Generally, vCenter Server and ESXi use the storage providers to obtain information about storage configuration, status, and storage data services offered in your environment. This information appears in the vSphere Client. The information helps you to make appropriate decisions about virtual machine placement, to set storage requirements, and to monitor your storage environment.
- Persistence Storage Providers
- Storage providers that manage arrays and storage abstractions, are called persistence storage providers. Providers that support Virtual Volumes or vSAN belong to this category. In addition to storage, persistence providers can provide other data services, such as replication.
- Data Service Providers
- Another category of providers is I/O filter storage providers, or data service providers. These providers offer data services that include host-based caching, compression, and encryption.
Both persistence storage and data service providers can belong to one of these categories.
- Built-in Storage Providers
- Built-in storage providers are offered by VMware. Typically, they do not require registration. For example, the storage providers that support vSAN or I/O filters are build-in and become registered automatically.
- Third-Party Storage Providers
- When a third party offers a storage provider, you typically must register the provider. An example of such a provider is the Virtual Volumes provider. You use the vSphere Client to register and manage each storage provider component.
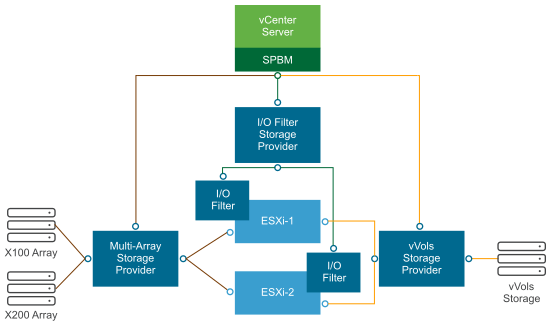
The following graphic illustrates how different types of storage providers facilitate communications between vCenter Server and ESXi and other components of your storage environment. For example, the components might include storage arrays, Virtual Volumes storage, and I/O filters.