The network can be one of the most vulnerable parts of any system. Your virtual machine network requires as much protection as your physical network. Using VLANs can improve networking security in your environment.
VLANs are an IEEE standard networking scheme with specific tagging methods that allow routing of packets to only those ports that are part of the VLAN. When properly configured, VLANs provide a dependable means for you to protect a set of virtual machines from accidental or malicious intrusions.
VLANs let you segment a physical network so that two machines in the network are unable to transmit packets back and forth unless they are part of the same VLAN. For example, accounting records and transactions are among a company’s most sensitive internal information. In a company whose sales, shipping, and accounting employees all use virtual machines in the same physical network, you might protect the virtual machines for the accounting department by setting up VLANs.
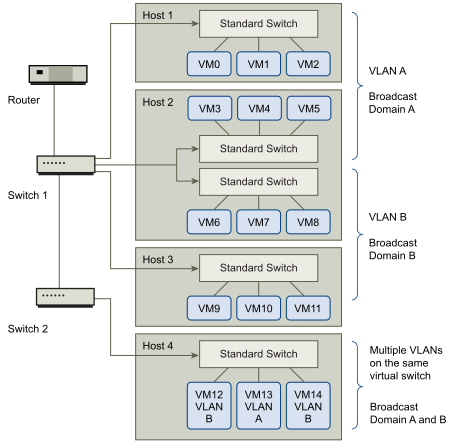
In this configuration, all employees in the accounting department use virtual machines in VLAN A and the employees in sales use virtual machines in VLAN B.
The router forwards packets containing accounting data to the switches. These packets are tagged for distribution to VLAN A only. Therefore, the data is confined to Broadcast Domain A and cannot be routed to Broadcast Domain B unless the router is configured to do so.
This VLAN configuration prevents the sales force from intercepting packets destined for the accounting department. It also prevents the accounting department from receiving packets intended for the sales group. The virtual machines serviced by a single virtual switch can be in different VLANs.
Security Considerations for VLANs
The way you set up VLANs to secure parts of a network depends on factors such as the guest operating system and the way your network equipment is configured.
ESXi features a complete IEEE 802.1q-compliant VLAN implementation. VMware cannot make specific recommendations on how to set up VLANs, but there are factors to consider when using a VLAN deployment as part of your security enforcement policy.
Secure VLANs
Administrators have several options for securing the VLANs in their vSphere environment.