After NSX-T migration from NSX Virtual Distributed Switch (N-VDS) to converged VDS (C-VDS), you must update impacted vSphere network resources in vRealize Automation to continue using those resources in new and existing cloud templates and deployments.
After N-VDS to C-VDS migration, your vSphere networks may appear to be missing from vRealize Automation network profiles in which they are members. To avoid losing these vSphere type networks, and continue to allocate them in existing and new deployments, you must manually update all listed C-VDS networks in vRealize Automation Cloud Assembly.
- Active Directory members who are assigned the Cloudadmin role in VMware Cloud on AWS prior to the N-VDS to C-VDS migration in NSX-T have the Cloudadmin role in VMware Cloud on AWS after N-VDS to C-VDS migration, and thus have the required access level to migrated C-VDS resources.
- Active Directory members who are not assigned the Cloudadmin role in VMware Cloud on AWS before N-VDS to C-VDS migration in NSX-T must be assigned the Cloudadmin role after the migration.
- For related information about VMware Cloud on AWS and vRealize Automation credentials, see Credentials required for working with cloud accounts in vRealize Automation.
This procedure is specific to actions needed in vRealize Automation to update vSphere networks after N-VDS to C-VDS migration has been performed in NSX-T. There is no action needed in vRealize Automation on NSX networks after N-VDS to C-VDS migration; NSX networks require no manual intervention after N-VDS to C-VDS migration.
NSX networks that are attached to vCenter cloud accounts, as well as to VMware Cloud on AWS cloud accounts, are supported and do not require the manual intervention described in this procedure. However, NSX networks that are attached to VMware Cloud on Dell cloud accounts may require the manual intervention described here. For related information, see VMware Cloud on AWS (VMConAWS) and VMware Cloud on Dell EMC Migration from N-VDS to VDS (82487).
While an NSX-T administrator can migrate NSX-T on VDS (N-VDS) network types to converged VDS (C-VDS) network types in NSX, this action impacts existing vSphere network resources in vRealize Automation. The vRealize Automation administrator can perform post-migration actions to reconcile those resources in vRealize Automation with the associated changes in NSX-T and vCenter Server. Note that C-VDS, or simply VDS, is also referred to elsewhere as vSphere 7 Virtual Distributed Switch (VDS).
For related information about NSX-T converged VDS (C-VDS), see VMware Knowledge Base article NSX-T on VDS (79872).
Example: vRealize Automation resources pre-migration
This example illustrates sample NSX-T resources in a sample vRealize Automation environment prior to N-VDS to C-VDS migration.
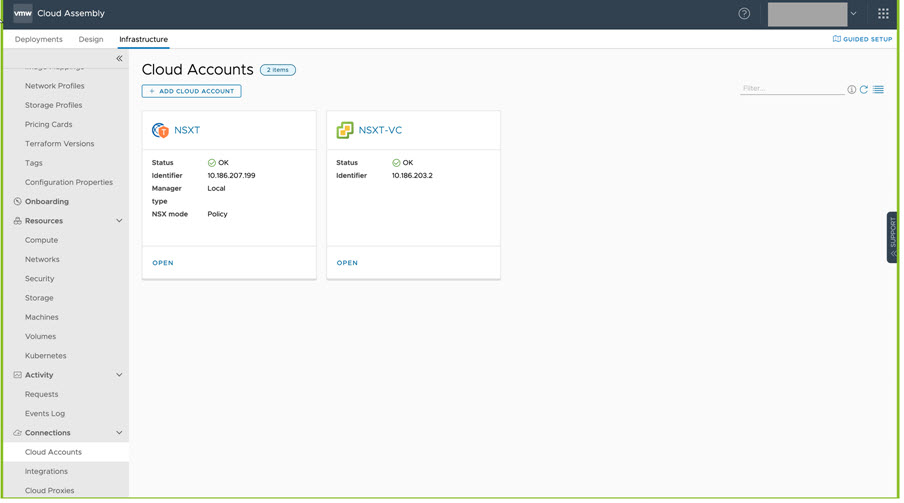
- This example contains NSX-T and vCenter cloud accounts, as shown below.
