This topic tells you how to enable OAuth 2.0 for VMware Tanzu RabbitMQ for Tanzu Application Service. This enables developers to access the RabbitMQ Management UI using their VMware Tanzu Application Service for VMs credentials.
Overview
OAuth enables developers to access the RabbitMQ Management UI using their TAS for VMs credentials instead of using the binding credentials from a service key. After enabling OAuth, developers are authenticated through a JSON Web Token (JWT) encoded OAuth access token obtained from User Account and Authentication (UAA).
NoteEnabling OAuth does not remove user credentials from service keys or from the internal backend of existing Tanzu RabbitMQ for Tanzu Application Service instances. However, you can no longer use these credentials to access the RabbitMQ Management UI.
Caution Manually rotating the JWT signing key using the UAA API is not supported. Doing so renders RabbitMQ Management UI inaccessible.
To configure OAuth for an on-demand offering:
Configure UAA Groups for RabbitMQ
To configure UAA groups:
Get Admin User Credentials for UAA
To fetch the UAA Admin Client secret from the Ops Manager UI:
- Click on the VMware Tanzu Application Service for VMs tile.
-
Click the Credentials tab.
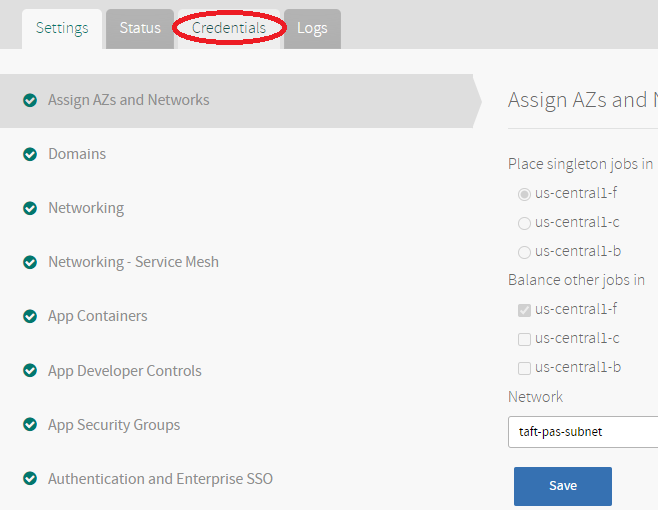
-
Locate the Admin Client Credentials in the UAA job.
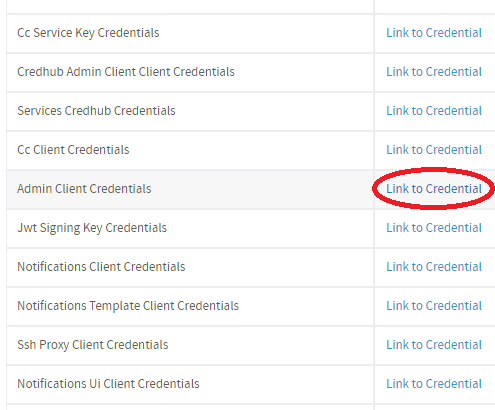
-
Click Link to Credential next to Admin Client Credentials.
- Record the text in the identity field (
UAA-ADMIN-CLIENT-IDENTITYin the next step) and password field (UAA-ADMIN-CLIENT-SECRETin the next step).
Install and Set up UAAC
To install and set up UAAC:
-
Install UAAC by running:
gem install cf-uaac -
Set up UAAC by running these commands:
uaac target UAA-URLuaac token client get UAA-ADMIN-CLIENT-IDENTITY -s UAA-ADMIN-CLIENT-SECRETWhere:
UAA-URLis the UAA URL.UAA-ADMIN-CLIENT-IDENTITYandUAA-ADMIN-CLIENT-SECRETare from the text you recorded in Get Admin User Credentials for UAA above.
Create a UAA Group
You must create a group for each space in TAS for VMs that contains, or is expected to contain, on-demand Tanzu RabbitMQ for Tanzu Application Service service instances.
To create a UAA group for a space:
-
Display the space GUID by running:
cf space SPACE-NAME --guidWhere
SPACE-NAMEis the name of the space. -
Record the space GUID.
