Learn how to create a distributed switch network for your virtual machines, and to associate VMkernel adapters, and add a distributed port group to a vSphere Distributed Switch.
Procedure
- On the vSphere Client Home page, click Networking and navigate to the distributed switch.
- Right-click the distributed switch and select Distributed port group > New distributed port group.
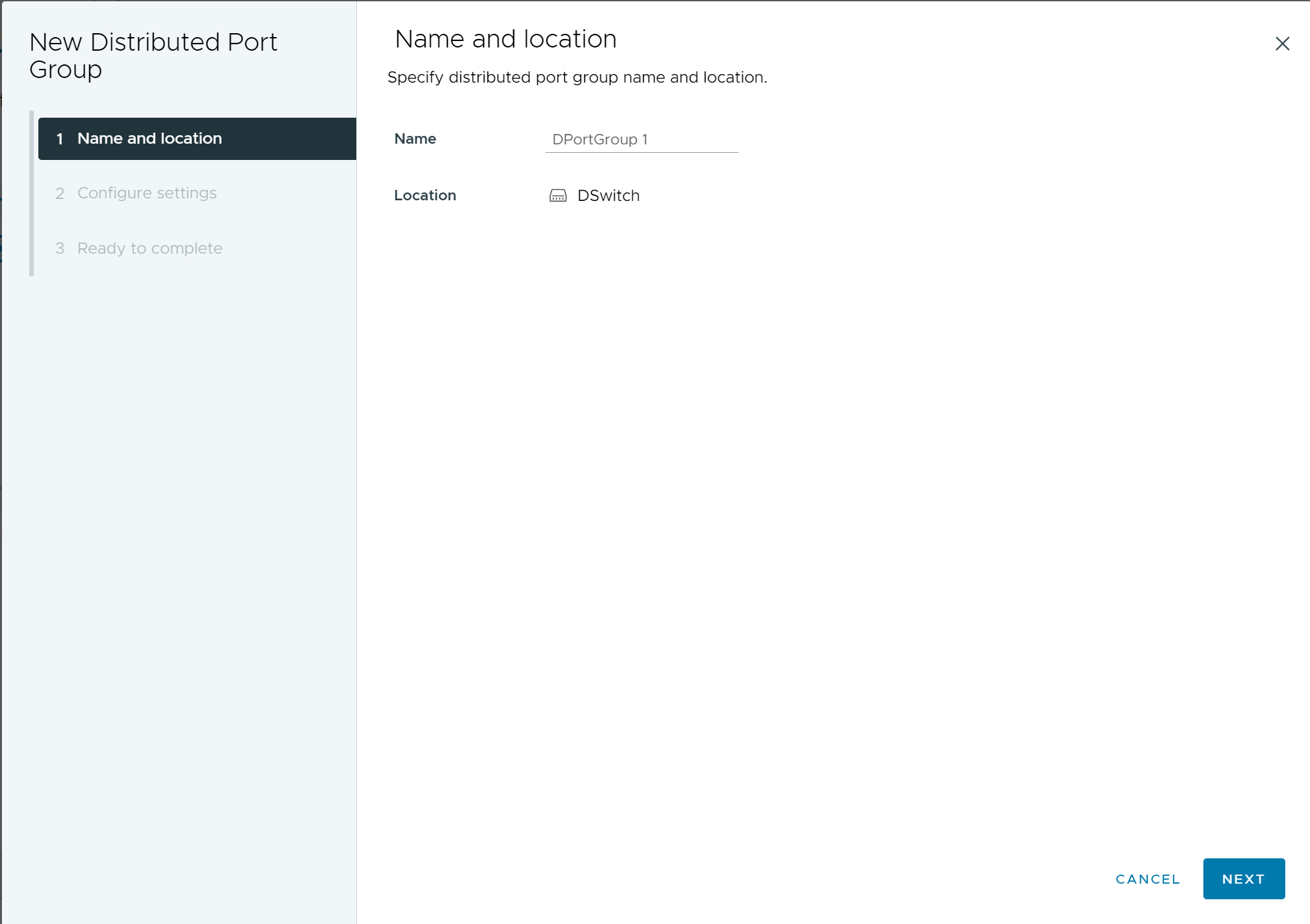
- On the Name and location page, enter the name of the new distributed port group, or accept the generated name, and click Next.
