Tanzu Salt system requirements
Use these Tanzu Salt system requirements to determine what your system can support.
Supported operating systems for Salt
Tanzu Salt runs on Salt, an open-source automation and configuration management engine. In order to begin using Tanzu Salt for configuration management, you also need to install and run the Salt minion service on any nodes that you intend to manage using Tanzu Salt.
Salt itself is designed to be operating system agnostic and can manage the nodes of most standard operating systems. For a list of supported Salt operating systems, see Salt Platform Support.
Supported operating systems for Tanzu Salt
The architecture for Tanzu Salt is best designed to operate on either:
- RHEL 7.4–7.9
- RHEL 8
- RHEL 9
- Photon OS 3
Alternate operating systems are supported only to the extent that they are compatible with RHEL.
Important:
If your version of RHEL 7 is lower than 7.4, you must update your OpenSSL version to 1.0.2k before running the installation script. If this version is not available to you through a yum update or your server does not have direct Internet access, retrieve the following packages from RedHat or from your preferred public mirror:
• openssl-1.0.2k-26.rpm
• openssl-libs-1.0.2k-26.rpm
Additional supported operating systems
Tanzu Salt also supports the following operating systems, although they are not recommended:
- Oracle Linux 7
- SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 (SLES 15)
- SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 (SLES 12)
Installing Tanzu Salt on these operating systems requires a manual installation method that should only be completed with a Tanzu Salt expert.
Determining minion architecture
In the context of Tanzu Salt, a minion generally refers to a node in your production environment that connects with and is managed by Tanzu Salt through one or more Salt masters.
Salt is designed to work with any operating system that might be running on a minion. This table lists the minimum memory requirements for the Salt minion service by operating systems:
| Operating system | Minimum memory requirements |
|---|---|
| MacOS minion | 4 GB RAM |
| Linux minion | 512 MB RAM |
| Windows minion | 4 GB RAM |
| Other network devices, including proxy minions | 40 MB RAM per controlled device |
Estimate the number of Salt master and minions
Although the throughput of your system is difficult to measure prior to installation, you can estimate your needs based on the number of minions (nodes) in your system that will be managed by Tanzu Salt. The last section of this guide provides additional measurements for determining your system throughput.
As you bring more Salt minions under management by Tanzu Salt, you might need to increase your system architecture to match.
This table lists the recommended number of Salt masters you might need based on the number of managed Salt minions (nodes) in your system:
| Minions | Salt masters (16 CPU/16 GB) |
|---|---|
| 5,000 | 1 |
| 10,000 | 2 |
| 15,000 | 3 |
| 20,000 | 4 |
| 25,000 | 5 |
| 30,000 | 6 |
| 35,000 | 7 |
| 40,000 | 8 |
| 45,000 | 9 |
| 50,000 | 10 |
| 55,000 | 11 |
| 60,000 | 12 |
| 65,000 | 13 |
| 70,000 | 14 |
| 75,000 | 15 |
| 80,000 | 16 |
| 85,000 | 17 |
| 90,000 | 18 |
| 95,000 | 19 |
| 100,000 | 20 |
Estimate the number of RaaS nodes you need
This table lists the recommended number of RaaS nodes you might need based on the number of managed Salt minions (nodes) in your system:
| Minions | RaaS nodes with 16 CPU/16 GB | RaaS nodes with 32 CPU/32 GB |
|---|---|---|
| 5,000 | 1 | |
| 10,000 | 1 | |
| 15,000 | 1 | |
| 20,000 | 1 | |
| 25,000 | 2 | |
| 30,000 | 2 | |
| 35,000 | 2 | |
| 40,000 | 2 | |
| 45,000 | 1 | 1 |
| 50,000 | 1 | 1 |
| 55,000 | 1 | 1 |
| 60,000 | 1 | 1 |
| 65,000 | 1 | 2 |
| 70,000 | 1 | 2 |
| 75,000 | 1 | 2 |
| 80,000 | 1 | 2 |
| 85,000 | 1 | 2 |
| 90,000 | 1 | 2 |
| 95,000 | 1 | 2 |
| 100,000 | 1 | 2 |
Estimate the number of PostgreSQL nodes you need
The next two tables list the recommended number of PostgreSQL database nodes you might need based on the number of managed Salt minions (nodes) in your system:
| Minions | PostgreSQL nodes with 8 CPU/8 GB | PostgreSQL nodes with 16 CPU/16 GB | PostgreSQL nodes with 24 CPU/24 GB | PostgreSQL nodes with 32 CPU/32 GB |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5,000 | 1 | |||
| 10,000 | 1 | |||
| 15,000 | 1 | |||
| 20,000 | 1 | |||
| 25,000 | 1 | |||
| 30,000 | 1 | |||
| 35,000 | 1 | |||
| 40,000 | 1 | |||
| 45,000 | 1 | |||
| 50,000 | 1 | |||
| 55,000 | 1 | |||
| 60,000 | 1 |