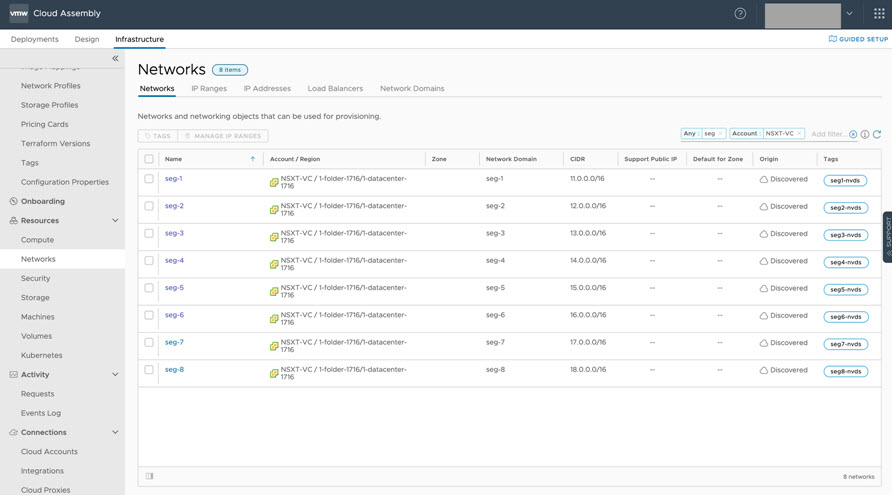
- The example contains several vSphere networks, as shown below.
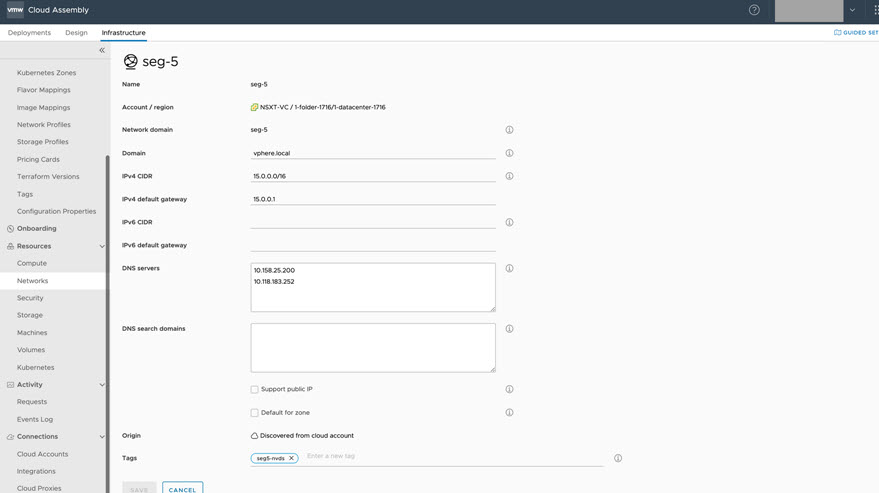
- The example network configuration contains CIDR and DNS settings, as shown below.
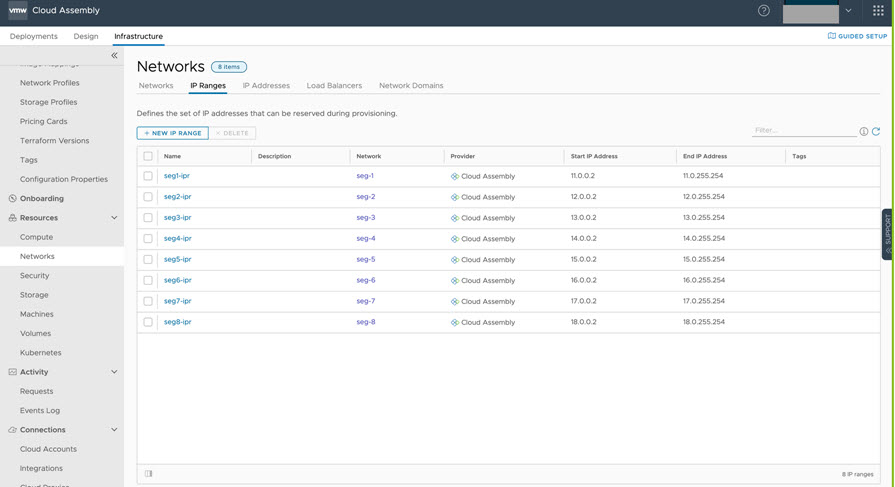
- The example also includes existing IP ranges, as shown below.