Figure 1. New Distributed Port Group - Name and Location
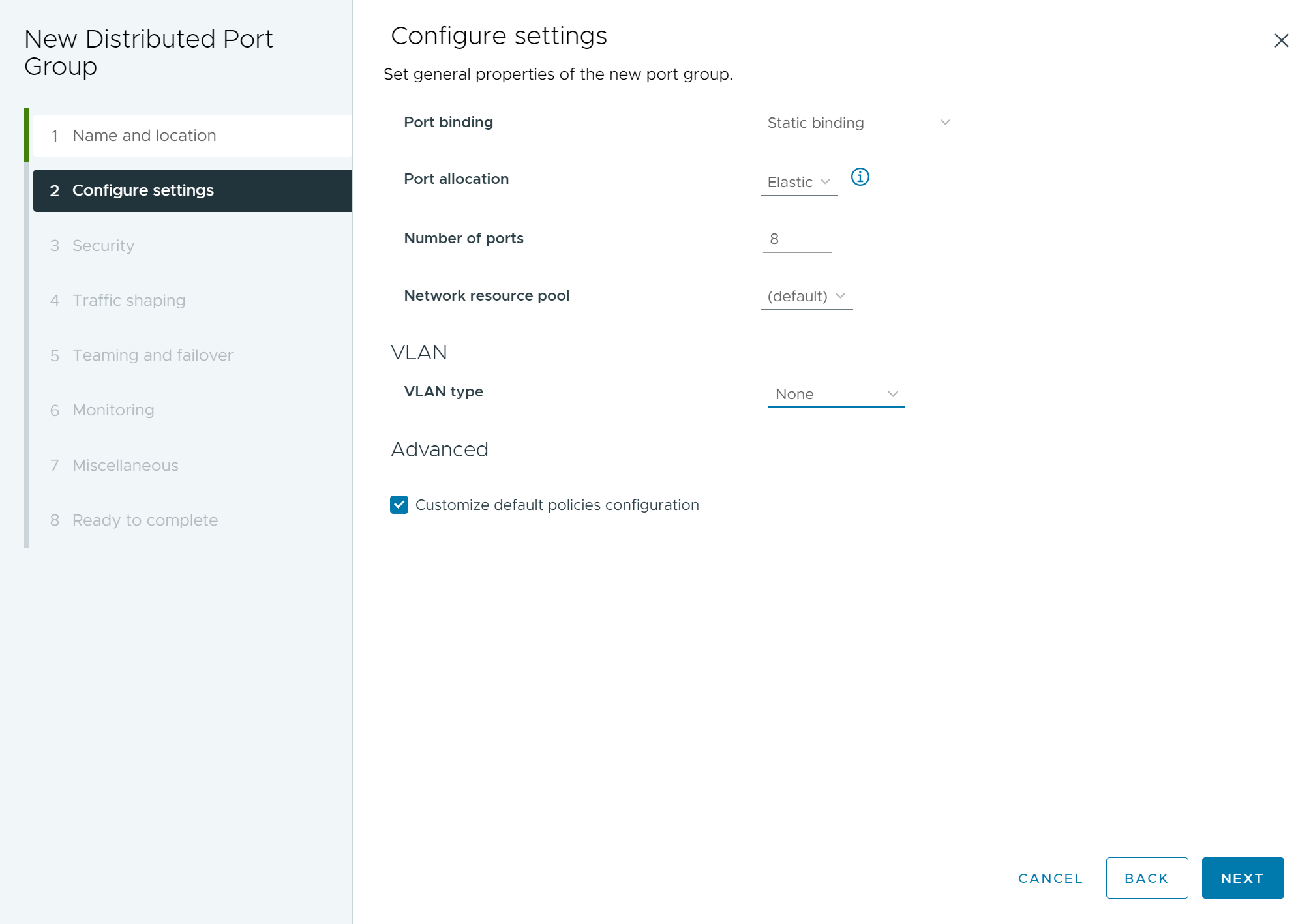
- On the Configure settings page, set the general properties for the new distributed port group.
Setting Description Port binding Select the ports that are assigned to virtual machines connected to this distributed port group.- Static binding: Assign a port to a virtual machine when the virtual machine connects to the distributed port group.
- Ephemeral - no binding: No port binding. You can assign a virtual machine to a distributed port group with ephemeral port binding also when connected to the host.
Port allocation - Elastic: The default number of ports is eight. When all the ports are assigned, a new set of eight ports is created.
- Fixed: The default number of ports is set to eight. When all the ports are assigned, no additional ports are created.
Number of ports Enter the number of ports on the distributed port group. Network resource pool To assign the new distributed port group to a user-defined network resource pool, use the drop-down menu If you have not created a network resource pool, this menu is empty. Note: You cannot assign Network Resource Pool if Network Offloads is enabled.VLAN Use the VLAN type drop-down menu to specify the type of VLAN traffic filtering and marking:- None: Do not use VLAN. Select None if you are using External Switch Tagging.
- VLAN: In the VLAN ID text box, enter a number between 1 and 4094 for Virtual Switch Tagging.
- VLAN trunking: Enter a VLAN trunk range.
Pass VLAN traffic with an ID to the guest OS. You can set multiple ranges and individual VLANs by using a comma-separated list. For example: 1702-1705, 1848-1849
Use this option for Virtual Guest Tagging.
- Private VLAN: Associate the traffic with a private VLAN created on the distributed switch. If you did not create any private VLANs, this menu is empty.
Advanced To customize the policy configurations for the new distributed port group, select this check box. Figure 2. New Distributed Port Group - Configure settings
- Click Next.
