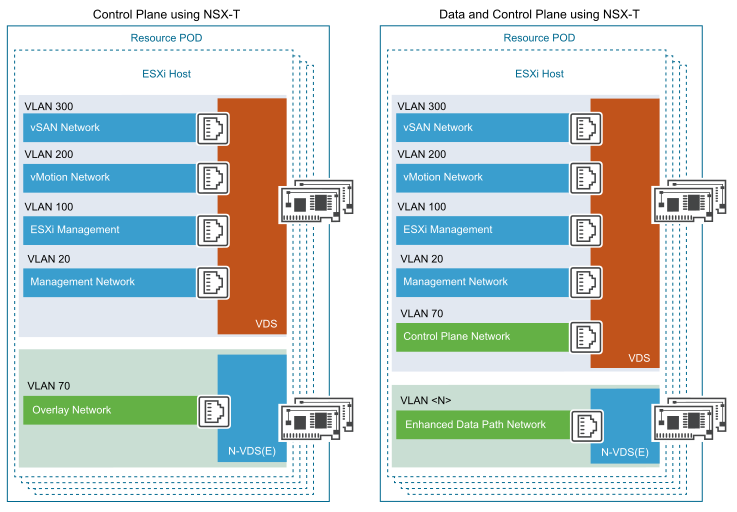
The Resource Pod networking is dependent on the network topology required by telco workloads that are deployed by tenants. This section describes the network building blocks.
Segment
Segments are the layer 2 networks created by NSX-T Data Center to provide connectivity between its services and the VMs. Segments form the basis of the tenant networks in the Telco Cloud Infrastructure OpenStack Edition platform. The primary component in the data plane of the transport nodes is N-VDS. N-VDS forwards traffic between components running on the transport node (that is between VMs) or between VMs and the physical network. In the latter case, N-VDS must own one or more physical interfaces (physical NICs) on the transport node. As with other virtual switches, an N-VDS cannot share a physical interface with another N-VDS. It can coexist with another N-VDS each using a separate set of physical NICs.
Logical Routing
The NSX-T Data Center platform provides the ability to interconnect both virtual and physical workloads that are deployed in different logical layer 2 networks. NSX-T enables the creation of network elements such as switches and routers as software logical constructs and embeds them in the hypervisor layer, abstracted from the underlying physical hardware.
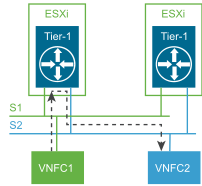
East-West Traffic
Configuring a gateway through the NSX Manager instantiates a gateway on each hypervisor. For the VNFs hosted on the same hypervisor, the East-West traffic does not leave the hypervisor for routing. The gateway is also responsible for routing East-West traffic between hypervisors. The tenants of the Telco Cloud Infrastructure OpenStack Edition platform deploy and manage the Tier-1 gateway for routing services between their respective tenant networks within their tenancy.
North-South Traffic
In addition to providing optimized distributed and centralized routing functions, NSX-T Data Center supports a multi-tiered routing model with a logical separation between the provider routing function and the tenant routing function. This way, the concept of multitenancy is built in the routing model. The top-tier gateway is called a Tier-0 gateway, whereas the bottom-tier gateway is called a Tier-1 gateway. Northbound, the Tier-0 gateway connects to one or more physical routers or layer 3 switches and serves as an on/off ramp to the physical infrastructure. Southbound, the Tier-0 gateway connects to one or more Tier-1 gateways.
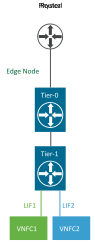
This model also eliminates the dependency on a physical infrastructure administrator to configure or change anything on the physical infrastructure when a new tenant is configured in the data center. For a new tenant, the Tier-0 gateway simply advertises the new tenant routes that are learned from the tenant Tier-1 gateway on the established routing adjacency with the physical infrastructure.