To define a role for role-based access controls (RBAC) in SaltStack Config, you must both define the permitted task and also assign resource access. A task is a specific operation that can be performed in the user interface, such a creating, editing, or running a job. A resource is an element of your environment, such specific masters, minions, targets, file data, etc.
Tasks
Tasks represent common use cases in SaltStack Config. Enabling a task gives the role all permissions required to complete the task.
The Tasks tab includes the following options.
| Task |
Description |
|---|---|
| Create and delete new targets |
Role can create new targets. Users assigned to this role can edit and delete targets they have created, or other targets defined under Resource Access. A target is the group of minions, across one or many Salt masters, that a job’s Salt command applies to. A Salt master can also be managed like a minion and can be a target if it is running the minion service. See Minions. |
| Modify pillar data |
Role can view, edit, and delete sensitive information stored in pillars. Users belonging to the role can edit or delete pillars they have created. They can also edit or delete other pillars if granted resource access (available through the API (RaaS) only). Pillars are structures of data defined on the Salt master and passed through to one or more minions, using targets. They allow confidential, targeted data to be securely sent only to the relevant minion. See Pillars. |
| Modify file server |
Role can view the file server, and can create, edit, or delete files. Users belonging to the role can edit or delete files they have created. They can also edit or delete other files if granted resource access (available through the API (RaaS) only). The file server is a location for storing both Salt-specific files, such as top files or state files, as well as files that can be distributed to minions, such as system configuration files. See File Server. |
| Run arbitrary commands on minions |
Role can trigger commands outside of a job for the Salt master to pick up. Role is not limited to running only commands included in a given job’s definition. Minions are nodes running the minion service, which can listen to commands from a Salt master and perform the requested tasks. See Minions. |
| Accept, delete, and reject keys |
Role can accept, delete, and reject minion keys as needed for initial configuration. A minion key allows encrypted communication between a Salt master and Salt minion. See Minion Keys. |
| Read and modify users, roles, permissions |
Role can view users and associated data, as well as edit roles and permissions settings. Note: This task applies only to the built-in Administrator and Superuser roles. Roles are used to define permissions for multiple users who share a common set of needs. |
| Run commands on Salt masters |
Role can run commands on Salt masters, such as to run orchestration. Commands run against the Salt master are also called Salt runners. Salt runners are modules used to execute convenience functions on the Salt master. See Jobs. Adding this permission allows the role to be able to use the salt-run option from the Run command feature under the Minions tab. |
| Compliance - create, edit, delete, and assess |
Role can create, edit, delete, and assess SaltStack SecOps Compliance policies. In addition to granting permission for this task, you must also define resource access for any targets you want the role to perform actions on. For example, if you want the This task does not allow the role to remediate SaltStack SecOps Compliance policies. SaltStack SecOps Compliance is an add-on to SaltStack Config that manages the security compliance posture for all the systems in your environment. See Using and Managing SaltStack SecOps for more information.
Note:
A SaltStack SecOps license is required. |
| Compliance - remediate |
Role can remediate any non-compliant minions detected in a SaltStack SecOps Compliance assessment. SaltStack SecOps Compliance is an add-on to SaltStack Config that manages the security compliance posture for all the systems in your environment. See Using and Managing SaltStack SecOps.
Note:
A SaltStack SecOps license is required. |
| Compliance - update SaltStack content |
Role can download updates to the SaltStack SecOps Compliance security library. |
| Vulnerability - create, edit, delete, and assess |
Role can create, edit, delete, and assess SaltStack SecOps Vulnerability policies. In addition to granting permission for this task, you must also define resource access for any targets you want the role to run assessments against. This task does not allow the role to remediate SaltStack SecOps Vulnerability policies. SaltStack SecOps Vulnerability is an add-on to SaltStack Config that manages vulnerabilities on all the systems in your environment. See Using and Managing SaltStack SecOps.
