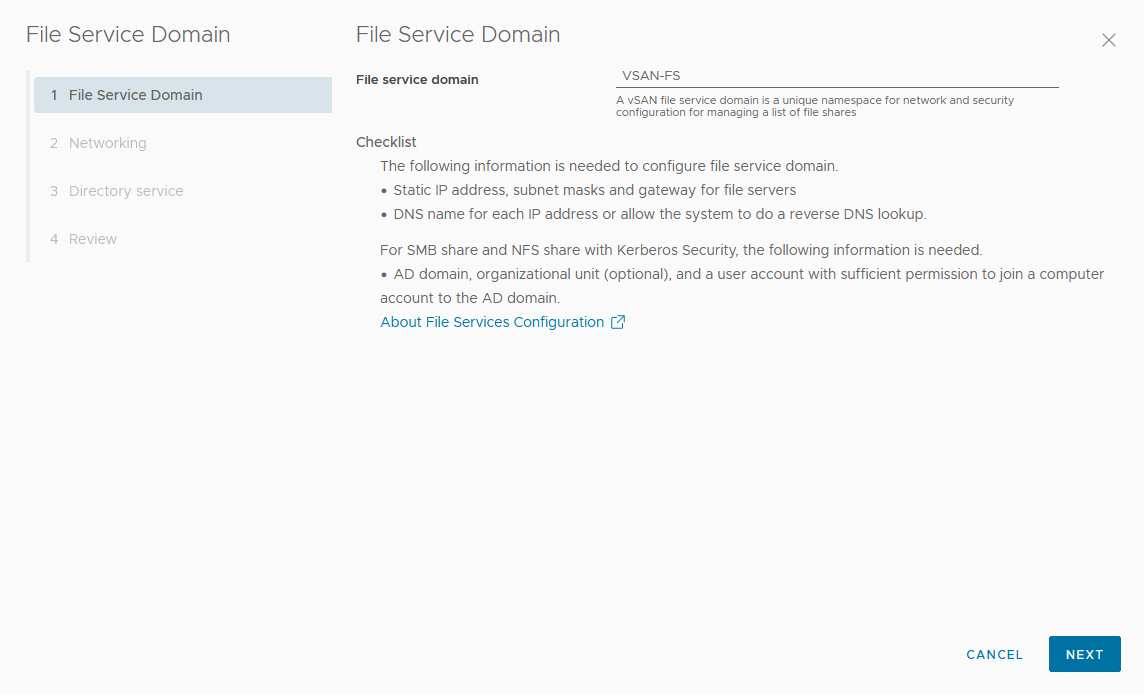
You can configure the File Service, which enable you to create file shares on your vSAN datastore.
Prerequisites
- Enable vSAN file service.
- Allocate static IP addresses as file server IPs from vSAN File Service network, each IP is the single point access to vSAN file shares.
- For best performance, the number of IP addresses must be equal to the number of hosts in the vSAN cluster.
- All the static IP addresses must be from the same subnet.
- Every static IP address has a corresponding FQDN, which must be part of the Forward lookup and Reverse lookup zones in the DNS server.
- If you are planning to create a Kerberos based SMB file share or a Kerberos based NFS file share, you need the following:
- Microsoft Active Directory (AD) domain to provide authentication to create an SMB file share or an NFS file share with the Kerberos security.
- (Optional) Active Directory Organizational Unit to create all file server computer objects.
- A domain user in the directory service with the sufficient privileges to create and delete computer objects.
Procedure
Results
The file service domain is configured. File servers are started with the IP addresses that were assigned during the vSAN File Service configuration process.