-
Create a UAA group using the space GUID and a RabbitMQ tag by running:
uaac group add p-rabbitmq_SPACE-GUID.tag:RABBITMQ-TAGWhere:
SPACE-GUIDis the space GUID.RABBITMQ-TAGmust be eithermonitoringoradministrator. The RabbitMQ tag dictates what the user is permitted to do. For more information about RabbitMQ tags, see the RabbitMQ documentation
For example:
$ uaac group add p-rabbitmq_64bd9d4d-d2c8-4207-bb76-91a245e67d9d.tag:monitoring
-
If you used the
monitoringtag, grant additional permissions to allow the user to view resources by running:uaac group add p-rabbitmq_SPACE-GUID.PERMISSION:VHOST-PATTERN/NAME-PATTERN[/ROUTING-KEY-PATTERN]Where:
SPACE-GUIDis the space GUID.PERMISSIONis an access permission –configure,read, orwrite.VHOST-PATTERNis a wildcard pattern for virtual hosts.NAME-PATTERNis a wildcard pattern for a resource name.ROUTING-KEY-PATTERNis an optional wildcard pattern for a routing key in topic authorization.
For example:
$ uaac group add 'p-rabbitmq_64bd9d4d-d2c8-4207-bb76-91a245e67d9d.read:*/*'
For more information about RabbitMQ permissions, see the OAuth plug-in documentation in GitHub.
The on-demand broker creates a separate UAA client with scope p-rabbitmq_SPACE-GUID for every new on-demand service instance. When an access token is created, UAA intersects the user groups with the client scopes. The intersection of these two fields are scopes that can be populated in the access token.
Configure Users for the RabbitMQ UAA Groups
You can either map external identity provider groups to the RabbitMQ UAA groups or add UAA members to the groups. Users gain the permissions specified by the RabbitMQ tag provided in the UAA group name.
Do one of the following:
-
Map the RabbitMQ UAA groups created above to your LDAP provider group by running the following command for every RabbitMQ UAA group:
uaac group map --name "RABBITMQ-UAA-GROUP" "GROUP-DISTINGUISHED-NAME"Where:
RABBITMQ-UAA-GROUPis the UAA group name created above. For example:p-rabbitmq_64bd9d4d-d2c8-4207-bb76-91a245e67d9d.tag:monitoring.GROUP-DISTINGUISHED-NAMEis the Distinguished Name (DN) of the LDAP group. For example:ou=operators,dc=example,dc=com.
-
Map the RabbitMQ UAA groups created above to your SAML IdP group by running the following command for every RabbitMQ UAA group:
uaac group map --name "RABBITMQ-UAA-GROUP" "GROUP-NAME" --origin "PROVIDER-NAME"Where:
RABBITMQ-UAA-GROUPis the UAA group name created above. For example:p-rabbitmq_64bd9d4d-d2c8-4207-bb76-91a245e67d9d.tag:monitoring.GROUP-NAMEis the name of the group in the SAML IdP.PROVIDER-NAMEis the name of the SAML IdP.
-
Add UAA members to UAA groups by running:
uaac member add RABBITMQ-UAA-GROUP USERNAMEWhere:
RABBITMQ-UAA-GROUPis the UAA group name created above. For example,p-rabbitmq_64bd9d4d-d2c8-4207-bb76-91a245e67d9d.tag:monitoring.USERNAMEis a UAA group member, such as a Cloud Foundry user.