Note:
A SaltStack SecOps license is required. |
| Vulnerability - remediate |
Role can remediate vulnerabilities detected in a SaltStack SecOps Vulnerability assessment. SaltStack SecOps Vulnerability is an add-on to SaltStack Config that manages vulnerabilities on all the systems in your environment. See Using and Managing SaltStack SecOps.
Note:
A SaltStack SecOps license is required. |
Resource access
The Resource Access tab allows you to define resource access for targets and jobs. A target is the group of minions, across one or many Salt masters, that a job’s Salt command applies to. A Salt master can also be managed like a minion and can be a target if it is running the minion service. Jobs are used to run remote execution tasks, apply states, and start Salt runners.
The different levels of resource access are described below:
- Targets
- Read Only - Role can view the indicated target and its details, but cannot edit or delete it.
- Read/Write - Role can view and edit the indicated target.
- Read/Write/Delete - Role can view, edit, and delete the indicated target.
- Jobs
- Read Only - Role can view the indicated job and its details, but cannot edit or delete it, or run the job.
- Read/Run - Role can view and run the indicated job.
- Read/Run/Write - Role can view and edit the indicated job, as well as run it.
- Read/Run/Write/Delete - Role can view, edit, and delete the indicated job, as well as run it.
- Other resource types - Access to the following resource types must be defined using the API (RaaS). See Setting API permissions, or contact an administrator for assistance.
- Files in the file server
- Pillar data
- Authentication configuration
All other resource types, (excluding jobs, targets, and those listed above) do not require any specific resource access settings.
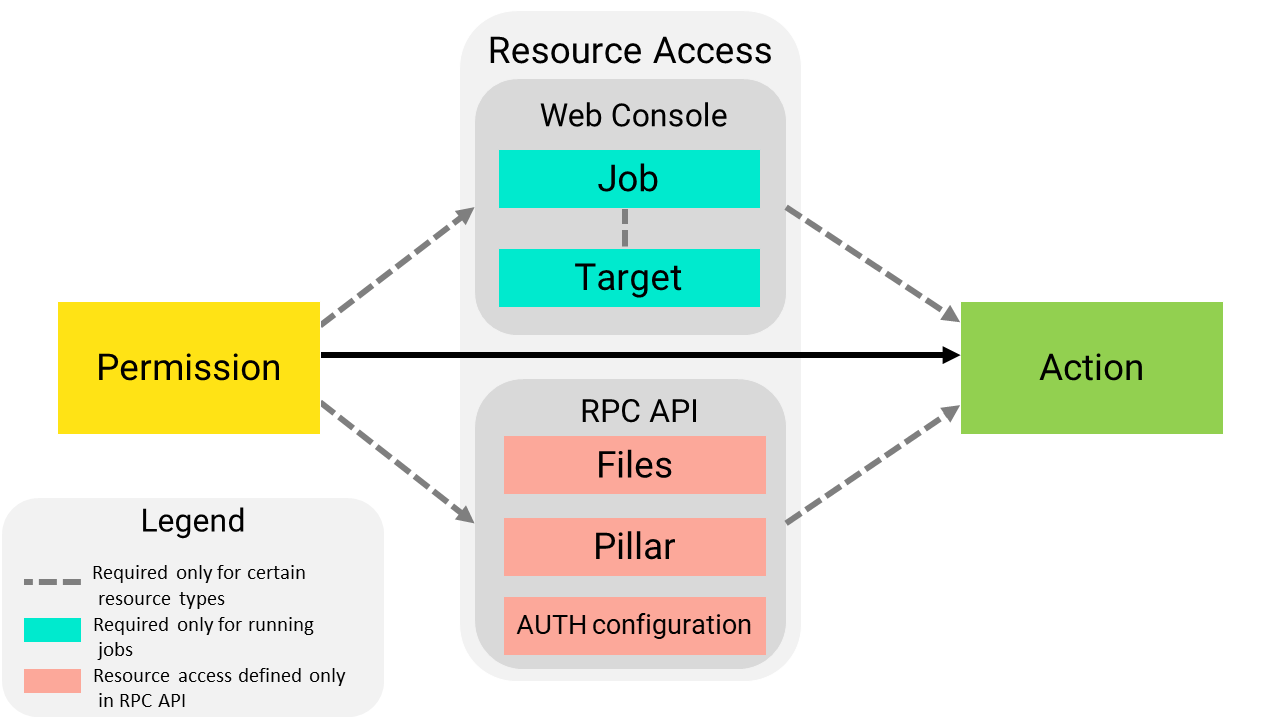
Difference between permitted tasks and resource access
A permitted task is broad category of allowed actions, whereas resource access is more granular, allowing you to specify a particular resource (such as a job or target) the action can be run against, as illustrated in the following diagram.