| Minions | PostgreSQL nodes with 48 CPU/48 GB | PostgreSQL nodes with 56 CPU/56 GB | PostgreSQL nodes with 64 CPU/64 GB |
|---|---|---|---|
| 65,000 | 1 | ||
| 70,000 | 1 | ||
| 75,000 | 1 | ||
| 80,000 | 1 | ||
| 85,000 | 1 | ||
| 90,000 | 1 | ||
| 95,000 | 1 | ||
| 100,000 | 1 |
Estimate the number of Redis nodes you need
The next two tables list the recommended number of Redis database nodes you might need based on the number of managed Salt minions (nodes) in your system:
| Minions | Redis nodes with 4 CPU/4 GB | Redis nodes with 8 CPU/8 GB | Redis nodes with 12 CPU/12 GB |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5,000 | 1 | ||
| 10,000 | 1 | ||
| 15,000 | 1 | ||
| 20,000 | 1 | ||
| 25,000 | 1 | ||
| 30,000 | 1 | ||
| 35,000 | 1 | ||
| 40,000 | 1 | ||
| 45,000 | 1 | ||
| 50,000 | 1 | ||
| 55,000 | 1 | ||
| 60,000 | 1 |
| Minions | Redis nodes with 16 CPU/16 GB | Redis nodes with 20 CPU/20 GB |
|---|---|---|
| 65,000 | 1 | |
| 70,000 | 1 | |
| 75,000 | 1 | |
| 80,000 | 1 | |
| 85,000 | 1 | |
| 90,000 | 1 | |
| 95,000 | 1 | |
| 100,000 | 1 |
Optimize your architecture after installation based on throughput
After you’ve completed your Tanzu Salt installation, you can use system monitoring metrics to better determine your system’s throughput and architectural needs.
When determining what to monitor, consider these factors:
- Amount of traffic on the event system - The event system (also sometimes referred to as the “event bus”) is used for inter-process communication by both Salt master and Salt minions. If your event bus is very busy, consider increasing your memory allocations.
- Job returns per hour - Tanzu Salt uses the term “jobs” to refer to each of the commands, tasks, and operations performed by Tanzu Salt. Each job sends its output to Tanzu Salt for reporting and data collection purposes. The number of job returns your system produces in a given hour can impact your architecture needs.
- Amount of pillar data - Pillar data is data that must be stored on the Salt master. Pillar is primarily used to store secrets or other highly sensitive data, such as account credentials, cryptographic keys, or passwords.The amount of data being stored on your Salt master (and later accessed by minions as needed) can impact your memory and data storage needs.
- Configuration Data - Map Files - These files are useful for storing non-sensitive data that you don’t want to place directly in your state files. Unlike Pillar data, these map files do not put additional resource strain on the salt masters.
- Amount of custom grains - Grains are used in Salt to target the minions for a particular job or command. Grains refer to the basic data and characteristics of each minion. Salt comes with many pre-built grains. For example, you can target minions by their operating system, domain name, IP address, kernel, memory, and many other system properties. You can also create custom grain data to distinguish one group of minions from another based on a characteristic you uniquely target for in your system. The number of custom grains you create can impact your architecture needs.
- Number of beacons and reactors - The beacon system is a monitoring tool that can listen for a variety of system processes on Salt minions. Beacons can trigger reactors, which can then help implement a change or troubleshoot an issue. For example, if a service’s response times out, the reactor system can restart the service. When coupled with reactors, beacons can create automated, pre-written responses to infrastructure and application issues. Reactors expand Salt with automated responses using pre-written remediation states. If your system has beacons and reactors that are activated regularly, that could increase your system architecture needs.
- Disk size needs - You might need to increase your disk size based on the number of minions being managed and for each year’s worth of data you need to keep in storage. For example, if you have a high-throughput system and your system is in a highly-regulated industry that requires 7-8 years of data retention, that might require higher disk size and storage capacity.
- Geographical location and distance between components - You might experience issues if there is a 65 ms latency or more between the Salt master and the server that is running Tanzu Salt (RaaS). Fortunately, Salt is less sensitive to latency between the Salt minion and Salt master. When placing these components, keep in mind that it is better to locate the master close to RaaS and minion farther away if necessary.
