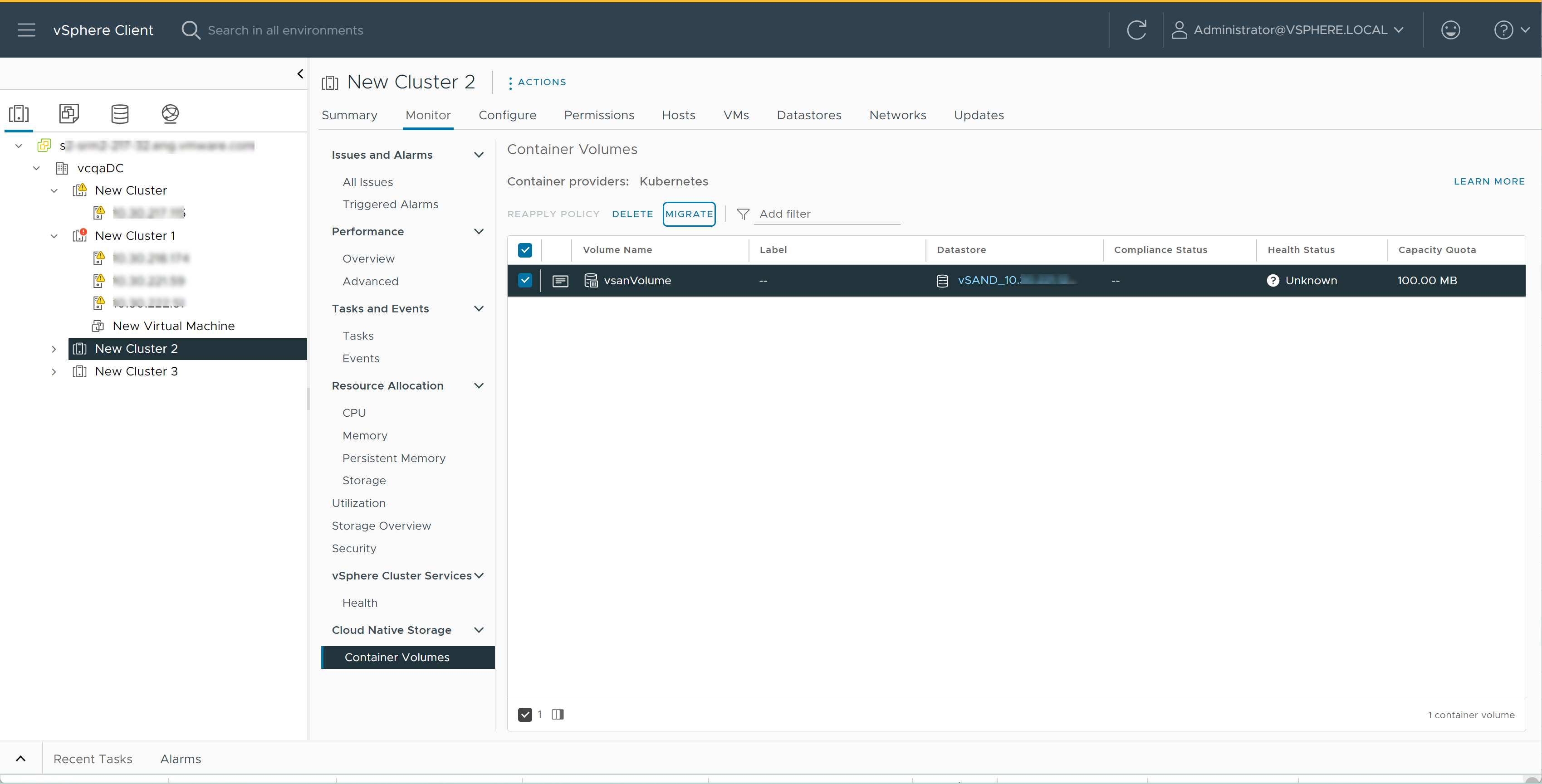
vSphere Cloud Native Storage supports migration of persistent container volumes between datastores.
Considerations and Limitations
When you perform the migration, keep in mind the following considerations:
- You can migrate only single block volumes.
- Make sure that original and target datastores are accessible to all nodes of the Kubernetes cluster. This applies to single zone deployments and to Kubernetes clusters deployed across multiple zones.
- If a volume is attached to a VM, the VM remains locked during volume relocation. If the volume you relocate is attached to a Kubernetes node VM, the system does not allow any other control operations on the VM. The operations include attaching or detaching other volumes to the VM, migrating the VM to a different datastore, changing any configuration of the VM, and so on.
- Cloud Native Storage does not support PMEM storage. Attempts to relocate a volume to a PMEM datastore fail.