- The example contains a network profile () which contains several N-VDS (N-VDS) networks, including , as shown below.
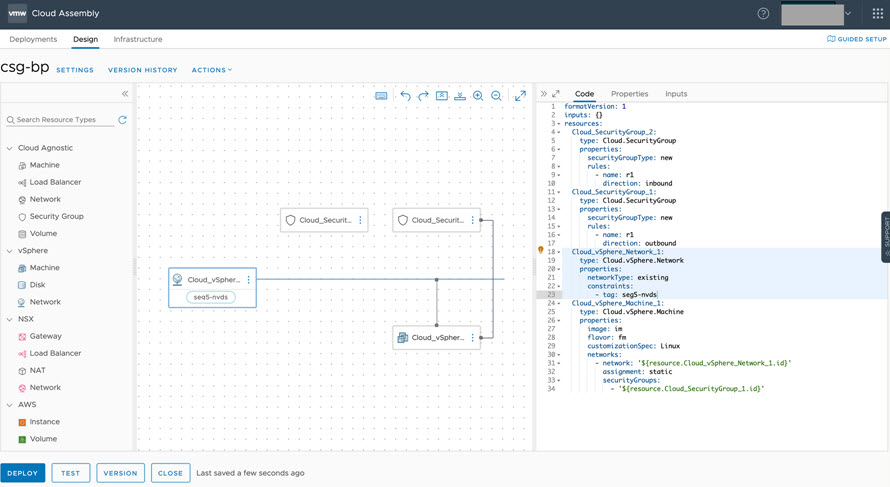
- In this example, the existing seg5 network component is shown in the following sample cloud template syntax. The network is tagged as an N-VDS network. We will illustrate needed post-migration updates to the seg5 network later in this example.
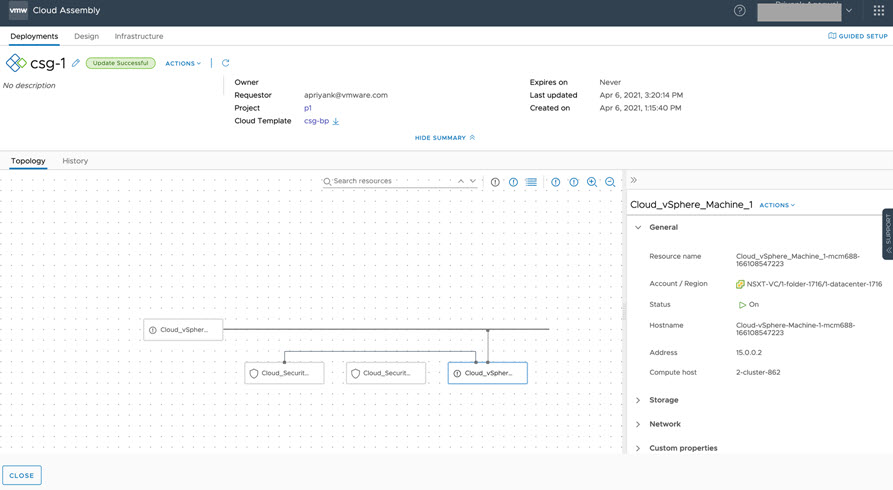
- The example cloud template generates the deployment, as shown below.
