Use case: How do I deploy minions using the API in a Linux environment
The goal of this use case is to programmatically install the Salt minion service on a minion by connecting a Linux VM to your Tanzu Salt environment.
Prerequisites
Before you can deploy a minion using the API in a Linux environment, you must:
- Have a Tanzu Salt environment with RaaS deployed.
- Have a Salt master and Salt minion installed.
- Have a Linux VM deployed.
- Ensure port 22 is not firewalled and available for minion use.
Procedure
-
Verify that the folder
etc/salt/cloud.deploy.dcontains a collection of these files. These files should match the OS distribution release as well as the Salt release that your system requires.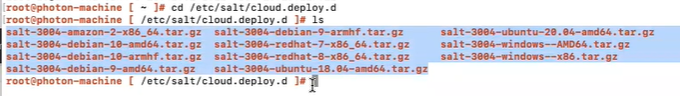
If you do not see the files, contact support.
Note:
Thexxxxin the filename, for example,salt-xxxx-redhat-8-x86_64-amd64.tar.gz, should match the version of the Salt master. To verify the version of the Salt master, run thesalt-master -Vcommand on the Salt master. -
If your environment is air-gapped, complete these steps:
-
Open the RaaS configuration file in
/etc/raas/raas. -
Add these lines to the configuration file:
minion_deployment: airgap_install: true -
Restart the RaaS service using the
service raas restartcommand.Note:
If you are using a hardened Linux VM, there are some situations where scripts cannot be run from/tmpon the VM.- If you are using Automation Assembler version 8.10.2 or higher: Add the
additionalAuthParamsproperty to the Tanzu Salt resource in your cloud template. For more information, see Add the SaltStack resource to the cloud template.
additionalAuthParams: profile: tmp_dir: /var/cache/salt- If you are using Automation Assembler version 8.10.1 or lower: Modify the
/etc/salt/cloud.providers.d/ssc\_saltify\_provider.conffile with
ssc_saltify_provider: driver: saltify tmp_dir: /var/cache/saltIf this configuration file does not exist, create it and add the setting above.
- If you are using Automation Assembler version 8.10.2 or higher: Add the
-
-
To identify the FQDN of the Salt master, run the
salt saltmaster grains.get fqdncommand in the Salt master’s terminal. -
Ensure that the FQDN is configured for the Salt master by running the
ping [FQDN]command.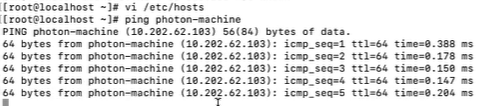
-
To open Python, run
python3. -
Make this API call using an SSEAPI client with the correct credentials for your environment:
from sseapiclient import APIClient client = APIClient('https://<master-ip>', '<ssc-username>', '<sscpassword>', ssl_validate_cert=False) client.api.minions.deploy_minion( master_id = '<master-id>', host_name_ip = '<prospective minion’s ip>', os = ‘<prospective minion’s os>’, minion_id = '<desired-minion-name-for-prospective-minion>', username = '<ssh-username-for-prospective-minion>', password = '<ssh-password-for-prospective-minion>', )The
deploy.minionfunction begins running in your Tanzu Salt environment. You can verify that the job is running in the Activity tab of the Tanzu Salt user interface.Note:
If you are deploying a minion from Automation Assembler, then this API call is performed by Automation Assembler.
The minion was successfully deployed and configured from your Linux environment and API call.
Verify that the minion was deployed successfully by running a test.ping command against the minion using the Run Command window or by running the \\* test.ping and \\* test.versions commands in the Salt master command window.