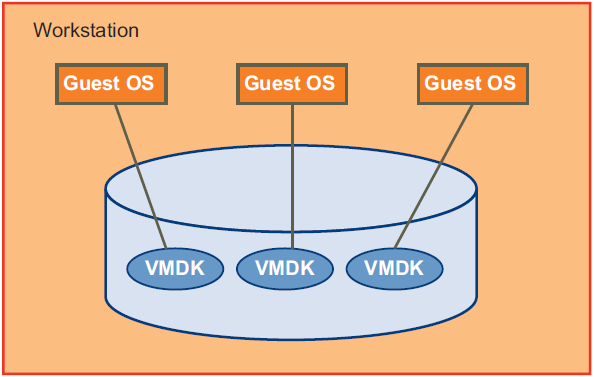
Analogous to a hard disk drive, virtual disk files represent the storage volumes of a virtual machine. Each is named with .vmdk suffix. On a system running VMware Workstation, file systems of each guest OS are kept in VMDK files hosted on the system’s physical disk. VMDK files can be accessed directly on the host.
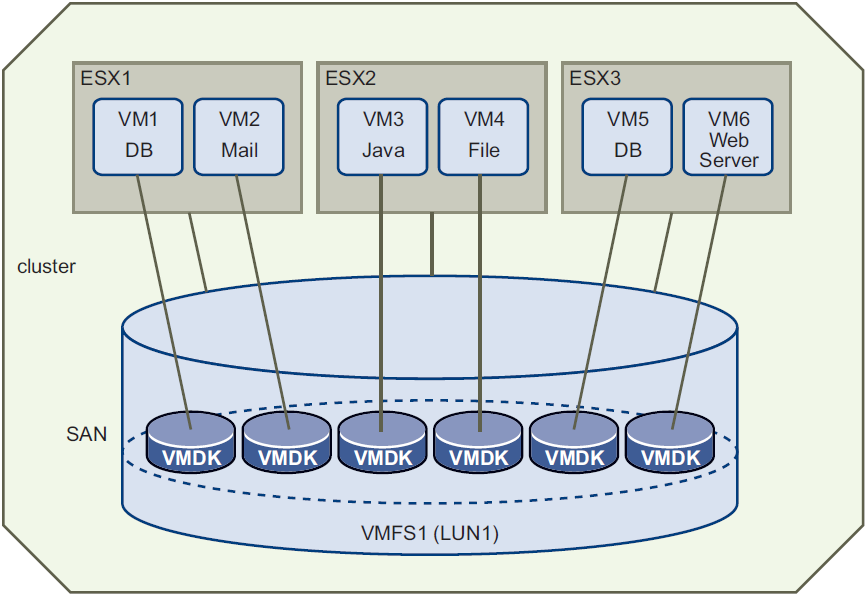
With the virtual machine file system (VMFS) on ESXi hosts, VMDK files again represent storage volumes of virtual machines. They are on VMFS, which often resides on shared storage in a cluster. The vCenter Server manages the cluster storage so it can migrate (vMotion) virtual machines from one ESXi host to another without moving VMDK files. VMFS storage is therefore called managed disk.
VMFS disk can reside on a storage area network (SAN) attached to ESXi hosts by Fibre Channel, iSCSI, or SAS connectors. It can also reside on network attached storage (NAS), or on directly attached disk.
Managed Disk on vSphere depicts the arrangement of managed disk, as VMDK files in a SAN based cluster. Hosted Disk on Workstation depicts hosted disk on VMware Workstation, as VMDK files on physical disk.
The VDDK supports both managed disk and hosted disk. Some functions are not supported for managed disk, and others are not supported for hosted disk, as noted in documentation. Managed virtual disk files larger than 2TB are supported by vSphere 5.5 and later.