQL Playground or a GraphQL client
- GitOps
- Tanzu Platform hub
-
Do the following in Tanzu Platform hub:
- Set the Project context to your Project.
- On the left navigation pane, expand Application Spaces.
- Click Spaces and then select your Space.
- Click the Applications tab and then select your application.
-
Locate the Environment Variables widget. This widget lists all variables with their current values, regardless of their sources.
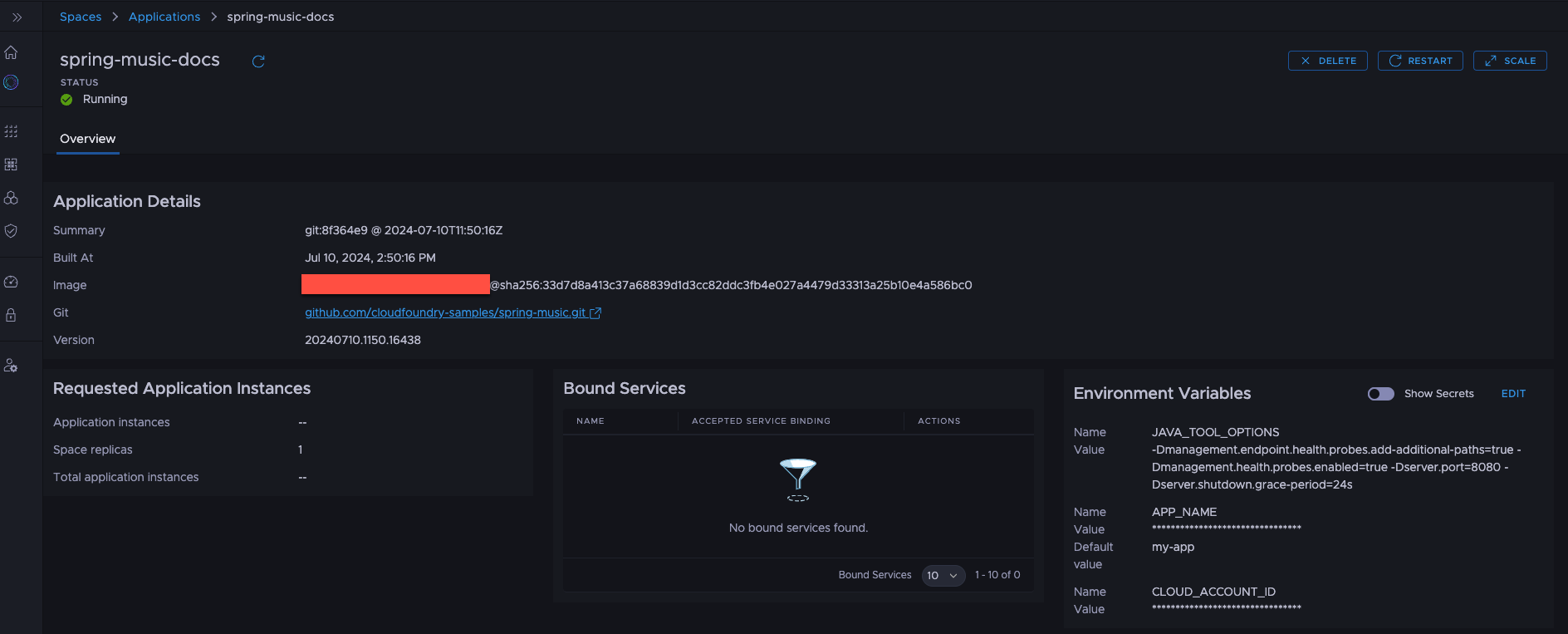
-
Click the Show Secrets button to reveal the secret values.
