You can choose the storage architecture and deployment option when creating a vSAN cluster.
Chose the vSAN storage architecture that best suits your resources and your needs.
vSAN Original Storage Architecture
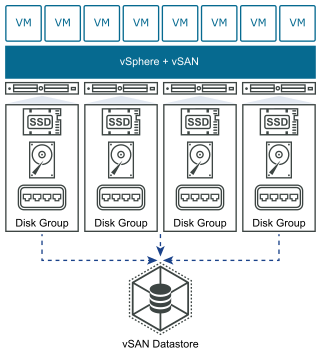
vSAN Original Storage Architecture (OSA) is designed for a wide range of storage devices, including flash solid state drives (SSD) and magnetic disk drives (HDD). Each host that contributes storage contains one or more disk groups. Each disk group contains one flash cache device and one or more capacity devices.

vSAN Express Storage Architecture
vSAN Express Storage Architecture (ESA) is designed for high-performance NVMe based TLC flash devices and high performance networks. Each host that contributes storage contains a single storage pool of four or more flash devices. Each flash device provides caching and capacity to the cluster.

Depending on your requirement, you can deploy vSAN in the following ways.
vSAN ReadyNode
The vSAN ReadyNode is a preconfigured solution of the vSAN software provided by VMware partners, such as Cisco, Dell, Fujitsu, IBM, and Supermicro. This solution includes validated server configuration in a tested, certified hardware form factor for vSAN deployment that is recommended by the server OEM and VMware. For information about the vSAN ReadyNode solution for a specific partner, visit the VMware Partner website.
User-Defined vSAN Cluster
You can build a vSAN cluster by selecting individual software and hardware components, such as drivers, firmware, and storage I/O controllers that are listed in the vSAN Compatibility Guide (VCG) website at http://www.vmware.com/resources/compatibility/search.php. You can choose any servers, storage I/O controllers, capacity and flash cache devices, memory, any number of cores you must have per CPU, that are certified and listed on the VCG website. Review the compatibility information on the VCG website before choosing software and hardware components, drivers, firmware, and storage I/O controllers that vSAN supports. When designing a vSAN cluster, use only devices, firmware, and drivers that are listed on the VCG website. Using software and hardware versions that are not listed in the VCG might cause cluster failure or unexpected data loss. For information about designing a vSAN cluster, see "Designing and Sizing a vSAN Cluster" in vSAN Planning and Deployment.
vSAN Deployment Options
This section covers the supported deployment options for vSAN clusters.
Single Site vSAN Cluster
A single site vSAN cluster consists of a minimum of three hosts. Typically, all hosts in a single site vSAN cluster reside at a single site, and are connected on the same Layer 2 network. All-flash configurations require 10 Gb network connections, and vSAN Express Storage Architecture requires 25 Gb network connections.
For more information, see Creating a Single Site vSAN Cluster.
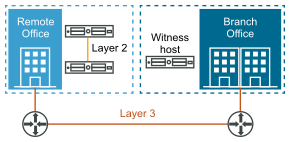
Two-Node vSAN Cluster
Two-node vSAN clusters are often used for remote office/branch office environments, typically running a small number of workloads that require high availability. A two-node vSAN cluster consists of two hosts at the same location, connected to the same network switch or directly connected. You can configure a two-node vSAN cluster that uses a third host as a witness, which can be located remotely from the branch office. Usually the witness resides at the main site, along with the vCenter Server.
For more information, see Creating a vSAN Stretched Cluster or Two-Node Cluster.
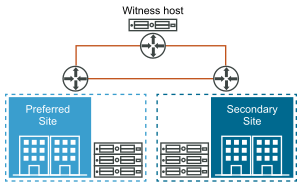
vSAN Stretched Cluster
A vSAN stretched cluster provides resiliency against the loss of an entire site. The hosts in a vSAN stretched cluster are distributed evenly across two sites. The two sites must have a network latency of no more than five milliseconds (5 ms). A vSAN witness host resides at a third site to provide the witness function. The witness also acts as tie-breaker in scenarios where a network partition occurs between the two data sites. Only metadata such as witness components is stored on the witness.
For more information, see Creating a vSAN Stretched Cluster or Two-Node Cluster.