The platform components are grouped into two distinct containments: Edge Management Domain and Edge Resource Domain. While the management domain is used to host the management components for edge sites, the resource domain is used to host the NSX Edge VMs and VNFs.
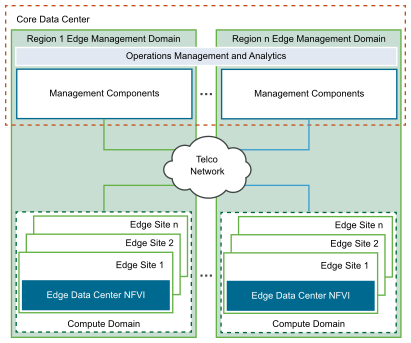
The preceding figure shows the building blocks for the edge. An Edge data center is mapped to an edge site. Edge sites (or Edge data centers) are grouped into regions and they have a corresponding instance of VIO deployed in the Core data center. The operations management and analytics components oversee the edge management instances. This section describes the physical and logical configuration of the edge building blocks.
- Telco Edge Management Domain
-
An Edge site follows the collapsed edge/resource pod design used in the vCloud NFV 3.1 reference architecture. This design entails a minimum of three servers (four recommended if using vSAN) to provide pooled compute resources to both the VNF workloads deployed at the site and to the NSX-T Data Center edge nodes.
The edge storage may be provided by any supported shared storage solution. This reference architecture uses vSAN as the storage provider.
Each server must have local disks for vSAN caching and capacity tiers. An All Flash vSAN is recommended for reliability and performance.
Each physical host must have a minimum of six physical NICs connected to a pair of ToR switches in a LAG configuration for redundancy. The pairing of the physical NICs and their distribution across the virtual switches is covered in later sections. The ToR switches connect to an external WAN Edge physical router to transport packets for Internet breakout and backhaul to the Core site.
- Telco Edge Compute Domain
-
Logically an edge site is a separate vSphere/vSAN cluster with hosts connecting to and managed by the vCenter Server that is a part of the management instance for the corresponding region. This edge cluster must host both the VNF workloads and the NSX-T Data Center edge nodes, and it must be sized accordingly.
The number of edge sites within a region are constrained by the configuration maximums of the management components for that region. When the maximum limit is reached, a new management instance is deployed to accommodate the growth.
The actual sizing depends on factors influenced by the inter-dependencies between management components and their configuration limits. For example, a single NSX-T Data Center 2.3 installation can manage a maximum of 768 hosts as the limiting factor, whereas a single vCenter Server 6.7 can manage up to 2000 hosts. The actual number of supported sites vary depending on the sizing of each site. All the edge sites need not be sized equally, but are sized based on their respective workload requirements.