Redis for VMware Tanzu Application Service offers on-demand and shared-VM service plans.
Learn about the architecture, lifecycle, and configurations of the on-demand plan, as well as networking information for the on-demand service.
For similar information for the Shared-VM plans, see Shared-VM Service offering.
Architecture of the on-demand plan
The p.redis service broker manages the on-demand service plan instances.
The following diagram shows the architecture of the service broker and on-demand plans and how the user’s app binds to a Redis instance.
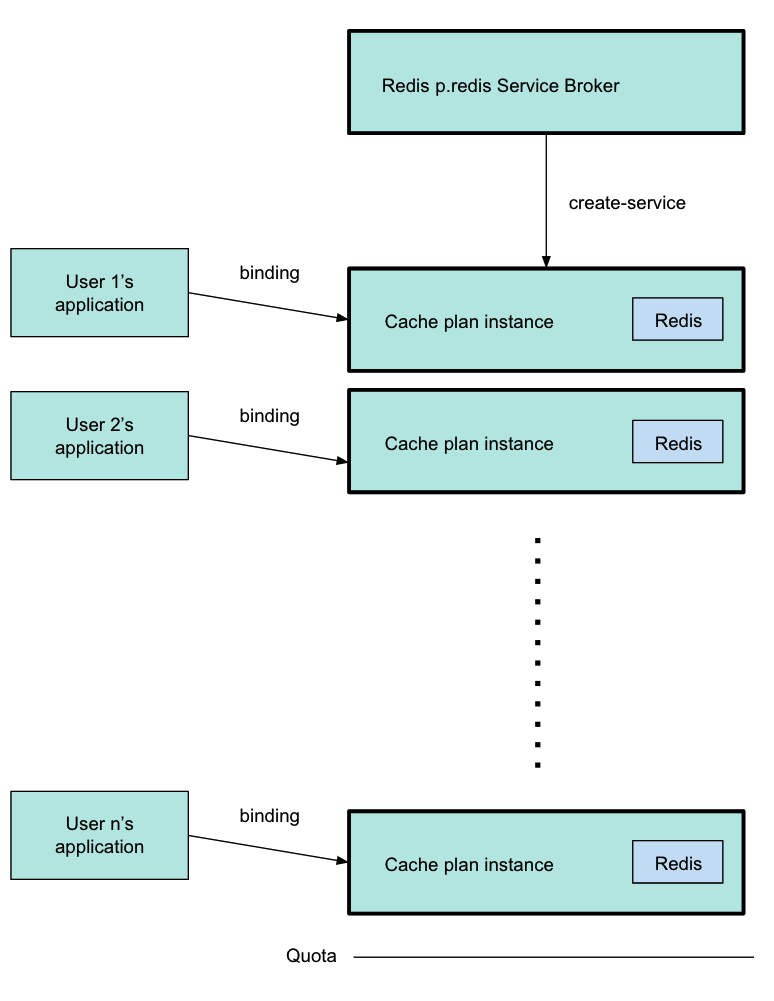
You can configure plans in Tanzu Operations Manager, and set global and per-plan quotas for the maximum number of instances.
Developers can create instances of each plan when needed, until a quota is reached, and bind their apps to the instances. The previous diagram shows the p.redis service broker pointing to a cache plan instance, which was created by running cf create-service. For more information about this command, see Create a Service Instance in Using Redis for VMware Tanzu Application Service.
The diagram shows three different users’ apps, each one bound to a separate cache plan instance. Each instance has its own VM. The line below the final instance shows that the quota has been reached, and developers cannot create more instances.
TLS in Redis for Tanzu Application Service
You can enable TLS to secure traffic between apps and service instances. In Redis for Tanzu Application Service, the available options are Optional and Not Configured.
TLS set to optional
When setting TLS to Optional within On-Demand Service Settings, both TLS and non-TLS connections are accepted. TLS traffic goes through a proxy as shown in the diagram below. Enabling TLS is not expected to noticeably reduce performance. This depends, however, on network infrastructure, application architecture, and other such resources being in good shape.
VMware recommends setting TLS as Optional, because it allows app developers to migrate to TLS connections regardless of whether traffic is restricted to just TLS connections.