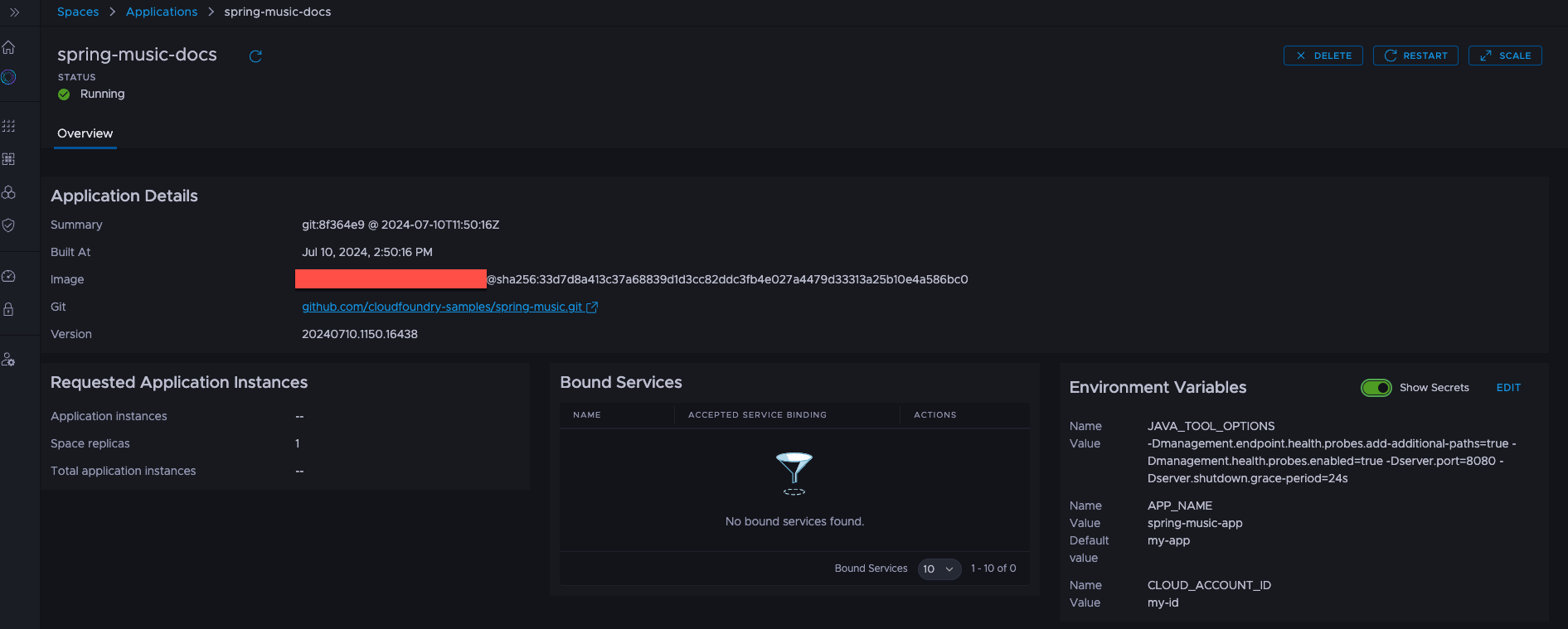
Note
Secret runtime variables take precedence over non-secret build-time variables. If there is a match between a non-secret variable and a secret variable, the value of the non-secret variable is displayed as Default value.
- Tanzu CLI
-
Use the Tanzu CLI as follows:
-
Use your Project by running:
tanzu project use PROJECT-NAME -
Use your Space by running:
tanzu space use SPACE-NAME -
Ensure that the application is deployed in the Space and view its environment variables by running:
tanzu app get CONTAINER-APP-NAME -
Set one or more environment variables by running:
tanzu app env set CONTAINER-APP-NAME KEY1=VALUE1 KEY2=VALUE2You can specify either new or existing variables. If you specify an existing variable, it is updated with the value that you define.
-
List the current environment variables by running:
tanzu app env list CONTAINER-APP-NAME --show-secretsThis command lists all variables with their current values, regardless of their source. Secret runtime variables take precedence over non-secret build-time variables. The
--show-secretsoption includes the secret values in the output. If--show-secretsis not used, the secret values are not included.You can also run
tanzu app getwith the--show-secretsoption to see secret environment variables:tanzu app get CONTAINER-APP-NAME --show-secrets -
Delete one or more secret environment variables by running:
tanzu app env delete CONTAINER-APP-NAME KEY1 KEY2Note
You cannot run
tanzu app env deleteto delete non-secret variables set at build-time because these variables are immutable. You can only runtanzu app env deleteto delete an overriding secret variable, which makes the variable revert to its initial build-time value.
