VMware Integrated OpenStack is the component that Telco Cloud Infrastructure OpenStack Edition exposes as the interface to the VNF services. It leverages the vCenter Server Appliance and NSX Manager to orchestrate compute, storage, network, and imaging infrastructure services from a single, programmable interface.
VMware Integrated OpenStack Overview
OpenStack is a cloud framework for creating an Infrastructure-as-a-Service (or IaaS) cloud. It provides cloud-style APIs and a plug-in model that enables a choice of virtual infrastructure technologies. OpenStack does not provide the virtual technologies, instead leverages the underlying hypervisor, networking, and storage from different vendors. VMware Integrated OpenStack (VIO) is a VMware production-grade OpenStack that consumes industry-leading VMware technologies. VIO leverages your existing VMware investment to simplify installation, upgrade, operations, monitoring, and so on. VIO is OpenStack powered and is validated through testing to provide API compatibility for OpenStack core services.
| Service |
API Coverage |
Release |
|---|---|---|
| Block Storage API and Extensions |
FULL |
Cinder v2.0, v3.0 |
| Compute Service API and Extensions |
FULL |
Nova v2.1 |
| Identity service API and Extensions |
FULL |
Keystone v3 |
| Image Service API |
FULL |
Glance v2.1 |
| Networking API and Extensions |
FULL |
Neutron v2.0 |
| Object Store API and Extensions (Tech Preview) |
FULL |
Swift v1.0 |
| Orchestration API |
FULL |
Heat v1.0 |
| Load Balancer |
FULL |
Octavia v2 |
| Metering and Data Collection Service API |
FULL |
Ceilometer / Panko/Ado |
| Key Manager Service |
FULL |
Barbican v2 |
VMware Integrated OpenStack Architecture
Based on virtual platform designs outlined in the platform tier, a three-pod design is recommended for production. Separate vSphere clusters are used for Management, Edge, and Compute.
-
Management Pod: OpenStack Control Plane and OpenStack Life Cycle Manager are deployed in the Management Pod.
-
Edge Pod: OpenStack Neutron DHCP, NAT, Metadata Proxy services reside in the Edge Pod.
-
Compute Pod: User VMs and VNF provisioned by OpenStack resides in the Compute Pod.
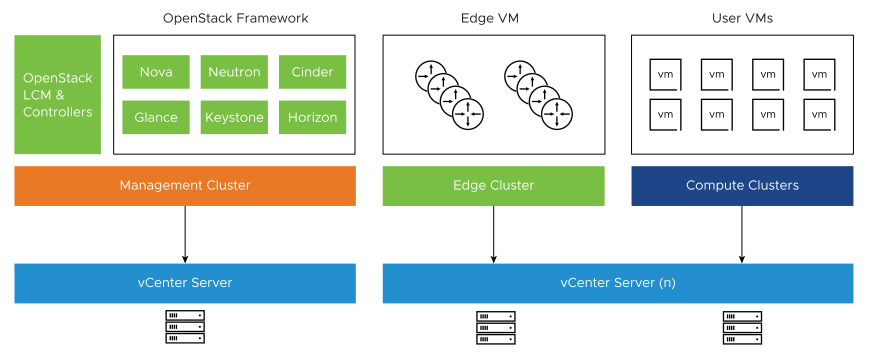
The management cluster requires at least three hosts, so that management components can run on different hosts and the failure of one host does not impact the control plane availability. The NSX Edge cluster requires a minimum of two hosts with at least one workload or compute cluster. You can deploy additional compute clusters based on application, scale, and SLA requirements. vCenter Server can support up to 64 hosts in a single cluster but is not recommended for environments with large churn, as large vSphere clusters add a delay in VM scheduling and boot time. In a deployment with a large number of concurrent operations, create new clusters when you need additional compute capacity.