VMware Integrated OpenStack Networking exposes OpenStack API for API access and offers cloud tenants a highly programmable infrastructure to build rich networking topologies and configure advanced network policies in the cloud.
VDS networking provides management connectivity between VIO control plane, vCenter Server, and NSX Manager. NSX Networking can be used to simplify OpenStack tenant networking. Dedicated VDS is used for each vSphere cluster. In addition to the networking required to manage the vSphere cluster, the following networks are used for a standard VIO-based deployment:
-
Management Network: Used for management access of VIO, ESXi hosts, NSX Manager, and so on.
-
API Network: Used by OpenStack users and tenants to access their OpenStack Project for provisioning and monitoring.
-
Transport Network: Used to enable tenant overlay networking.
-
External network: Routable IP address space within the NSX-T fabric. External networks can be shared across all OpenStack Tenants/projects or dedicated to a Single Tenant or project.
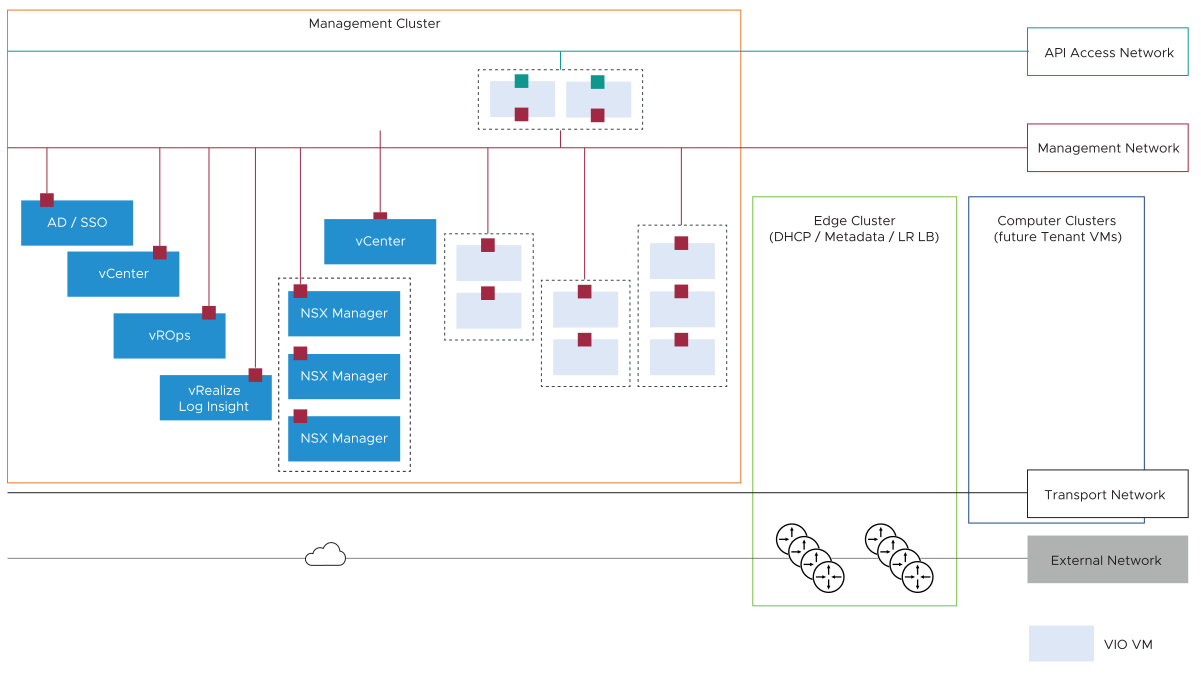
API and Management VLANs provide API and management access for cloud admins and OpenStack users. Both networks are control plane only. External and Geneve transport networks are data plane networks supporting communication to and from the VMs/VNFs. External networks allow VMs to access the Internet or intranet, while the transport network is used to enable tenant networking to support VNF to VNF communication within the data center. Except for the transport network, deploy the OpenStack networks using routable IP address space within the service provider network domain.
NSX-T Data Center requires a minimum of 1600 MTU size for overlay traffic. The recommended MTU size is 9000.