VMware Telco Cloud Automation (TCA) is a unified orchestrator. It onboards and orchestrates workloads seamlessly from VM and container-based infrastructures for adaptive service-delivery foundation. It distributes workloads from the core to the edge and from private to public clouds for unified orchestration.
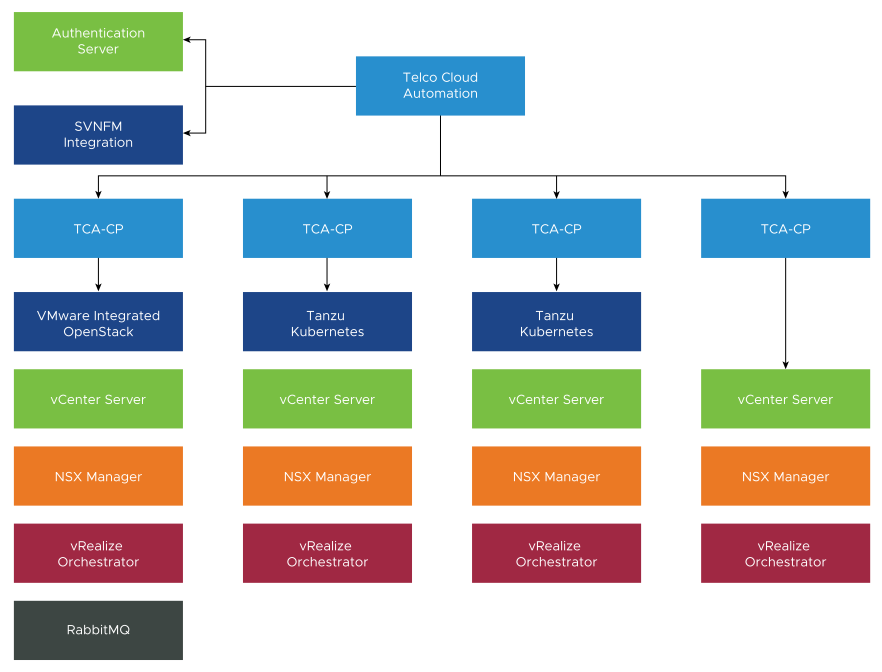
TCA Architecture
TCA provides orchestration and management services for Telco clouds.
-
TCA-Control Plane: The virtual infrastructure in the Telco edge, aggregation, and core sites are connected using the TCA-Control Plane (TCA-CP). TCA-CP provides infrastructure for placing workloads across clouds using TCA. It supports several types of Virtual Infrastructure Manager (VIM) such as VMware vCenter Server, Kubernetes, and so on. TCA connects with TCA-CP to communicate with the VIMs. TCA-CP is deployed as an OVA. The VIMs are cloud platforms. A dedicated instance of TCA-CP is required for each non-Kubernetes VIM.
-
Platform Services Controller (PSC): PSC is used for authentication and Single Sign-On (SSO) for TCA.
-
SVNFM: Any SOL 003 SVNFM can be registered with TCA.
-
NSX Manager: TCA communicates with NSX Manager through the VIM layer. A single instance of the NSX Manager can be used to support multiple VIM types.
-
vRealize Orchestrator: vRealize Orchestrator registers with TCA-CP and runs customized workflows for CNF onboarding and day 2 life cycle management.
-
RabbitMQ: RabbitMQ tracks VMware Cloud Director and VMware Integrated OpenStack notifications and it is not required for Telco Cloud Platform.
TCA Persona
The following key stakeholders are involved in the end-to-end service management, life cycle management, and operations of the Telco cloud native solution:
| Persona |
Role |
|---|---|
| CNF Vendor / Partners |
CNF vendors / partners supply HELM charts and container images. |
| Read access to NF Catalog |
|
| CNF Deployer / Operator |
Read access to NF Catalog |
| Responsible for CNF LCM through TCA (ability to self-manage CNF) |
|
| CNF Developer / Operator |
Develops CNF CSAR by working with vendors. |
| Maintains CNF catalog. |
|
| Responsible for CNF LCM through TCA (ability to self-manage CNF) |
|
| Updates Harbor with HELM and Container images. |
|
| TKG Admin |
Kubernetes Cluster Admin for one or more Tanzu Standard for Telco Kubernetes clusters |
| Deploys K8s Clusters to pre-assigned Resource Pool. |
|
|
|
| Works with CNF Developer to supply CNF dependencies (Container images, OS packages, and so on) |
|
| Worker node dimensioning |
|
| Deploys CNF monitoring/logging tools (Prometheus / Grafana/ fluentd). |
|
| Kubernetes API/CLI access to K8s clusters associated with CNF deployment |
|
| TCA Admin / System Admin |
Onboards TCA User / Partner access. |
| Adds new VIM Infrastructure and associates with TCP-CP. |
|
| Infrastructure monitoring through vRealize |
|
| Creates and maintains vCenter Resource Pools for Tanzu Kubernetes Clusters. |
|
| Creates and maintains Tanzu Kubernetes Cluster Template. |
|
| Deploys and maintains Harbor repository. |
|
| Deploys and maintains Kubernetes bootstrap process. |
|
| Performs TCA/TCA-CP/Harbor/Infra/Infra Monitoring and upgrades. |
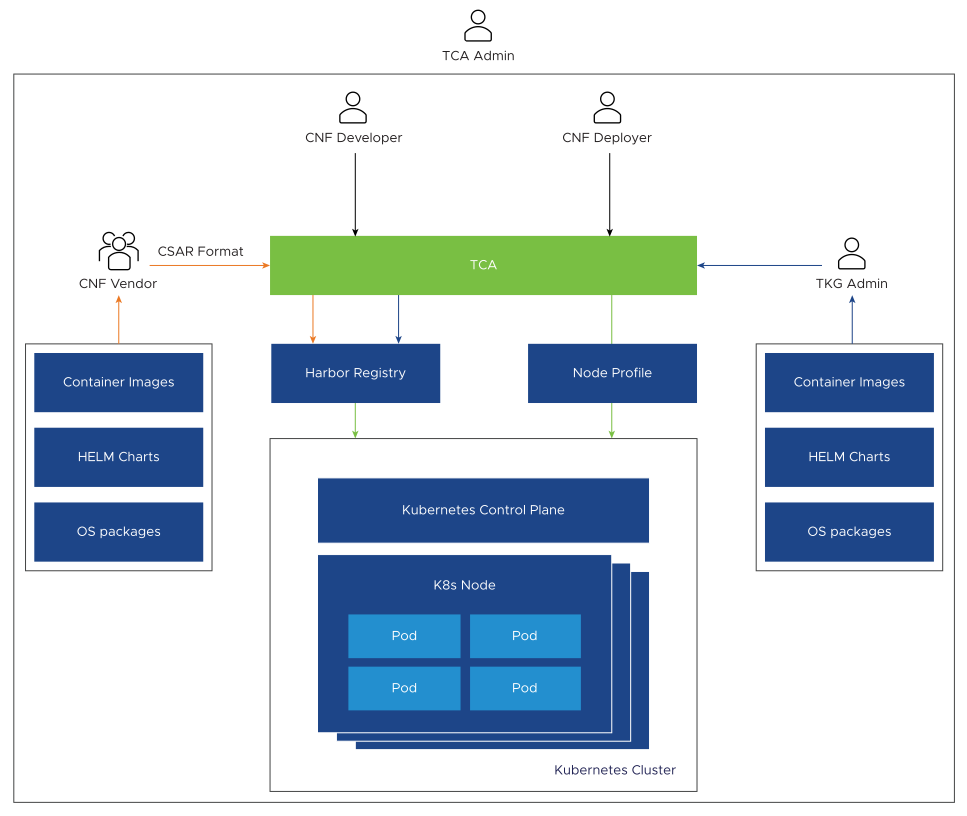
Virtual Infrastructure Management