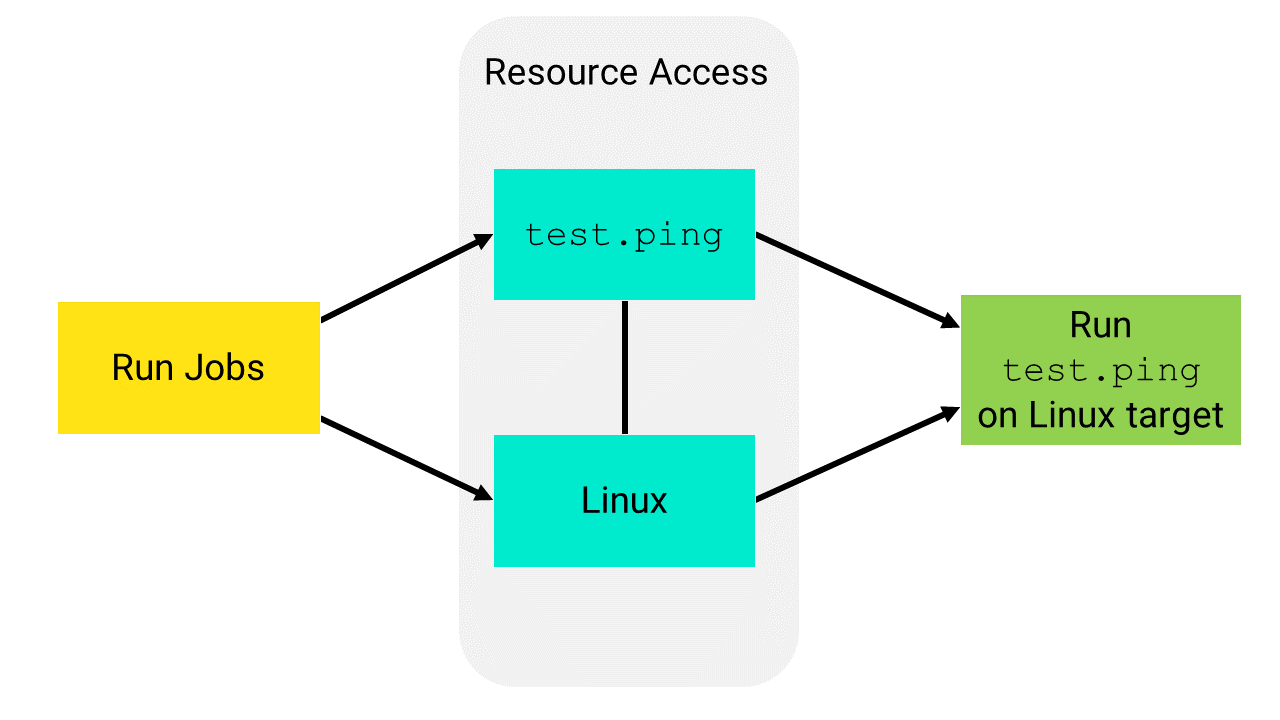
In the following example, a role can run test.ping on the Linux target group. The role has the following permissions settings:
- Read access to the Linux target
- Read/Run access to a job that includes the
test.pingcommand
Cloned roles inherit permitted tasks from the original role by default. Cloned roles do not inherit resource access, which must be defined separately. See Assigning access to a job or target.