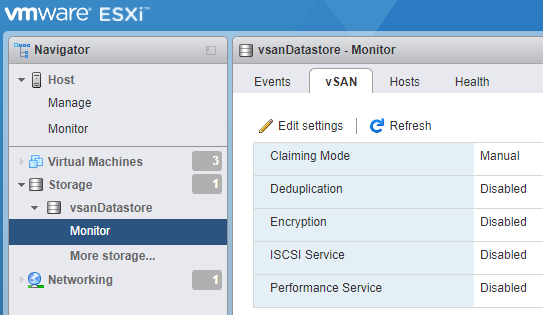
You can use the VMware Host Client to monitor the vSAN environment of your ESXi host.
vSAN Concepts
VMware vSAN uses a software-defined approach that creates shared storage for virtual machines.
It virtualizes the local physical storage resources of ESXi hosts and turns them into pools of storage that can be divided and assigned to virtual machines and applications according to their quality-of-service requirements. vSAN is implemented directly in the ESXi hypervisor.
You can configure vSAN to work as either a hybrid or all-flash cluster. In hybrid clusters, flash devices are used for the cache layer and magnetic disks are used for the storage capacity layer. In all-flash clusters, flash devices are used for both cache and capacity.
You can activate vSAN on existing host clusters, or when you create a new cluster. vSAN aggregates all local capacity devices into a single datastore shared by all hosts in the vSAN cluster. You can expand the datastore by adding capacity devices or hosts with capacity devices to the cluster. vSAN works best when all ESXi hosts in the cluster share similar or identical configurations across all cluster members, including similar or identical storage configurations. This consistent configuration balances virtual machine storage components across all devices and hosts in the cluster. Hosts without any local devices also can participate and run their virtual machines on the vSAN datastore.
In vSAN Original Storage Architecture (OSA), each host that contributes storage devices to the vSAN datastore must provide at least one device for flash cache and at least one device for capacity. The devices on the contributing host form one or more disk groups. Each disk group contains one flash cache device, and one or multiple capacity devices for persistent storage. Each host can be configured to use multiple disk groups.
In vSAN Express Storage Architecture (ESA), all storage devices claimed by vSAN contribute to capacity and performance. Each host's storage devices claimed by vSAN form a storage pool. The storage pool represents the amount of caching and capacity provided by the host to the vSAN datastore.
For best practices, capacity considerations, and general recommendations about designing and sizing a vSAN cluster, see the VMware vSAN Design and Sizing Guide.
Characteristics of vSAN
The following characteristics apply to vSAN, its clusters, and datastores.
| Supported Features | Description |
|---|---|
| Shared storage support | vSAN supports VMware features that require shared storage, such as HA, vMotion, and DRS. For example, if a host becomes overloaded, DRS can migrate virtual machines to other hosts in the cluster. |
| On-disk format | vSAN on-disk virtual file format provides highly scalable snapshot and clone management support per vSAN cluster. For information about the number of virtual machine snapshots and clones supported per vSAN cluster, see the Configuration Maximums documentation. |
| All-flash and hybrid configurations | vSAN can be configured for all-flash or hybrid cluster. |
| Fault domains | vSAN supports configuring fault domains to protect hosts from rack or chassis failures when the vSAN cluster spans across multiple racks or blade server chassis in a data center. |
| File service | vSAN file service enables you to create file shares in the vSAN datastore that client workstations or VMs can access. |
| iSCSI target service | vSAN iSCSI target service enables hosts and physical workloads that reside outside the vSAN cluster to access the vSAN datastore. |
| Stretched cluster and Two node cluster | vSAN supports stretched clusters that span across two geographic locations. |
| Support for Windows Server Failover Clusters (WSFC) | vSAN 6.7 Update 3 and later releases support SCSI-3 Persistent Reservations (SCSI3-PR) on a virtual disk level required by Windows Server Failover Cluster (WSFC) to arbitrate an access to a shared disk between nodes. Support of SCSI-3 PRs enables configuration of WSFC with a disk resource shared between VMs natively on vSAN datastores.
Currently the following configurations are supported:
Note: Microsoft SQL Server 2012 or later running on Microsoft Windows Server 2012 or later has been qualified on
vSAN.
|
| vSAN health service | vSAN health service includes preconfigured health check tests to monitor, troubleshoot, diagnose the cause of cluster component problems, and identify any potential risk. |
| vSAN performance service | vSAN performance service includes statistical charts used to monitor IOPS, throughput, latency, and congestion. You can monitor performance of a vSAN cluster, host, disk group, disk, and VMs. |
| Integration with vSphere storage features | vSAN integrates with vSphere data management features traditionally used with VMFS and NFS storage. These features include snapshots, linked clones, and vSphere Replication. |
| Virtual Machine Storage Policies | vSAN works with VM storage policies to support a VM-centric approach to storage management. If you do not assign a storage policy to the virtual machine during deployment, the vSAN Default Storage Policy is automatically assigned to the VM. |
| Rapid provisioning | vSAN enables rapid provisioning of storage in the vCenter Server® during virtual machine creation and deployment operations. |
| Deduplication and compression | vSAN performs block-level deduplication and compression to save storage space. When you enable deduplication and compression on a vSAN all-flash cluster, redundant data within each disk group is reduced. Deduplication and compression is a cluster-wide setting, but the functions are applied on a disk group basis. Compression-only vSAN is applied on a per-disk basis. |
| Data at rest encryption | vSAN provides data at rest encryption. Data is encrypted after all other processing, such as deduplication, is performed. Data at rest encryption protects data on storage devices, in case a device is removed from the cluster. |
| Data in transit encryption | vSAN can encrypt data in transit across hosts in the cluster. When you enable data-in-transit encryption, vSAN encrypts all data and metadata traffic between hosts. |
| SDK support | The VMware vSAN SDK is an extension of the VMware vSphere Management SDK. It includes documentation, libraries and code examples that help developers automate installation, configuration, monitoring, and troubleshooting of vSAN. |
Monitor vSAN in the VMware Host Client
You can use the VMware Host Client to monitor the vSAN environment of your ESXi host.
Prerequisites
vSAN service must be enabled in the vSphere Client before you can view the vSAN related screens for a datastore.
Procedure
Edit Settings for a vSAN Datastore
You can edit the settings for a vSAN datastore when you must exit from a misconfigured state of the current host.
You can only edit the Claiming Mode and Deduplication settings for a vSAN datastore. These changes take effect only on the current host. They are not synced to the other hosts participating into the vSAN cluster.