The Management Pod contains the components that manage the vCloud NFV runtime environment.
vCenter Server
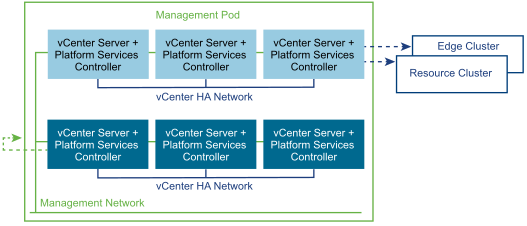
The Management Pod is implemented as a cluster that is managed by the first vCenter Server instance. To form the foundation of a carrier grade virtualized infrastructure, the components of the Management Pod benefit from the cluster features such as resource management, high availability, and resiliency. A second vCenter Server is deployed in the Management Pod to oversee the Edge and Resource Pods.
Each vCenter Server instance is a virtual appliance that is deployed with an embedded database and an embedded Platform Services Controller. The vCenter® Server Appliance™ is preconfigured, hardened, and fast to deploy. The appliance allows for a simplified design, eases management, and reduces administrative efforts. vCenter Server Appliance availability is ensured by using a vCenter High Availability (vCenter HA) cluster. The vCenter HA cluster consists of one active node that serves client requests, one passive node as a backup in the event of failure, and one quorum node that is called a witness node. Replication between nodes by using a dedicated vCenter HA network ensures that vCenter Server Appliance data is always synchronized and up-to-date.
The Platform Services Controller contains common infrastructure security services such as VMware vCenter® Single Sign-On, VMware Certificate Authority, licensing, service registration, and certificate management services. The Platform Services Controller handles identity management for administrators and applications that interact with the vSphere platform. The Platform Services Controller and its related services are embedded within the vCenter Server Appliance. This eliminates the need for separate Platform Services Controller VM instances and their corresponding load balancers, thus simplifying its deployment and administration and reducing the management components footprint.
Data backup and restore of each vCenter Server instance and its embedded Platform Services Controller is provided by using the native backup service that is built in the appliances. This backup is performed to a separate storage system by using network protocols such as SFTP, HTTPS, and SCP.
When vCenter HA is used with an embedded Platform Services Controller, the environment setup is as follows:
VMware NSX-T Data Center
NSX Manager. The management plane for the NSX-T system. It provides the ability to create, configure, and monitor NSX-T Data Center components, such as logical switches, and NSX Edge Nodes. NSX Manager provides an aggregated system view and is the centralized network management component of NSX-T Data Center. It provides a method for monitoring and troubleshooting workloads that are attached to the virtual networks that NSX-T Data Center creates. NSX-T Data Center provides configuration and orchestration of logical networking components such as logical switching and routing, networking services, Edge services, security services, and distributed firewall capabilities.
NSX Manager is deployed as a single node that uses vSphere HA for high availability. NSX Manager communicates with its controller and Edge clusters over a common management network. The management components of the vCloud NFV platform communicate over the same management network to request network services from NSX-T Data Manager.
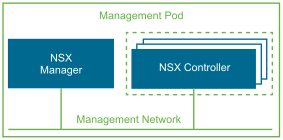
NSX Controller . An advanced distributed state management system that controls virtual networks and overlay transport tunnels. NSX Controller is deployed as a cluster of highly available virtual appliances that are responsible for the programmatic deployment of virtual networks across the entire NSX-T Data Center architecture. The control plane is split in two parts in NSX-T Data Center, the central control plane (CCP), which runs on the NSX Controller cluster nodes, and the local control plane (LCP), which runs on the transport nodes, adjacent to the data plane it controls. The Central Control Plane computes some ephemeral runtime state based on configuration from the management plane and disseminates information reported through the local control plane by the data plane elements. The Local Control Plane monitors local link status, computes most ephemeral runtime state based on updates from data plane and CCP, and pushes stateless configuration to forwarding engines. The LCP shares fate with the data plane element that hosts it. The NSX-T Data Center Central Control Plane (CCP) is logically separated from all data plane traffic, therefore any failure in the control plane does not affect the existing data plane operations. Traffic does not pass through the controller, instead the controller is responsible for providing configuration to other NSX Controller components such as the logical switches, logical routers, and edge configuration. Stability and reliability of data transport are central concerns in networking.
To further enhance the high availability and scalability, the NSX Controller is deployed in a cluster of three instances in the Management cluster. Anti-affinity rules are configured to ensure that the controller instances reside on separate hosts to protect against host failures.
VMware vCloud Director for Service Providers
VMware vCloud Director for Service Providers is an abstraction layer that operates on top of the other VIM components, vCenter Server, and NSX Manager. A highly available vCloud Director implementation that uses multiple load balanced vCloud Director cells are deployed in a vCloud Director Server Group. All cells in the server group are stateless and use a shared highly available clustered database. Each cell contains all the software components required for vCloud Director. A cell can run on its own, but multiple cells running in an active-active cluster are used for scalability and redundancy.
vCloud Director builds a secure, multitenant virtual environment by pooling virtual infrastructure resources to virtual data centers (VDCs) and exposing them to users through Web-based portals and APIs as fully-automated, catalog-based services.
A fundamental concept in vCloud Director is that of the tenant. A tenant is a logically isolated construct representing a customer, department, network function, or service, used to carve out infrastructure resources and deploy VNF workloads. vCloud Director isolates administrative boundaries to NFVI tenants. VNF workload resource consumption is therefore segmented from other VNF workloads, even though the VNFs can share the same resources.
vCloud Director implements the open and publicly available vCloud API, which provides compatibility, interoperability, and programmatic extensibility to network equipment providers (NEPs) and their VNF Managers. The vCloud Director capabilities can be extended to create adaptors to external systems including OSS/BSS.