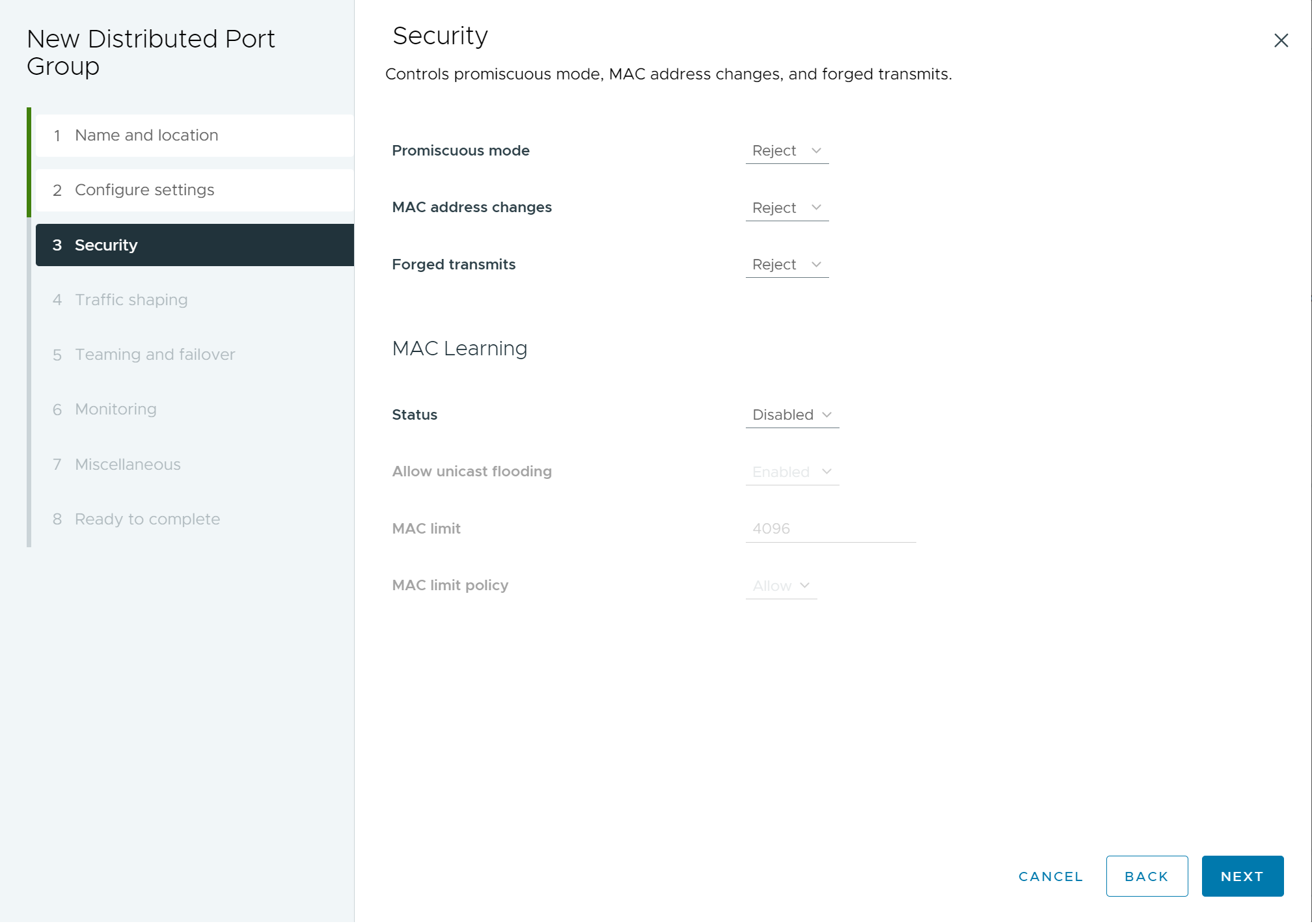
- (Optional) On the Security page, edit the security exceptions and click Next.
Setting Description Promiscuous mode - Reject: Placing an adapter in promiscuous mode from the guest operating system does not result in receiving frames for other virtual machines.
- Accept: If an adapter is placed in promiscuous mode from the guest operating system, the switch allows the guest adapter to receive all frames passed on the switch in compliance with the active VLAN policy for the port where the adapter is connected.
Firewalls, port scanners, intrusion detection systems, and so on, must run in promiscuous mode.
MAC address changes The MAC address change feature allows a VM to change its MAC address. A VM connected to a port can run an administrative command to change the MAC address of its vNIC and still send and receive traffic on that vNIC.
- Reject: If the option is set to Reject and the guest OS changes the MAC address of the adapter to a value different from the address in the .vmx configuration file, then the switch drops all inbound frames to the virtual machine adapter.
If the guest OS changes the MAC address back, the virtual machine receives frames again.
- Accept: If the guest OS changes the MAC address of a network adapter, the adapter receives frames to its new address.
Forged Transmits - Reject: The switch drops any outbound frame with a source MAC address that is different from the one in the .vmx configuration file.
- Accept: The switch does not perform filtering and permits all outbound frames.
Figure 3. New Distributed Port Group - Security
- (Optional) On the Security page, edit the MAC Learning policy and click Next.