Configure OAuth in Ops Manager
To configure OAuth in the Tanzu RabbitMQ for Tanzu Application Service tile:
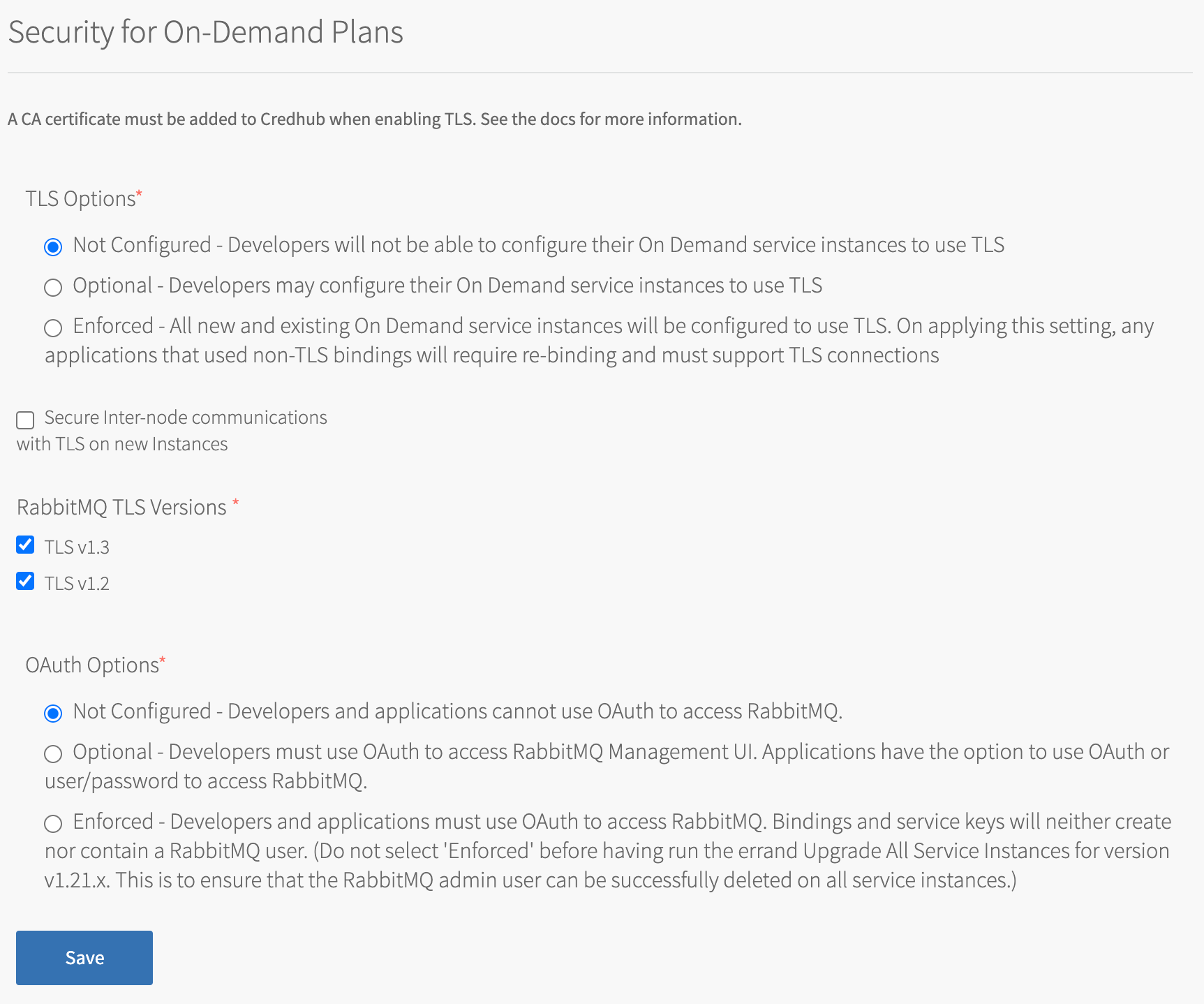
- Go to the Security for On-Demand Plans section of the Tanzu RabbitMQ for Tanzu Application Service tile.
-
There are three different OAuth Options: Not Configured, Optional, and Enforced:
- Not Configured does not use OAuth.
- Optional enforces OAuth for developers accessing the RabbitMQ Management UI. Apps accessing RabbitMQ can use either basic authentication or OAuth.
- Enforced enforces OAuth for both developers and apps to access RabbitMQ. No user is created or returned as part of a service binding or service key creation. To ensure RabbitMQ does not store any user credentials, delete all service bindings and service keys, and then run the Upgrade All Service Instances errand after upgrading to
1.21.xand before enforcing OAuth.
- Not Configured does not use OAuth.
-
Click Save.
- Go back to Ops Manager Installation Dashboard > Review Pending Changes.
- Click Apply Changes to apply the changes to the Tanzu RabbitMQ for Tanzu Application Service tile.