The option to enforce TLS only is not supported in Redis for Tanzu Application Service.
Steeltoe and Spring apps use the TLS port by default, if it is available. Other apps might require further configuration to make use of the correct port.
The following diagram shows how apps communicate with on-demand Redis instances when you set TLS to Optional.
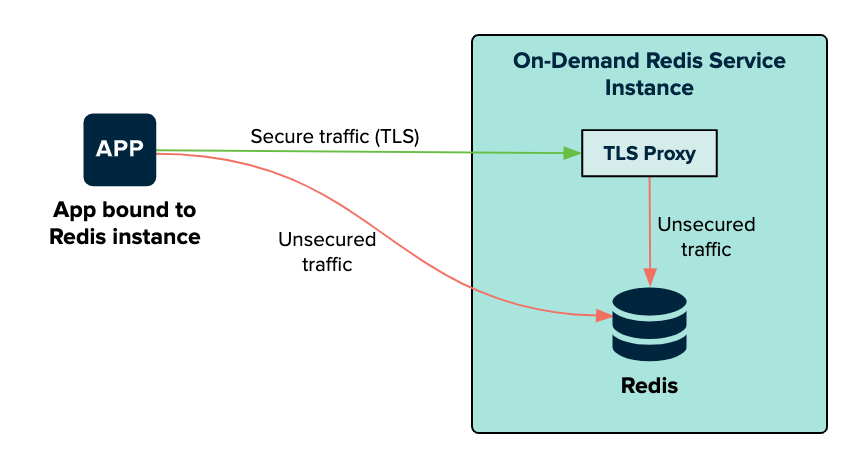
The bound app can connect to the Redis service on the on-demand Redis service instance VM through a TLS proxy or connect directly. The TLS proxy and Redis are both on the Redis service instance. The traffic is secure from the app to the TLS proxy. When on the service instance, the traffic from the TLS proxy to Redis is unsecured.
TLS set to not configured
When setting TLS to Not Configured within the On-Demand Service Settings, the communication with service instances remains unchanged from Redis for Pivotal Cloud Foundry v2.1 and earlier.
The following diagram shows how apps communicate with on-demand Redis instances when you set TLS to Not Configured.
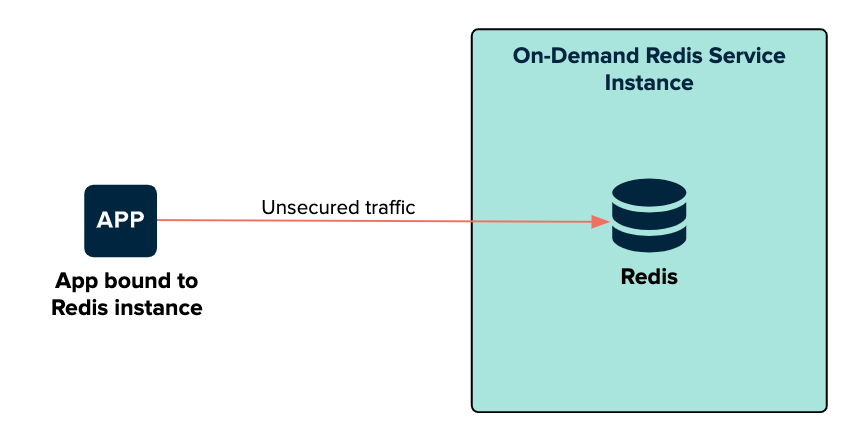
The bound app connects directly to the Redis service on the on-demand Redis service instance VM. The traffic on this connection is unsecured.
On-demand service plans
Redis for Tanzu Application Service offers on-demand plans as the p.redis service within the tile. On-demand plans are best suited to caching. Redis for Tanzu Application Service has tailored the default configuration to this use case.
The default on-demand plan is the On-Demand Cache Plan. Service instances of this plan are deployed to a dedicated VM. VMware recommends that you configure these VMs to have 2.5 times more persistent disk than memory.
You can customize service plans by configuring the Plan name, Plan description, Server VM type, and Server Disk type. You can add and configure as many service plans as required.
Features of on-demand service plans
- Each on-demand service instance is deployed to its own VM and is suitable for production workloads.