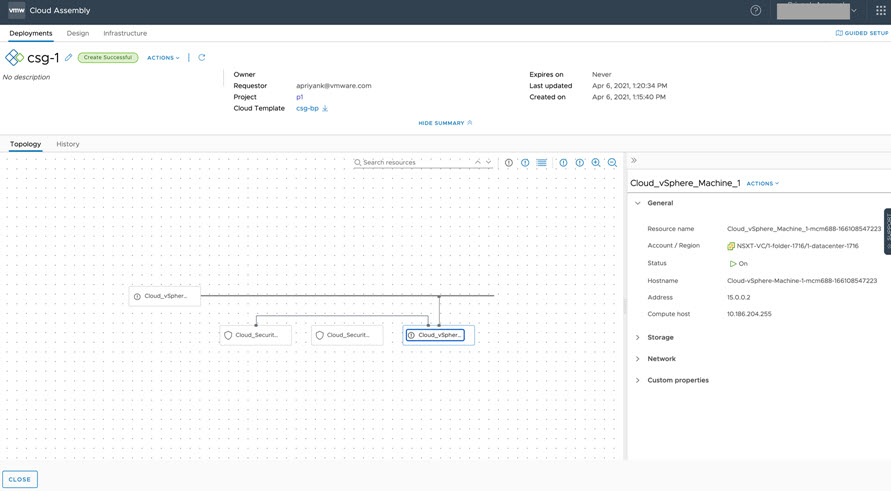
- The example machine IP addresses are displayed in the sample deployment, as shown below.
Example: Post-migration Step 1 – Run data collection after N-VDS to C-VDS migration and enumeration
In the above section, screen shots were used to illustrate the infrastructure used in an example vRealize Automation environment, concluding with the output cloud template and deployment.
After you or another administrator perform N-VDS to C-VDS migration in NSX-T, wait at least 10 minutes to allow vRealize Automation to perform its periodic data collection and enumeration process to fetch and display impacted resources in vRealize Automation.
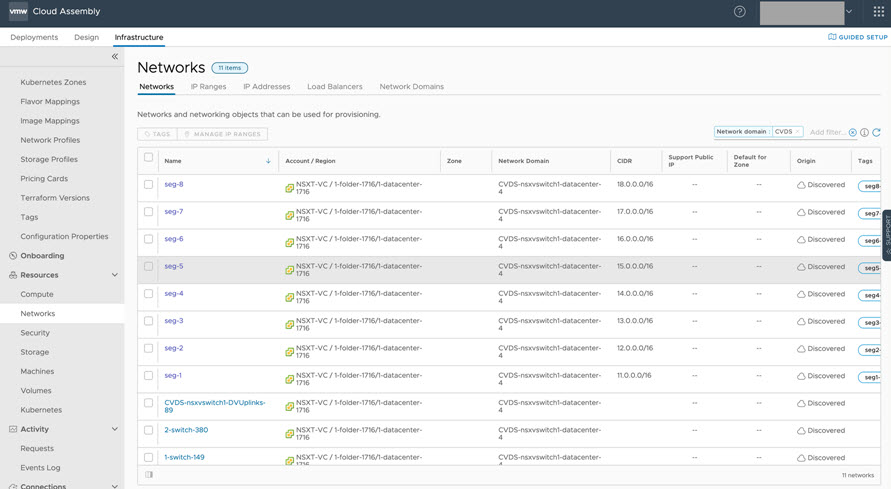
After allowing vRealize Automation data collection to complete, click to view and access available C-VDS networks. Notice the seg5 network, as shown below.
Example: Post-migration Step 2 – Add previously defined CIDR and DNS to migrated C-VDS networks
Edit a migrated C-VDS network to add CIDR and DNS details that had been specified in the pre-migration N-VDS definition and change the network tagging.
- Add CIDR and DNS details that had been defined in its pre-migration N-VDS definition
- Add a new tag for the sample C-VDS seg-5 network segment, such as seg5-cvds.