-
- GraphQL
-
To use a GraphQL client or Tanzu Platform hub GraphQL Playground to read and modify the environment variables of a running app:
-
Construct a Space context to pass in the request variables. For example:
{ "context": { "path": "project/PROJECT-ID/space/SPACE-NAME", "namespace": "default" } } -
Obtain an access token and set it in the request header section as in this example:
{ "Authorization": "Bearer ACCESS-TOKEN" } -
Create, update, or delete secret environment variables by using a single mutation. See this example:
mutation updateEnvVars($context: KubernetesResourceContextInput!) { applicationEngineMutation(context: $context) { mutateContainerApp { mutateEnvVars(containerAppName: "CONTAINER-APP-NAME", vars: [{key: "KEY1", value: "VALUE1"}, {key: "KEY2", value: "VALUE2"}, {key: "KEY-TO-DELETE"}]) { spec { secretEnv { name secretKeyRef { key name } } } } } } }This GraphQL example creates new, or updates existing, variables
KEY1andKEY2, and it deletes theKEY-TO-DELETEvariable by omitting its value. This GraphQL example does not modify the other container app variables. -
Query the environment variables and their values. See this example:
query queryEnvVars($context: KubernetesResourceContextInput) { applicationEngineQuery(context: $context) { queryContainerApps(name: ["CONTAINER-APP-NAME"]) { edges { node { relationships { secretEnvReferencedSecrets { secrets { name data { key value } } } } } } containerapps { spec { nonSecretEnv { name value } secretEnv { name secretKeyRef { key name } } } } } } }This example API query obtains the following low-level data directly from the underlying resources:
-
The key-value pairs of the non-secret variables under
applicationEngineQuery.queryContainerApps.containerapps.spec.nonSecretEnv -
The key for each secret variable and a reference to the Kubernetes secret that contains the key value
To see the actual value for a given secret variable from the
secretEnvsection, find the secret variable’ssecretKeyRefto find the relevant entry inapplicationEngineQuery.queryContainerApps.edges.node.relationships.secretEnvReferencedSecrets.secrets. The secret name matches the one insecretKeyRef.nameand the key within the secret data is the same assecretKeyRef.key. -
-
- GitOps
-
You can also modify secret environment variables by modifying the Kubernetes resources of a Space directly.
-
From within the context of your Space, get the
kubeconfigby running:tanzu context current -
Copy the path to the
kubeconfigfrom theKube config:section of the output. -
Set your
KUBECONFIGby running:export KUBECONFIG=<COPIED-PATH> -
Apply the secrets that contain your environment variable values by running:
kubectl create secret generic SECRET-NAME --from-literal=KEY1=VALUE1 --from-literal=KEY2=VALUE2 -
Reference the secrets from the
ContainerAppspecification by running:kubectl edit containerapps.apps.tanzu.vmware.com CONTAINER-APP-NAME -
Add the following section to the specification:
secretEnv: - name: KEY1 secretKeyRef: key: KEY1 name: SECRET-NAME - name: KEY2 secretKeyRef: key: KEY2 name: SECRET-NAMENote
Ensure that the specification is valid by verifying that the referenced secrets, and the keys that they contain, exist.
You can reference an arbitrary number of secrets. The system ensures that if a referenced value changes, the container app restarts with the new value. Secrets that you reference in a
ContainerAppspecification remain immutable if you later use the Tanzu CLI or GraphQL to override or delete them. Changes are applied only by modifying theContainerAppspecification and referencing a different secret.Caution
If you name a secret
CONTAINER-APP-NAME-env, this secret is mutable and someone can override or delete it by using the Tanzu CLI or GraphQL. - Delete a secret environment variable by removing its entry from the
spec.secretEnvlist.
-