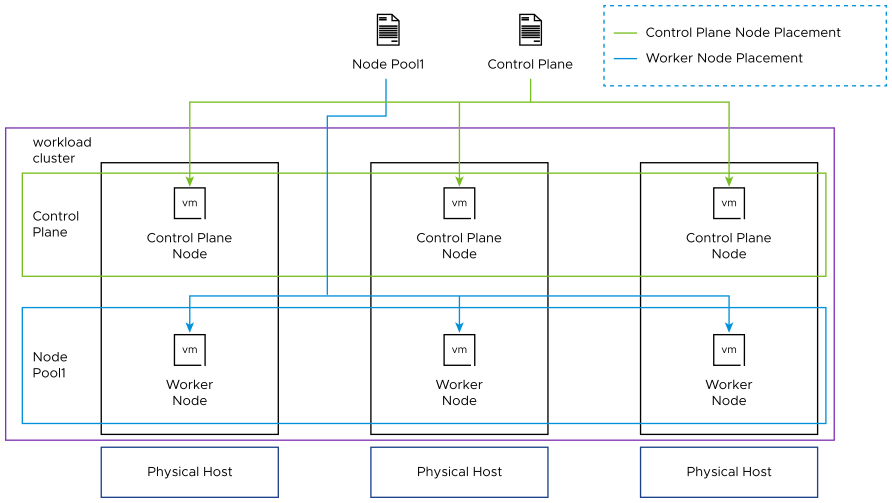
Anti-affinity rule for K8s worker nodes is enabled in VMware Telco Cloud Automation by default. Anti-affinity is specific to workload clusters and ensures that the nodes deployed are spread across different hosts.
Consider the following example where a label
node.cluster.x-k8s.io/esxi-host is added to each worker node to indicate the host on which the anti-affinity rule is applied. Based on the node to which anti-affinity is applicable, you can control the anti-affinity rules on that node.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-app
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
replicas: 3
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
topologySpreadConstraints:
- maxSkew: 1
topologyKey: node.cluster.x-k8s.io/esxi-host
whenUnsatisfiable: DoNotSchedule
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
nodeSelector:
"telco.vmware.com/nodepool": "npg-1"
containers:
- name: nginx-server
image: harbor-repo.vmware.com/ecp_snc/nginx:1.23.1
In the preceding example, topologySpreadConstraints is used to control the anti-affinity rules based on the host node.cluster.x-k8s.io/esxi-host and nodeSelector is used to apply the anti-affinity rule within the node pool npg-1.
By default, workload clusters on vSphere and standalone management clusters follow anti-affinity rules to deploy node pool workers and control plane nodes on different ESXi hosts.
The following diagram illustrates the node placements when the anti-affinity rules are enabled.