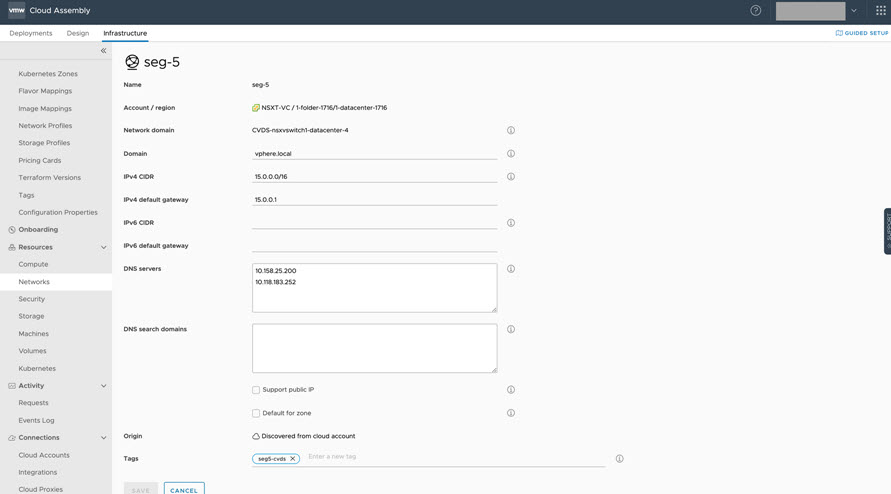
Note that the original N-VDS seg-5 network was tagged as seg5-nvds, as seen in earlier screens. The change in resource tagging details is required by network reconfiguration. vRealize Automation requires that you include a different tag name in the cloud template for the C-VDS network than the tag used in the original N-VDS network. The changed tagging identifies a change in the cloud template when generating a valid redeployment.
Example: Post-migration Step 3 – Add updated IP range information
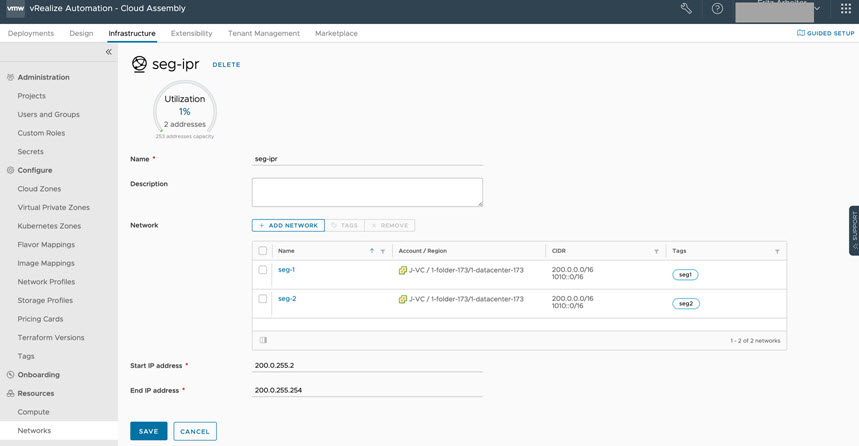
You can edit network IP ranges to IP range details that had been specified in the pre-migration N-VDS definition, by using a command line API or by using a menu sequence in vRealize Automation.
- Option 1: Use the API to update IP range data, as shown in the following sample screen.

- Option 2: Use the user interface to update IP range data, as shown in the following sample screen.
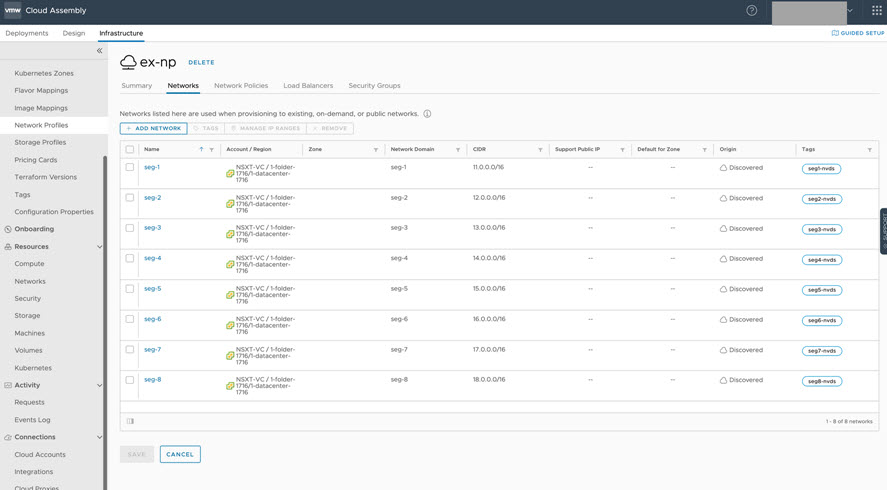
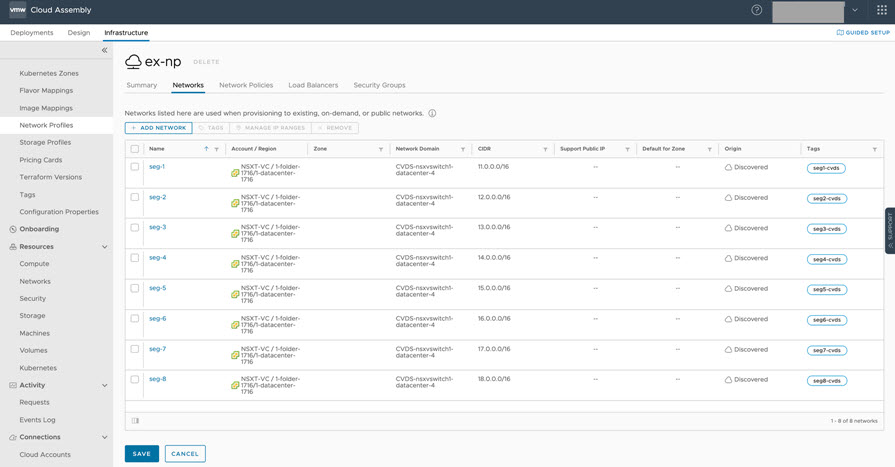