- Business-critical operations - You might experience issues if there is high latency (>200ms) between the Salt master and the server that is running Tanzu Salt (RaaS)."
Based on these factors, consider incrementally increasing your resources and monitor the impact to your system’s performance. For example, increasing your memory allocations by 4GB RAM with 4 CPUs.
The following image shows an example of a high availability Tanzu Salt architecture design:
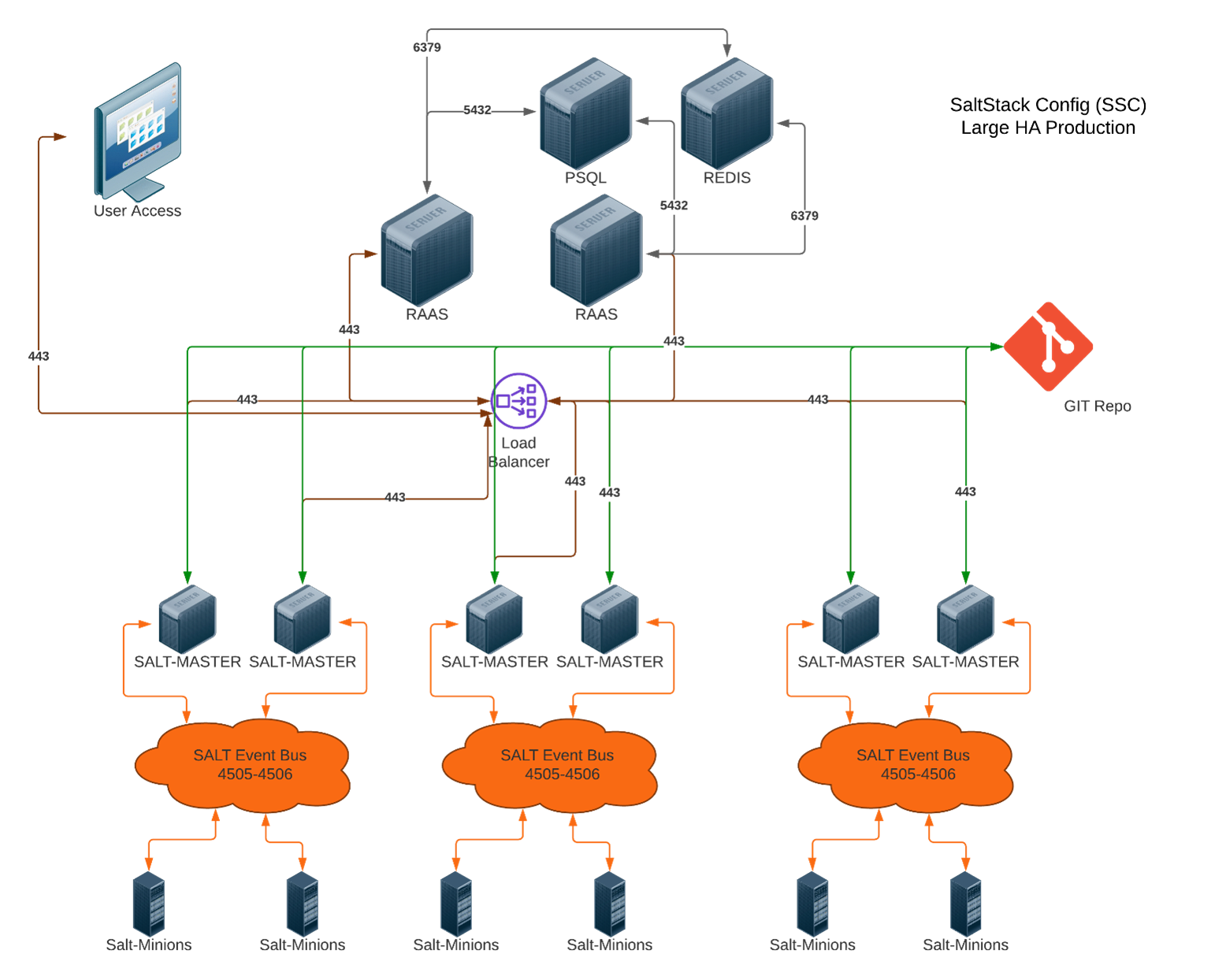
As this image illustrates, many high availability systems connect to multiple Salt masters. High availability systems also often build redundancy into the PostgreSQL database and Redis databases so that one can fail over to another. Keep in mind that the current high availability solutions for PostgreSQL and Redis only support manual failovers.