- The service plans are operator-configured and enabled. When enabled, app developers can view the available plans in the Marketplace and provision a Redis instance from that plan.
- Operators can update the cache plan settings, including the VM size and disk size, after the plans have been created.
- Operators and app developers can change certain Redis configurations from the default.
- The default
maxmemory-policyisallkeys-lruand can be updated for other cache policies. - On-Demand Redis supports Redis Database Backup (RDB) snapshots, but not Append-Only File (AOF) persistence. For more information, see Redis Persistence in the Redis documentation.
- The maximum number of instances is managed by a per-plan and global quota.
For information about setting quotas, see Setting Limits for On-Demand Service Instances.
Configuration of on-demand service plans
For on-demand plans, certain Redis configurations can be set by the operator during plan configuration, and by the app developer during instance provisioning. Other Redis configurations cannot be changed from the default.
Operator configurable Redis settings
The Redis settings that an operator can configure in the tile UI include:
- Redis Client Timeout
- Redis TCP Keepalive
- Max Clients
- Service Gateway
- Custom VM Extensions
- Lua Scripting
- Plan Quota
For more information, see Configure On-Demand Plan settings.
App developer configurable Redis settings
The Redis settings that an app developer can configure include:
maxmemory-policynotify-keyspace-eventsslowlog-log-slower-thanslowlog-max-len
For more information, see Customize an On-Demand Service Instance.
Operator notes for on-demand service plans
- Instances of the on-demand plan can be deployed until their number reaches either an operator-set per-plan quota or a global quota. For information about setting quotas, see Setting Limits for On-Demand Service Instances.
- Instances are provisioned based on the On-Demand Services SDK and service broker adapter associated with this plan.
maxmemoryinredis.confis set to 45% of the system memory.- Any on-demand plan can be deactivated from the plan page in Tanzu Operations Manager.
Known limitations for on-demand service plans
Limitations for the on-demand service include:
-
Operators must not downsize the VMs or disk size as this can cause data loss in pre-existing instances.
-
Operators can update certain plan settings after the plans have been created. To ensure upgrades happen across all instances, set the upgrade instances errand to On.
-
If you update the VM size, disk size, or the Redis configuration settings, thereby enabling Lua Scripting, max-clients, timeout, and TCP keepalive, the settings are implemented in all existing instances.
