HotAdd is a VMware feature where devices can be added “hot” while a virtual machine is running. Besides SCSI disk, virtual machines can add additional CPUs and memory capacity.
HotAdd is a good way to get virtual disk data from a virtual machine to a backup appliance (or backup proxy) for sending to the media server. The attached HotAdd disk is shown in the figure below.
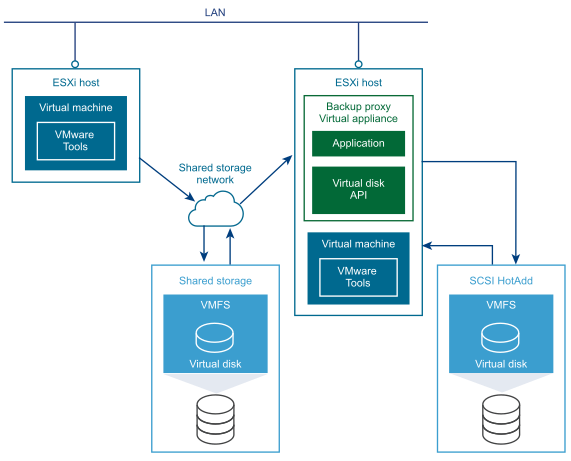
Running the backup proxy as a virtual machine has two advantages: it is easy to move a virtual machine to a new media server, and it can back up local storage without using the LAN, although this incurs more overhead on the physical ESXi host than when using SAN transport mode.
If backup software runs in a virtual appliance, it can take a snapshot and create a linked clone of the target virtual machine, then attach and read the linked clone’s virtual disks for backup. This involves a SCSI HotAdd on the ESXi host where the target VM and backup proxy are running. Virtual disks of the linked clone are HotAdded to the backup proxy. The target virtual machine continues to run during backup.
VixTransport handles the temporary linked clone and hot attachment of virtual disks. VixDiskLib opens and reads the HotAdded disks as a “whole disk” VMDK (virtual disk on the local host). This strategy works only on virtual machines with SCSI disks and is not supported for backing up virtual IDE disks. HotAdd transport also works with virtual machines stored on NFS partitions.