Setting Description Status Enable or disable the MAC learning feature. The default is disabled. Allow unicast flooding When a packet that is received by a port has an unknown destination MAC address, the packet is dropped. With unknown unicast flooding enabled, the port floods unknown unicast traffic to every port on the switch that has MAC learning and unknown unicast flooding enabled. This property is enabled by default, if MAC learning is enabled. MAC Limit The number of MAC addresses that can be learned is configurable. The maximum value is 4096 per port, which is the default. MAC Limit Policy The policy for when the MAC limit is reached. The options are: - Drop - Packets from an unknown source MAC address are dropped. Packets inbound to this MAC address will be treated as unknown unicast. The port will receive the packets only if it has unknown unicast flooding enabled.
- Allow - Packets from an unknown source MAC address are forwarded although the address will not be learned. Packets inbound to this MAC address will be treated as unknown unicast. The port will receive the packets only if it has unknown unicast flooding enabled.
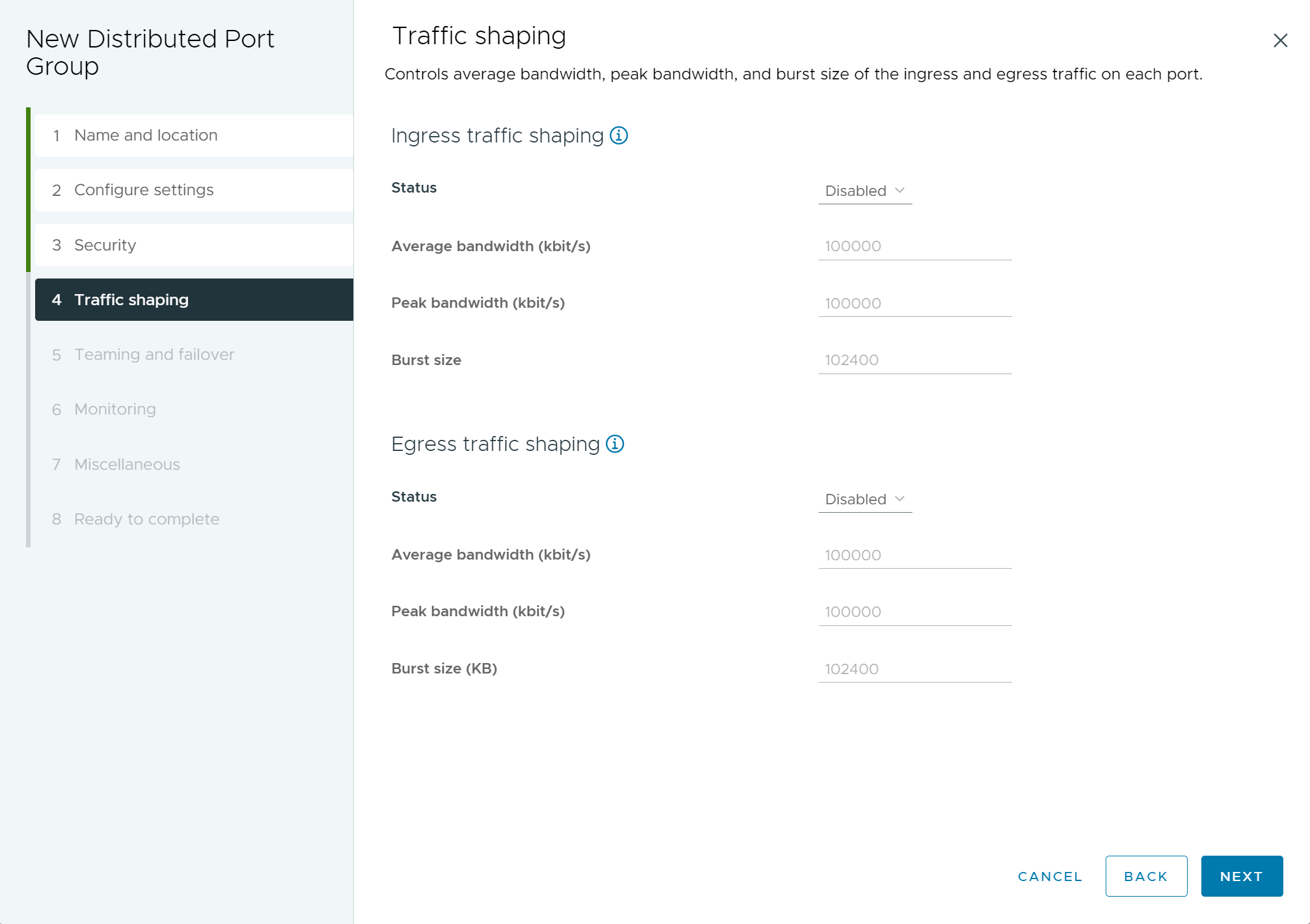
- (Optional) On the Traffic shaping page, enable or disable Ingress or Egress traffic shaping and click Next.