Lifecycle for on-demand service plan
Here is the lifecycle of Redis for Tanzu Application Service, from an operator installing the tile through an app developer using the service then an operator deleting the tile.
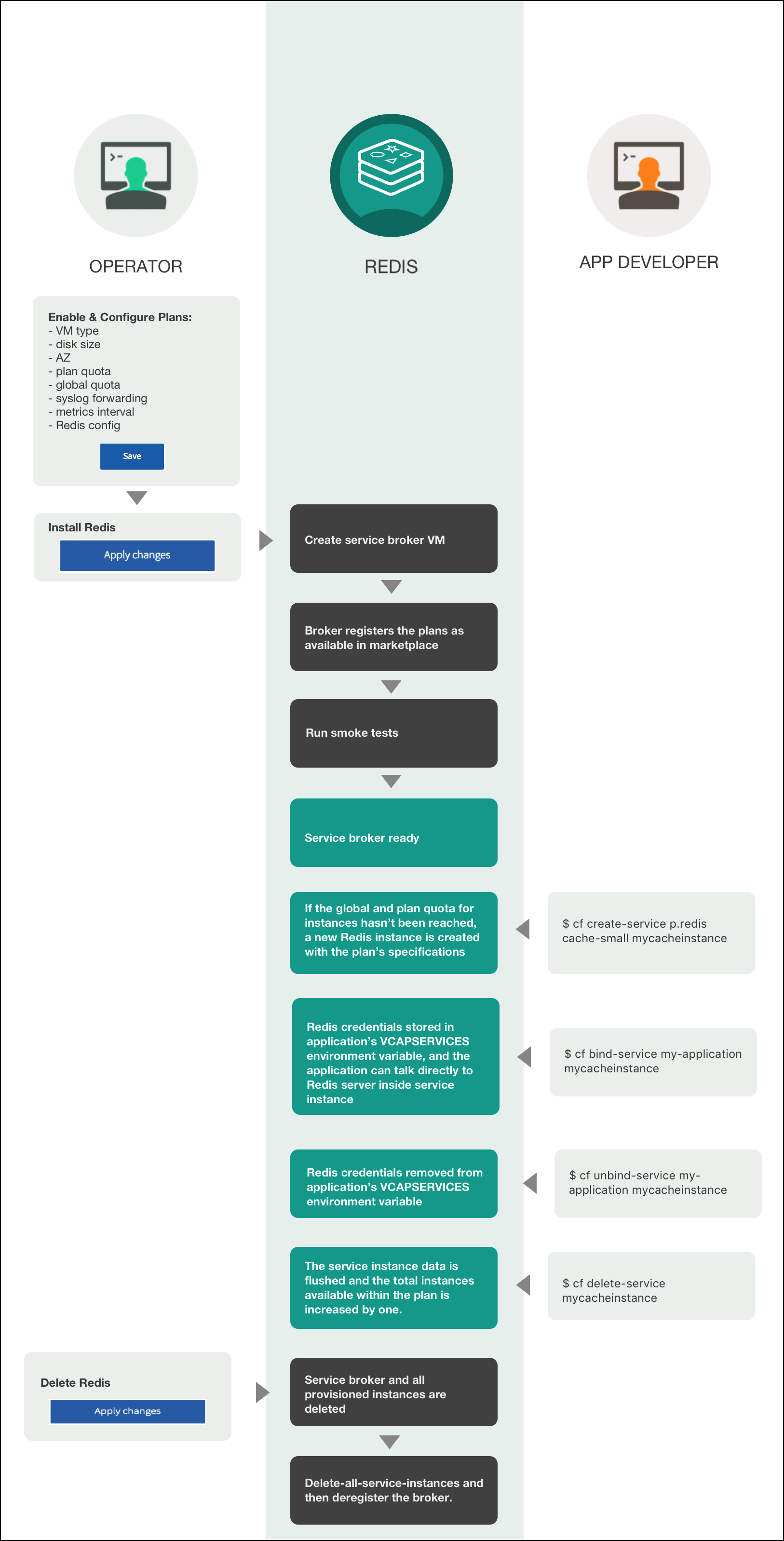
Installation
Operators do the following to install Redis for Tanzu Application Service:
-
Enable and configure plans:
- VM type
- Disk size
- Availability Zone (AZ)
- Plan quota
- Global quota
- Syslog forwarding
- Metrics interval
- Backup destination
- Metrics interval
- Redis config
- Click Save
-
Install Redis
- Click Apply changes
After the operator click Apply Changes, Redis for Tanzu Application Service does the following:
- Creates a service broker VM
- Broker registers the plans as available in marketplace
- Run smoke tests
- Service broker ready
Using Redis for Tanzu Application Service
After you have installed Redis for Tanzu Application Service, developers can create service instances, bind and unbind the service instances to apps, and delete service instances.
Create service
When a developer runs the cf create-service command, for example:
$ cf create-service p-redis cache-small mycacheinstance
Redis for Tanzu Application Service does the following:
- If the global and plan quota for instances has not been reached, a new Redis instance is created with the plan’s specifications.
Bind service
When a developer runs the cf bind-service command, for example:
$ cf bind-service my-application mycacheinstance
Redis for Tanzu Application Service does the following:
- Redis credentials are stored in the app’s
VCAP_SERVICESenvironment variable and the app can communicate directly with the Redis server inside the service instance
Unbind service
When a developer runs the cf unbind-service command, for example:
$ cf unbind-service my-application mycacheinstance
Redis for Tanzu Application Service does the following:
- Redis credentials are removed from the app’s
VCAP_SERVICESenvironment variable
Delete service
When a developer runs the cf delete-service command, for example:
$ cf delete-service mycacheinstance
Redis for Tanzu Application Service does the following:
- The service instance data is flushed and the total instances available within the plan is increased by one
Deletion
You can do the following to delete Redis for Tanzu Application Service:
- Delete Redis:
- Click Apply Changes
After you click Apply Changes, Redis for Tanzu Application Service does the following:
- Service broker and all provisioned instances are deleted.
- Delete-all-service-instances and then deregister the broker.