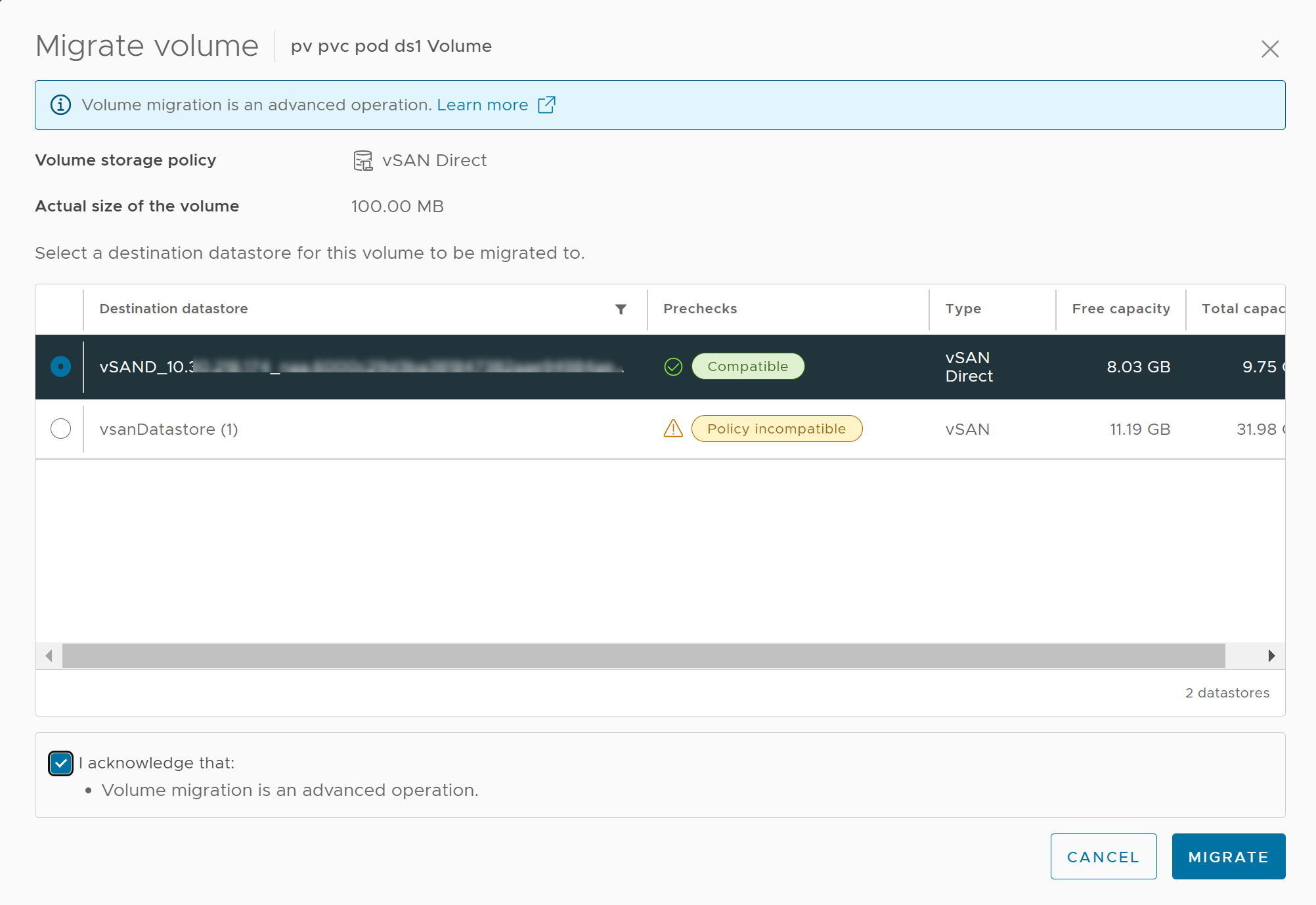
- The target datastore must have sufficient free capacity to accommodate the migrated volume. If the free space of a datastore is less than the volume size, you cannot select the datastore for migration.
- The vSphere Client does not support automatic storage policy changes during the migration operation. However, the system doesn’t prevent you from selecting a datastore with incompatible policy as a target datastore for migration.
- After the migration, you can locate the virtual disk that backs the volume in one of the following folders on a target datastore:
- FCD directory on the datastore.
- VM folder if the volume is attached to a VM.
For additional details, see the VMware Knowledge Base article 90607.
Migrate Container Volumes
You can use the vSphere Client to migrate the persistent container volumes.
Prerequisites
- Make sure that the target datastore has sufficient free capacity to accommodate the migrated volume.
- Make sure you have permissions for the target datastore.