To provide failover capabilities if the primary VMware Identity Manager data center becomes unavailable, you must deploy VMware Identity Manager in a secondary data center.
For disaster recovery, the recommendation is to use VMware Site Recovery Manager. See Performing Disaster Recovery for VMware Identity Manager Using Site Recovery Manager. If you do not meet the requirements for Site Recovery Manager, implement the following approach.
By using a secondary data center, end users can log in and use applications with minimal downtime. Also, with a secondary data center, you can upgrade VMware Identity Manager to the next version with minimal downtime. See Upgrading VMware Identity Manager with Minimal Downtime.
A typical deployment using a secondary data center is shown here.
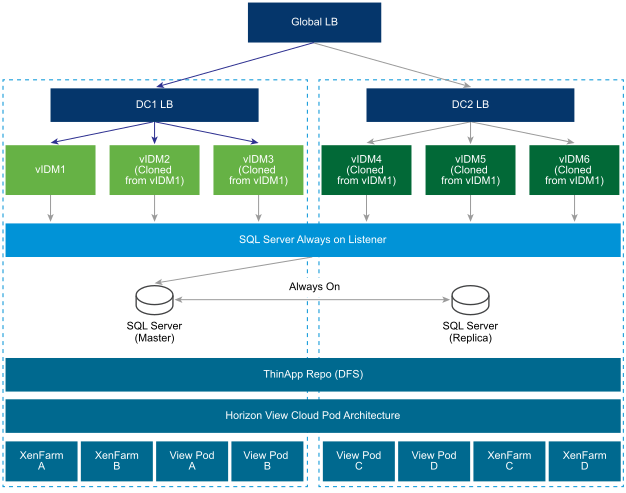
Follow these guidelines for a multiple data center deployment.
- Cluster Deployment: You must deploy a set of VMware Identity Manager virtual appliances in two separate data centers.
- A set of three or more VMware Identity Manager virtual appliances as one cluster in one data center.
- Another set of three or more VMware Identity Manager virtual appliances as another cluster in a second data center.
- Database: VMware Identity Manager uses the database to store data. For a multiple data center deployment, replication of the database between the two data centers is crucial. Refer to your database documentation about how to set up a database in multiple data centers. For example, with SQL Server, using Always On deployment is preferable. See Overview of Always On Availability Groups (SQL Server) on the Microsoft website for information. VMware Identity Manager functionalities are designed for minimal latency between the database and the VMware Identity Manager appliance. Therefore, appliances in one data center are designed to connect to the database in the same data center.
- Not Active-Active: VMware Identity Manager does not support an Active-Active deployment where users can be served from both data centers at the same time. The secondary data center is a hot stand-by and can be used to provide business continuity for end users. VMware Identity Manager appliances in the secondary data center are in a read-only mode. Therefore, after a failover to that data center, most admin operations, like adding users or applications, or entitling users, will not work.
- Fail-Back to Primary: In most failure scenarios, you can fail back to the primary data center after that data center is back to normal. See Failback to Primary Data Center for information.
- Promote Secondary to Primary: If an extended data center failure occurs, the secondary data center can be promoted to primary. See Promoting Secondary Data Center to Primary Data Center for information.
- Fully Qualified Domain Name: The fully qualified domain name to access VMware Identity Manager must be the same in all data centers.
-
Audits: VMware Identity Manager uses Elasticsearch embedded in the VMware Identity Manager appliance for auditing, reports, and directory sync logs. Create separate Elasticsearch clusters in each data center. See Setting up a Secondary Data Center for more information.
- Active Directory: VMware Identity Manager can connect to Active Directory using the LDAP API or using Integrated Windows Authentication. With both of these methods, VMware Identity Manager can use Active Directory SRV records to reach the appropriate domain controller in each data center.
- Windows Apps: VMware Identity Manager supports accessing Windows apps using ThinApp, and Windows Apps and Desktops using Horizon View or Citrix technologies. Delivering these resources from a data center that is closer to the user, also called Geo-Affinity, is important. Note the following about Windows resources:
- ThinApps - VMware Identity Manager supports Windows Distributed File Systems as a ThinApp repository. Use the Windows Distributed File Systems documentation to set up appropriate location-specific policies.
- Horizon View (with Cloud Pod Architecture) - VMware Identity Manager supports Horizon Cloud Pod Architecture. Horizon Cloud Pod Architecture provides Geo-Affinity using global entitlements. See "Integrating Cloud Pod Architecture Deployments" in Setting up Resources in VMware Identity Manager for information. No additional changes are required for a VMware Identity Manager multiple data center deployment.
- Horizon View (without Cloud Pod Architecture) - If Horizon Cloud Pod Architecture is not enabled in your environment, you cannot enable Geo-Affinity. After a fail-over event, you can manually switch VMware Identity Manager to run Horizon View resources from the View pods configured in the secondary data center. See Configure Failover Order of Horizon View and Citrix-published Resources for more information.
-
Citrix Resources - Similar to Horizon View (without Cloud Pod Architecture), you cannot enable Geo-Affinity for Citrix resources. After a fail-over event, you can manually switch VMware Identity Manager to run Citrix resources from the XenFarms configured in the secondary data center. See Configure Failover Order of Horizon View and Citrix-published Resources for more information.