Example: Post-migration Step 4 – Update network profiles to correct missing networks
Post-migration, N-VDS networks are reconciled and deleted from vRealize Automation Cloud Assembly after data collection and enumeration. Impacted network profiles (such as the example ex-np) have missing networks. To correct the missing networks issue, update each N-VDS network as a C-VDS network, as shown below.
Example: Post-migration Step 5 – Update network constraints in cloud templates
For existing deployments, you must update network constraints in cloud template to match the new C-VDS networks in the updated network profiles. Updated network constraints are also needed to perform iterative deployments and to reconfigure networks from their original vSphere N-VDS representation to vSphere C-VDS representation.
For new deployments, the specified C-VDS resources are used, thus this step is not required. Iterative deployments and network reconfiguration simply work as designed.
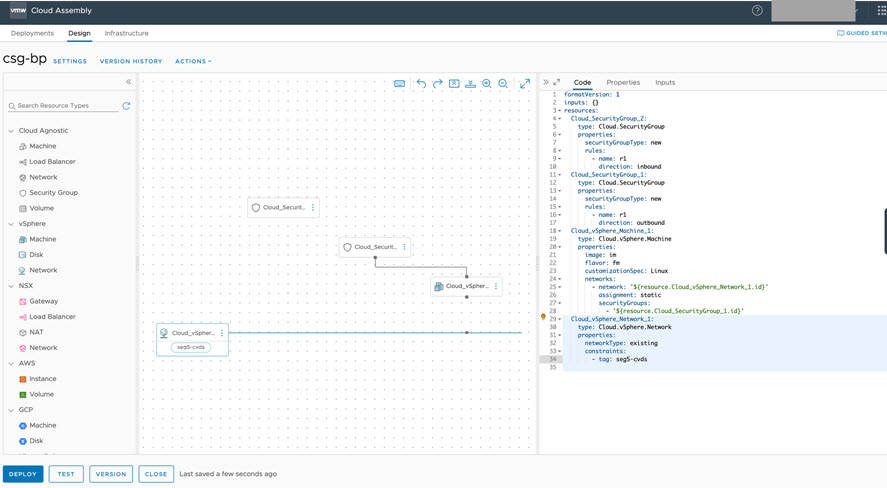
- For this example, change network constraints in the cloud template from seg5-nvds to seg5-cvds, as shown below.