Setting Description Status If you enable either Ingress traffic shaping or Egress traffic shaping, you are setting limits on the amount of networking bandwidth allocated for each virtual adapter associated with this particular port group. If you disable the policy, services have a free, clear connection to the physical network by default. Note: You cannot assign traffic shaping policies if Network Offloads Compatibility enabled.Average bandwidth This feature establishes the number of bits per second to allow across a port, averaged over time. It is the allowed average load. Peak bandwidth The maximum number of bits per second to allow across a port when it is sending and receiving a burst of traffic. It tops the bandwidth used by a port whenever it is using its burst bonus. Burst size The maximum number of bytes to allow in a burst. If this parameter is set, a port can gain a burst bonus when it does not use all its allocated bandwidth. Whenever the port needs more bandwidth than specified by Average bandwidth, it can temporarily transmit data at a faster speed if a burst bonus is available. This parameter tops the number of bytes that can be accumulated in the burst bonus and as a result transferred at a faster speed. Figure 4. New Distributed Port Group - Traffic shaping
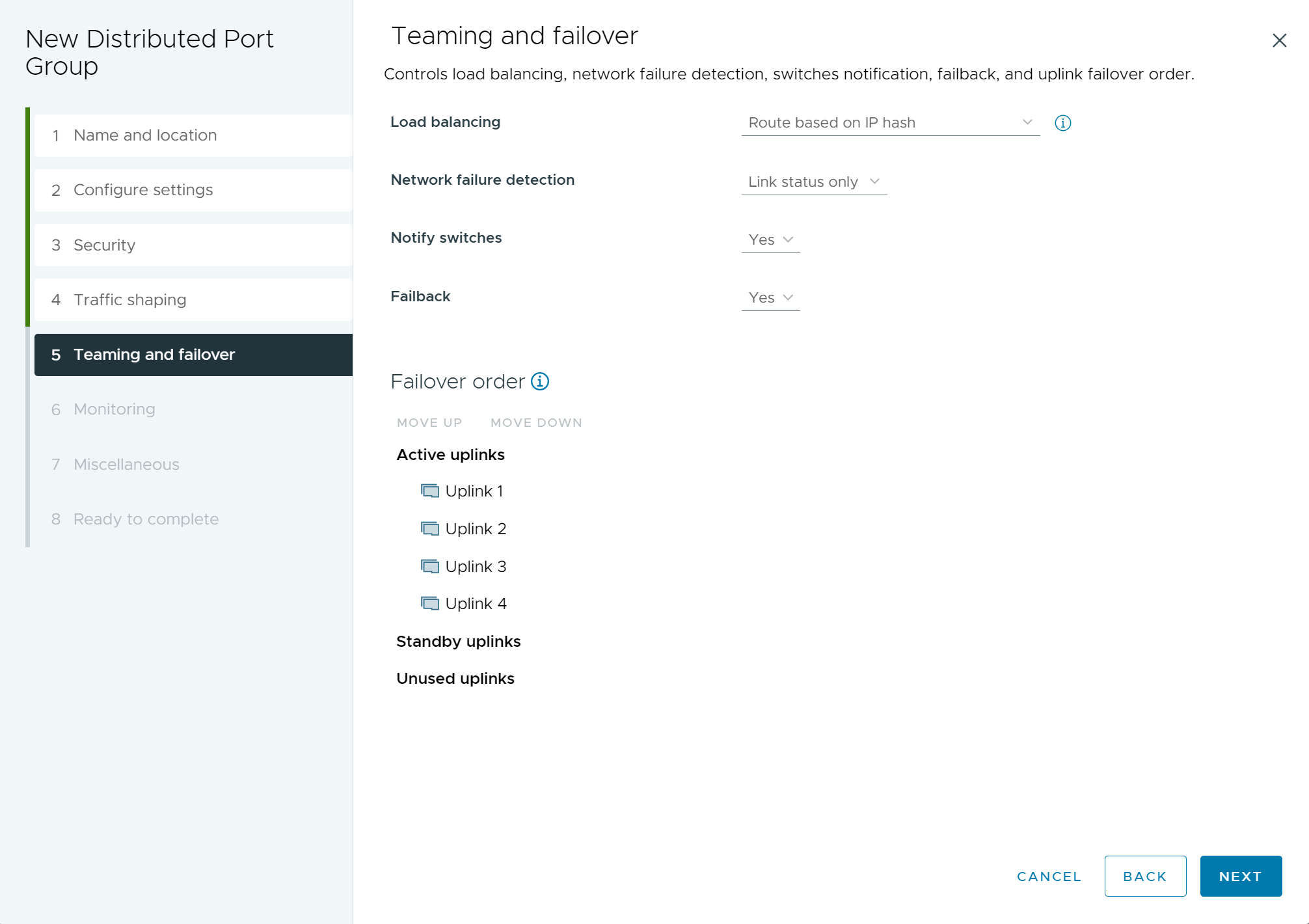
- (Optional) On the Teaming and failover page, edit the settings and click Next.
Setting Description Load balancing Specify the way an uplink is selected. - Route based on originating virtual port: Select an uplink based on the virtual port where the traffic entered the distributed switch.
