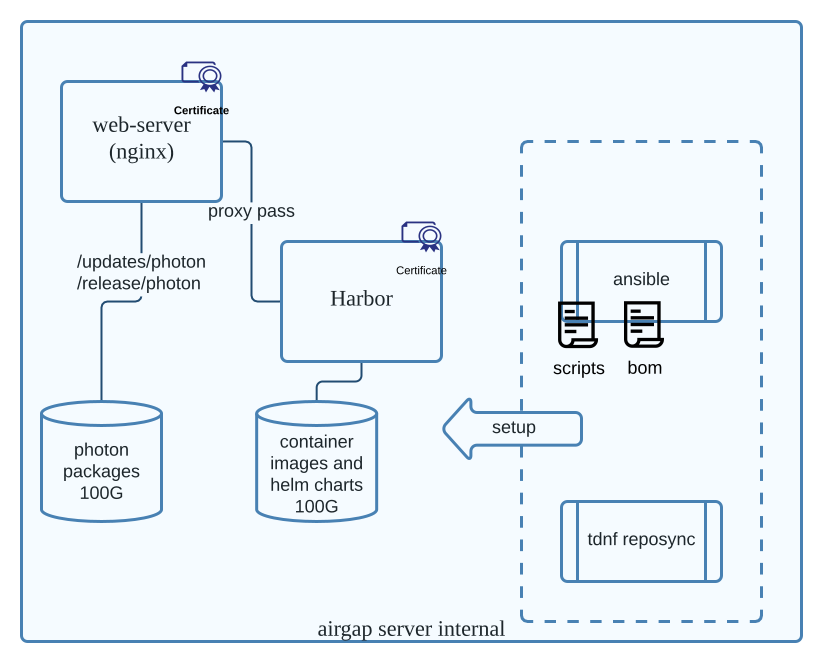
The airgap server repository is used to hold the container images for the VMware Telco Cloud Automation Containers as a Service (CaaS) system and the packages for Kubernetes cluster node customization.
This section introduces a Photon OS VM-based approach for setting up a new airgap server for the VMware Telco Cloud Automation system in an Internet-restricted or air-gapped environment.
The airgap server allows the VMware Telco Cloud Automation cluster to pull and download the required images and packages by providing a single HTTPS service. You do not require internet access if the airgap server is well set up and serves the VMware Telco Cloud Automation system.
The sources of VMware Telco Cloud Automation-dependent container images and Photon OS repositories maintained by VMware are located at certain websites on the Internet. In general, you must set up the airgap server to synchronize the images and packages from specific sites on the Internet and set up the image download service for the local VMware Telco Cloud Automation system. Therefore, Internet access is required only when synchronizing the images and packages to the airgap server.
- Restricted Internet Deployment
- No Internet Deployment
Restricted Internet Deployment
In the restricted Internet Deployment environment, an internal airgap server with certain traffic is allowed to access the internet. You must set up the airgap server in the same environment as the VMware Telco Cloud Automation system.
- Connect the airgap server to the Internet through an HTTP/S proxy. Set the proxy to the airgap virtual machine and set
NO_PROXYto let the Internet traffic pass through the proxy server. This way, the VMware Telco Cloud Automation system can reach the airgap server directly through the Local Area Network.Note: For proxy setting, only a trusted proxy server that does not require the user to inject a private CA certificate into the airgap server is supported. For information about setting up the proxy server, see step 2 of Set up the Airgap Server. - Connect the airgap server to the Internet through routing and SNAT. You can configure the firewall to allow specific traffic from the airgap server to access the repository resources.
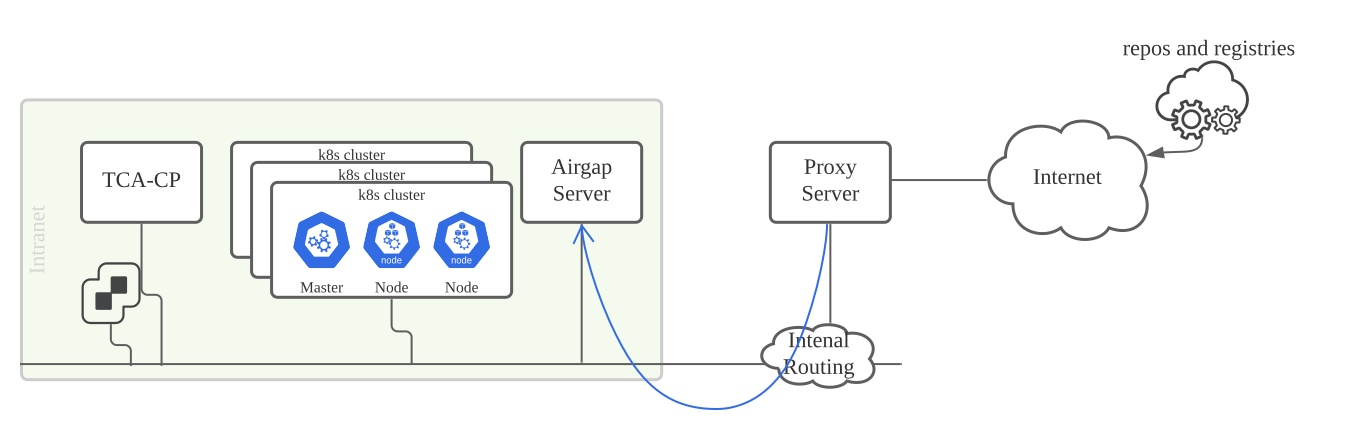
This guide lists the steps for deploying an airgap server in an environment with restricted Internet access.
No Internet Deployment
- Set up the airgap server on an Internet available environment.
- Copy or move the airgap server to the target Intranet environment.
- Export the built airgap server to an OVA, and upload it to an internal file server.
- Import the airgap server OVA to the target no-Internet environment and configure it with the correct networking and certificate settings.

Airgap Server Components
- Nginx daemon - Dispatches the file requests for fetching resources from the local datastore or the Harbor server. It also provides a single HTTPS registry and Photon OS repository service to the local VMware Telco Cloud Automation system.
- Harbor - Holds the required container images for the VMware Telco Cloud Automation system to run. Harbor is an open source project that provides container image registry service. It maintains all the dependent container images that are pulled from the Internet and serves the local Kubernetes cluster container image pulling process.
- Reposync - A tool to synchronize the Photon OS packages from the Internet.
- BOM Files - Describes the container images that are BOM-dependent by the VMware Telco Cloud Automation system.
- Scripts - Help set up the internal components of the airgap server. These scripts start the services, load the BOM files, pull images from public registries and publishes to the local Harbor repository on the airgap server.