TCA Administrators can onboard, view, and manage the entire Telco Cloud Platform virtual infrastructure through the TCA console. Details about each cloud such as Cloud Name, Cloud URL, Cloud Type, Tenant Name, Connection Status, and Tags can be displayed graphically or as an aggregate list based on the geographic location. TCA Admin can then use roles, permissions, and tags to provide resource separation between the VIM, Users, and Network Functions.
CaaS Subsystem Overview
The CaaS subsystem allows Telco Cloud Platform operators to create and manage Kubernetes clusters and Cloud-native 5G workloads. VMware Telco Cloud platform uses VMware Tanzu Standard for Telco to create Kubernetes clusters.
Using VMware Telco Cloud Automation, the TCA admins can create Telco management and workload templates to reduce repetitive parts of Kubernetes cluster creation while standardizing cluster sizing and capabilities. A typical template can include a grouping of workers nodes through Node Pool, control and worker node sizing, Container Networking, Storage class, and CPU affinity policies.
After the TCA Admin publishes the Kubernetes Cluster templates, the TKG admin can consume those templates by deploying and managing various types of Kubernetes clusters on different vSphere clusters that best meet CNF requirements.
The CaaS subsystem access control is fully backed by RBAC. The TKG admins have full access to Kubernetes clusters under their management, including direct console access to Kubernetes nodes and API. CNF developers and deployers can gain deployment access to Kubernetes cluster through the TCA console.
CNF Management Overview
Cloud-native Network Function (CNF) management encompasses onboarding, designing, and publishing of the SOL001-compliant CSAR packages to the TCA Network Function catalog. TCA maintains the CSAR configuration integrity and provides a Network Function Designer for CNF developers to update and release newer iterations in the Network Function catalog.
Network Function Designer is a visual design tool within VMware Telco Cloud Automation. It generates SOL001-compliant TOSCA descriptors based on the 5G core deployment requirements. A TOSCA descriptor consists of instantiation parameters and operational behaviors of the CNF for life cycle management.
Network functions from different vendors have their own and unique set of infrastructure requirements. A CNF developer can include the CSAR package infrastructure requirements to instantiate and operate a 5G CNF. VMware Telco Cloud Automation attempts to customize worker node configuration based on those requirements through the VMware Telco NodeConfig Operator. The Telco NodeConfig Operator is a K8s operator that handles the node OS customization, performance tuning, and upgrade. Instead of static resource pre-allocation during the Kubernetes cluster instantiation, the NodeConfig Operator defers resource binding of expensive network resources such as SR-IOV VF and Huge Pages to the CNF instantiation. When new workloads are instantiated through TCA, TCA automatically assigns more resources to the Kubernetes cluster to accommodate new workloads.
Access policies for CNF Catalogs and Inventory are roles and permissions based. Custom policies can be created in TCA to offer self-managed capabilities required by CNF Developers and Deployers.