- Route based on IP hash: Select an uplink based on a hash of the source and destination IP addresses of each packet. For non-IP packets, whatever is at those offsets is used to compute the hash.
- Route based on source MAC hash: Select an uplink based on a hash of the source Ethernet.
- Route based on physical NIC load: Select an uplink based on the current loads of physical NICs.
- Use explicit failover order: Always use the highest order uplink from the list of Active adapters which passes failover detection criteria.
Note: IP-based teaming requires that the physical switch is configured with EtherChannel. For all other options, disable EtherChannel.Network failure detection Specify the method to use for failover detection. - Link status only: Relies solely on the link status that the network adapter provides. This option detects failures, such as cable pulls and physical switch power failures, but not configuration errors, such as a physical switch port being blocked by spanning tree or that is misconfigured to the wrong VLAN or cable pulls on the other side of a physical switch.
- Beacon probing: Sends out and listens for beacon probes on all NICs in the team and uses this information, in addition to link status, to determine link failure. This detects many of the failures previously mentioned that are not detected by link status alone.
Note: Do not use beacon probing with IP-hash load-balancing.Notify switches Select Yes or No to notify switches in case of failover. If you select Yes, whenever a virtual NIC is connected to the distributed switch or whenever that virtual NIC’s traffic can be routed over a different physical NIC in the team because of a failover event, a notification is sent out over the network to update the lookup tables on physical switches. In almost all cases, this process is desirable for the lowest latency of failover occurrences and migrations with vMotion.
