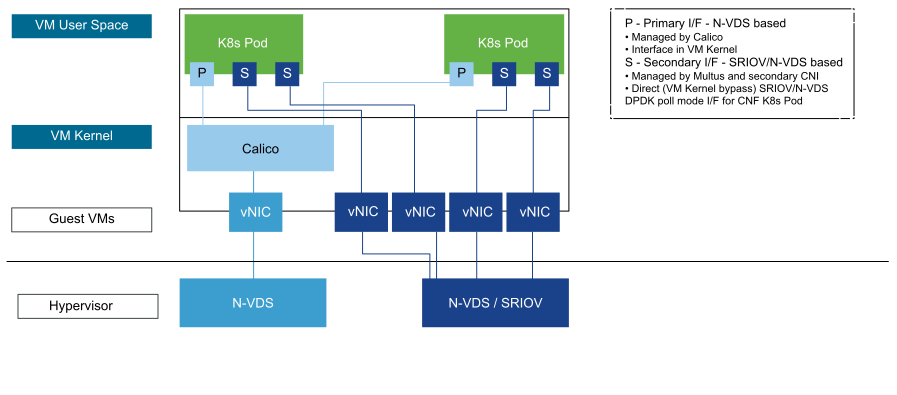
5G CNFs require advanced networking services to support receive and transmit at high speed with low latency. The realization of advanced network capabilities must be achieved without deviating from the default networking abstraction provided by Kubernetes. The Cloud Native Networking design focuses on the ability to support multiple NICS in a Pod, where the primary NIC is dedicated to Kubernetes for management and the ability to attach additional networks dedicated to data forwarding.
Kubernetes Primary Interface with Calico
Each node must have a management interface. The management and pod IP addresses must be routable for the Kubernetes health check to work. After the Tanzu Kubernetes cluster is deployed, Calico networking is automatically enabled to provide Pod-to-Pod communication within the cluster.
Design Recommendation |
Design Justification |
Design Implication |
|---|---|---|
Each node must have at least one management network interface. |
Management interface is used by K8s Pods to communicate within the Kubernetes cluster. |
Nine vNICs remaining for the CNF data plane traffic. |
Use a dedicated Kubernetes Node IP block per NSX-T fabric.
|
Dedicated subnet simplifies troubleshooting and routing. |
|
Allocate a dedicated Kubernetes Pod IP block, if 110.96.0.0/11 cannot be used. |
|
The IP block must not overlap with Multus IP blocks. For Multus requirements, see the Secondary CNI Plugin section. |
Allocate a dedicated Kubernetes Service IP block if 110.64.0.0/13 cannot be used. |
|
|
Secondary CNI Plugins
Multiple network interfaces can be realized by Multus, by working with the Calico and additional upstream CNI plugins. Calico is responsible for creating the primary or default networks for every pod. Additional interfaces can be both SR-IOV or NVDS-Enhanced interfaces managed through Multus by using secondary CNI plugins. An IP Address Management (IPAM) instance assigned to the secondary interface is independent of the primary or default network.
The following figure illustrates the multus deployment architecture:
Design Recommendation |
Design Justification |
Design Implication |
|---|---|---|
Enable Multus integration with the Kubernetes API server to provision both Kernel-based and passthrough network devices to a data plane CNF. |
|
Multus is an upstream plugin and follows the community support model. |
Deploy the SR-IOV network device plugin to enable DPDK passthrough for workloads that require SR-IOV or NVDS-Enhanced (ENS). |
The SR-IOV network device plugin is a Kubernetes device plugin for discovering and advertising SR-IOV and ENS network virtual functions that are available on a Kubernetes host. |
|
Ensure that only vNICs that meet performance requirements are exposed to the CNI and device plugin. |
Based on the type of vNICs or passthrough interfaces, update the SR-IOV device plugin configMap to allow vNICs intended to be available to the Kubernetes scheduler and Kubelet. |
None |
Deploy the host-device CNI plugin to attach SR-IOV or ENS VF to a pod without DPDK. |
|
|
Assign a dedicated IP block for additional container interfaces (MULTUS). Note: This address block must not overlap with the primary container interface. |
The SR-IOV host-device CNI or macvlan Container Plugin uses this IP block to assign addresses to additional Kubernetes pod interfaces. |
|
External Service Access
By default, 5GC components deployed in a Tanzu Kubernetes cluster have private IPs routable only within the cluster. To expose services outside the cluster, NodePort or Ingress can be used.
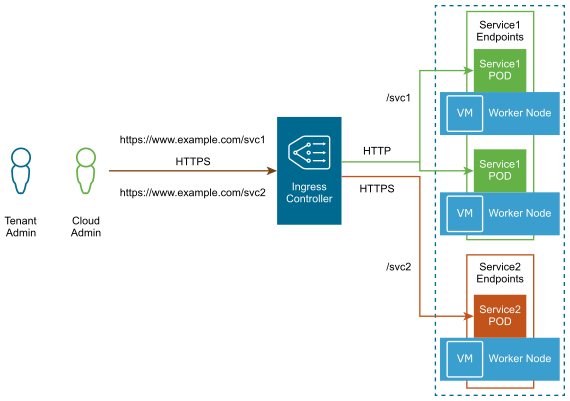
NodePort: NodePort uses the Kube proxy to provide NAT capability through the K8s cluster node IP. Since NodePort leverages the cluster node for forwarding, it can support a wide variety of protocols, including SCTP, commonly used for Telco applications.
Ingress: For HTTP-based traffic, Ingress is an API object that describes a collection of rules to allow external access to cluster services. An Ingress can be configured to provide externally reachable URLs, load balance traffic, terminate SSL, and offer name-based virtual hosting. A controller is required to implement the Ingress resource.
The following table summarizes when to use NodePort or Ingress:
HTTP/HTTPS |
SCTP and others |
|
|---|---|---|
NodePort |
Yes |
Yes |
Ingress |
Yes |
No |