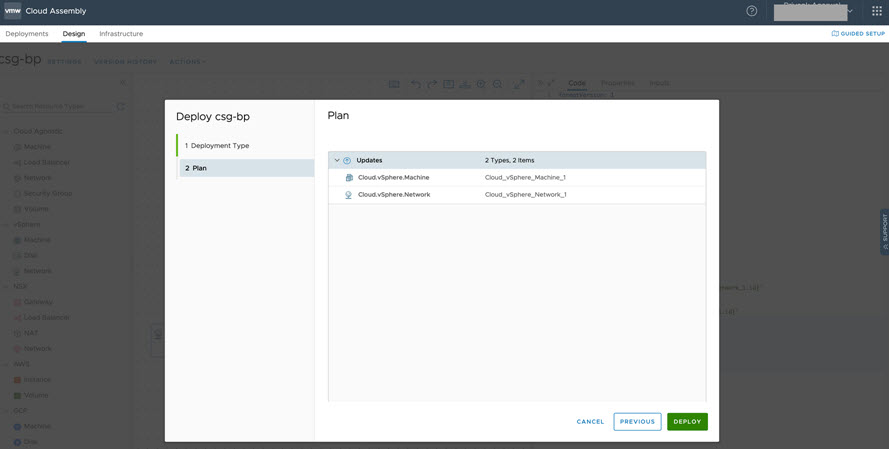
- Perform an iterative deployment to reconfigure the network, as shown below.
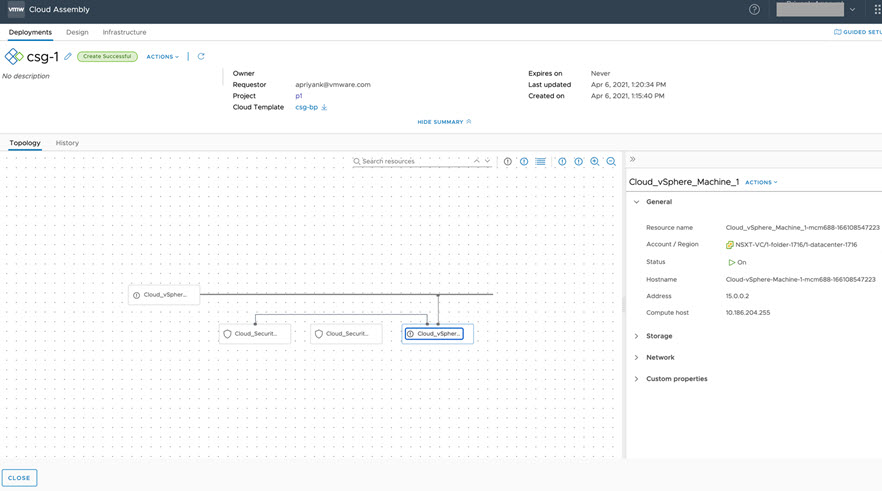
- After successful redeployment, notice that the network custom properties display the updated constraints, as shown below.
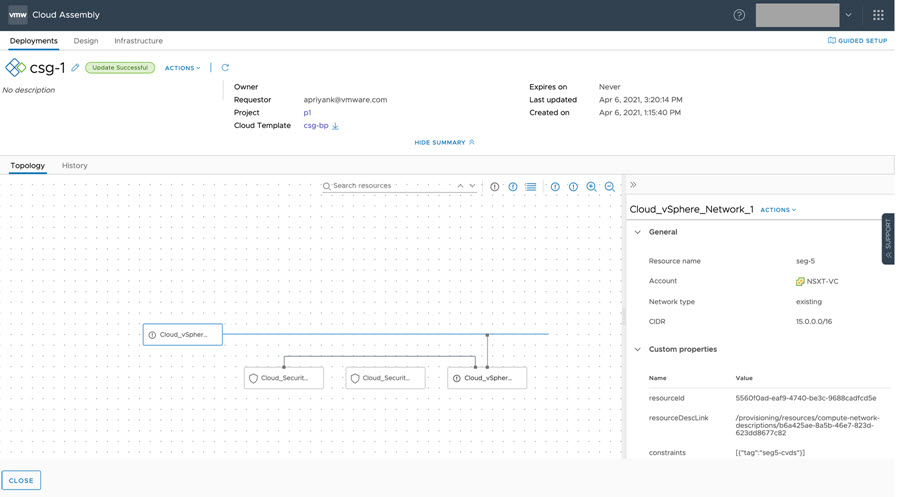
Because the IP range was updated earlier with the new C-VDS data, the machine IP address does not change in the redeployment, as shown below.