If the Notify switches is set to Yes, then all the connected ports, port groups, and distributed switches are connected back to the host when vCenter Server reconnects with ESXi hosts.
Note: Do not use this option when the virtual machines using the port group are using Microsoft Network Load Balancing in unicast mode. No such issue exists with NLB running in multicast mode.Failback Select Yes or No to disable or enable failback. This option determines how a physical adapter is returned to active duty after recovering from a failure. If failback is set to Yes (default), the adapter is returned to active duty immediately upon recovery, displacing the standby adapter that took over its slot, if any. If failback is set to No, a failed adapter is left inactive even after recovery until another currently active adapter fails, requiring its replacement.
Failover order Specify how to distribute the workload for uplinks. To use some uplinks but reserve others for emergencies if the uplinks in use fail, set this condition by moving them into different groups: - Active uplinks: Continue to use the uplink when the network adapter connectivity is up and active.
- Standby uplinks : Use this uplink if one of the active adapters' connectivity is down.
- Unused uplinks : Do not use this uplink.
Note: When using IP-hash load-balancing, do not configure standby uplinks.Figure 5. New Distributed Port Group - Teaming and failover
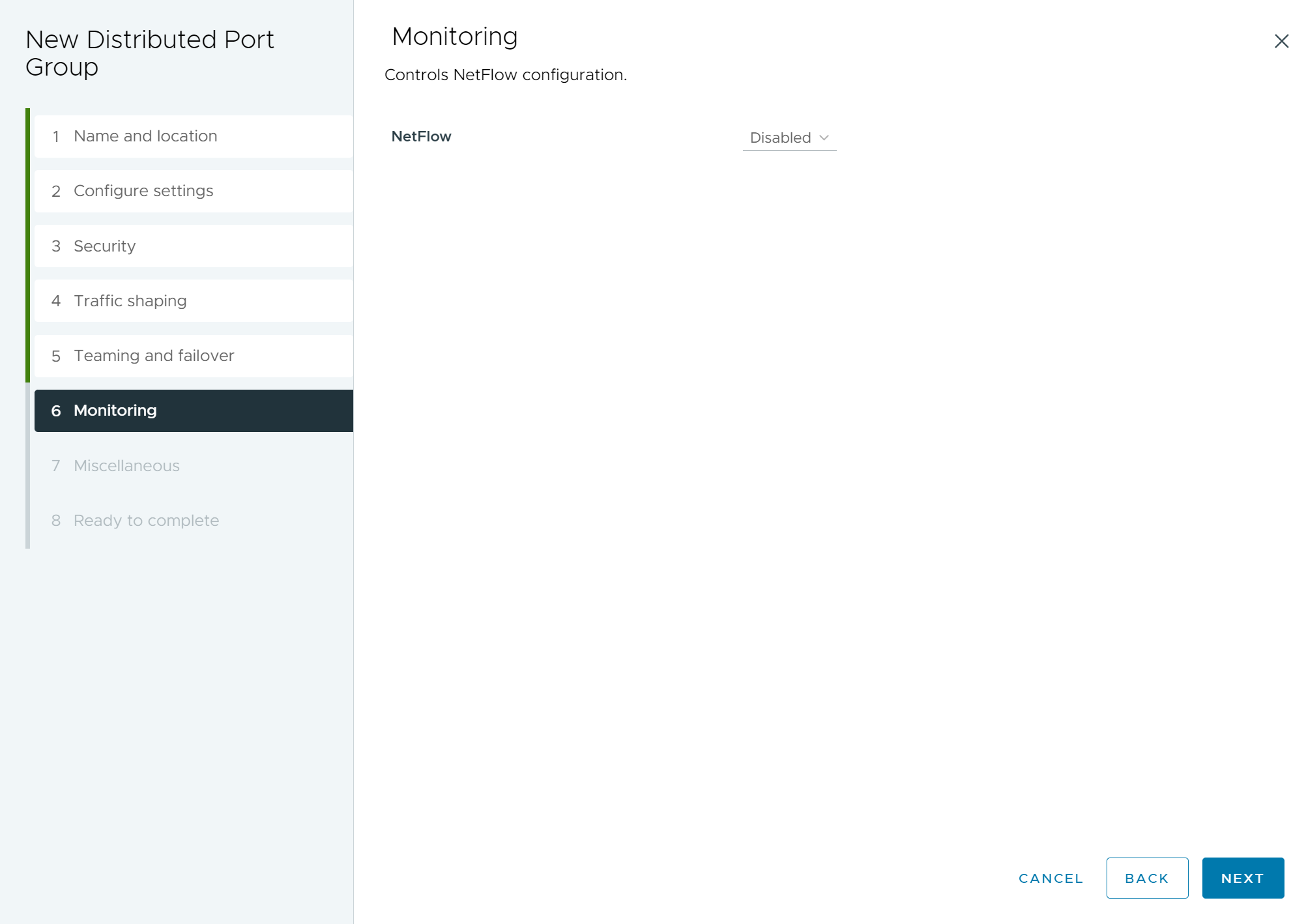
- (Optional) On the Monitoring page, enable or disable NetFlow and click Next.
Setting Description Disabled NetFlow is disabled on the distributed port group. Enabled NetFlow is enabled on the distributed port group. NetFlow settings can be configured at the vSphere Distributed Switch level. Figure 6. New Distributed Port Group - Monitoring
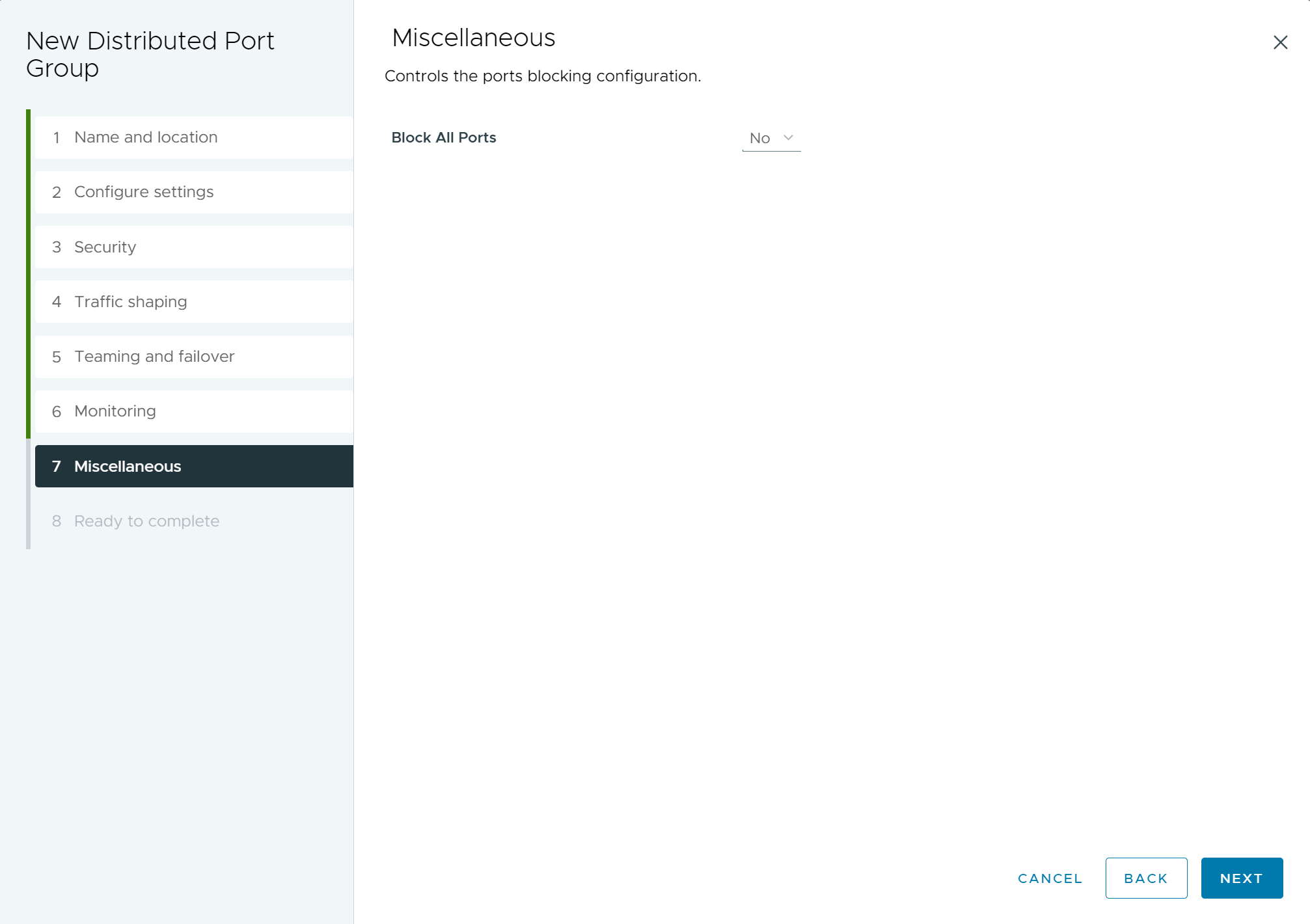
- (Optional) On the Miscellaneous page, select Yes or No and click Next.
Selecting Yes shuts down all ports in the port group. This action can disrupt the normal network operations of the hosts or virtual machines using the ports.
Figure 7. New Distributed Port Group - Miscellaneous
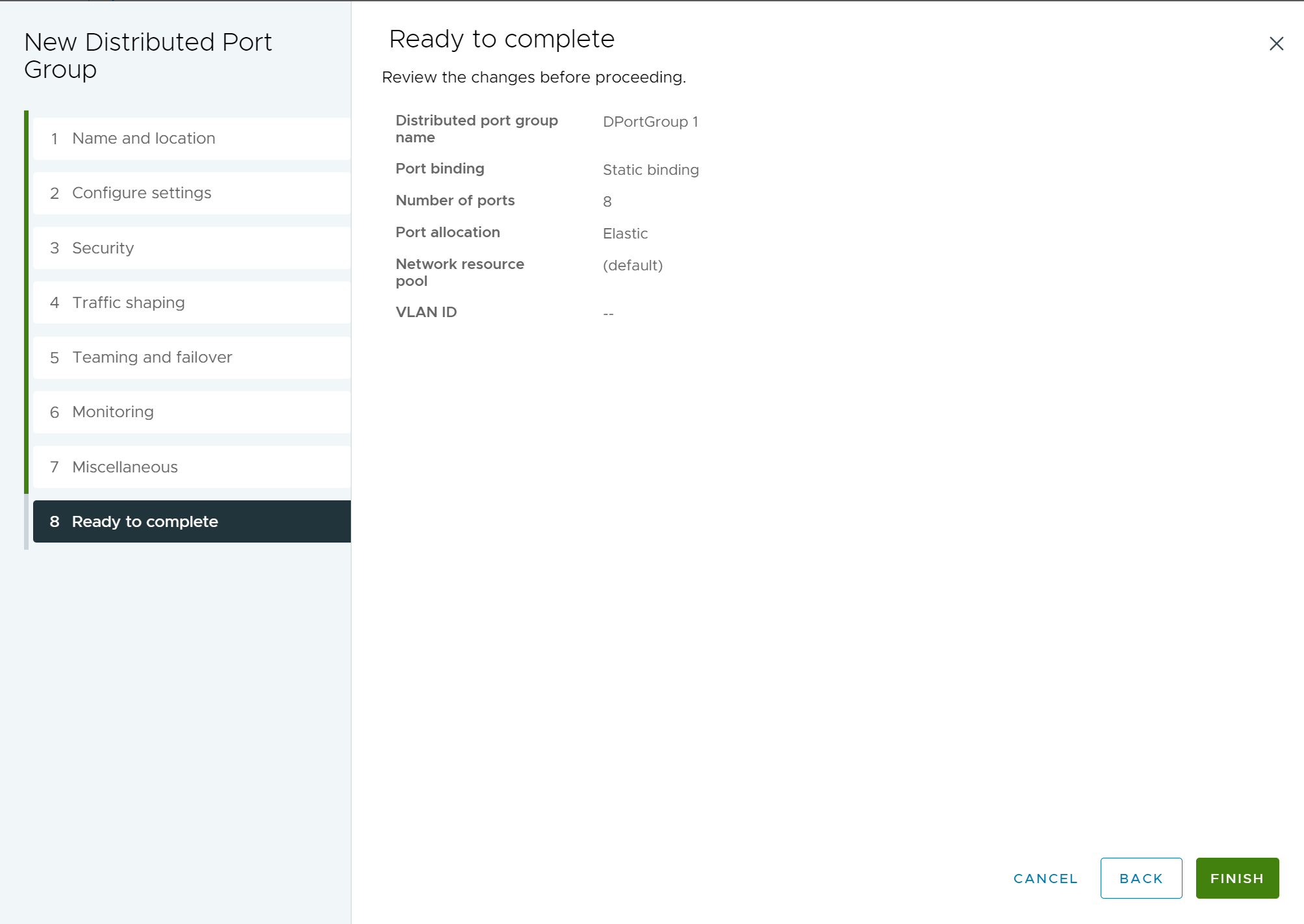
- On the Ready to complete page, review your settings and click Finish.
To change any settings, click the Back button.
Figure 8. New Distributed Port Group - Ready to complete