Here you will find information about the Spring Cloud Services deployment model and more that might be useful in operating its services or client apps.
Tanzu Operations Manager administrators can use Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to manage which operators can make deployment changes, view credentials, and manage user roles in Ops Manager. Therefore, your role permissions might not allow you to perform every procedure in this operator guide. For more information about roles in Ops Manager, see Understand Roles in Ops Manager.
Service instance management
A service instance is assigned a GUID at provision time. The service instance is backed by a Spring Boot app deployed in the "p-spring-cloud-services" org to a space named after the service instance GUID:
Config Server
p-spring-cloud-servicesorg /[GUID]space / config-server: A Spring Cloud Config server app.
Service Registry
p-spring-cloud-servicesorg /[GUID]space / service-registry: A Spring Cloud Netflix Eureka server app.
Access service instance backing applications in Apps Manager
To view a backing app for a service instance in Apps Manager, get the service instance's GUID and look for the corresponding space in the "p-spring-cloud-services" org.
Run the cf service command with the --guid flag. Copy the service instance GUID.
$ cf service --guid my-config-server
c0795bce-127b-40b4-9ab4-75c31205a02a
Log into Apps Manager as an admin user and select the "p-spring-cloud-services" org.
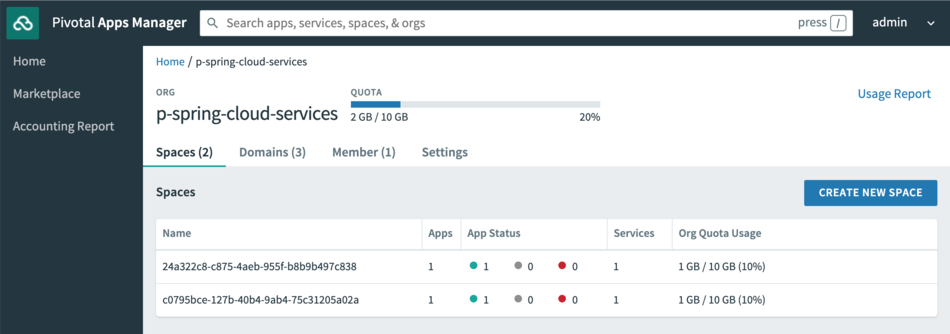
The service instance's backing app is deployed in the space named after the service instance GUID.
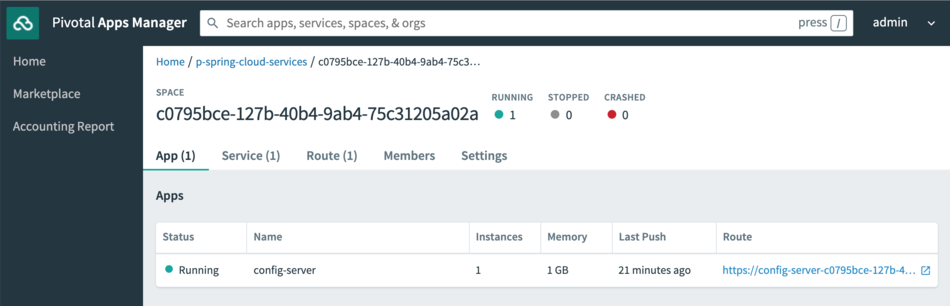
Access service instance backing applications using the cf CLI
To view a backing app for a service instance using the Cloud Foundry Command Line Interface (cf CLI), get the service instance's GUID and look for the corresponding space in the "p-spring-cloud-services" org.
Run the cf service command with the --guid flag. Copy the service instance GUID.
$ cf service --guid my-config-server
c0795bce-127b-40b4-9ab4-75c31205a02a
Target the p-spring-cloud-services org and the space, which is named after the GUID of the service instance:
$ cf target -o p-spring-cloud-services -s c0795bce-127b-40b4-9ab4-75c31205a02a
api endpoint: https://api.sys.example.com
api version: 2.131.0
user: admin
org: p-spring-cloud-services
space: c0795bce-127b-40b4-9ab4-75c31205a02a
The app is in the dedicated space named after the service instance GUID:
$ cf apps
Getting apps in org p-spring-cloud-services / space c0795bce-127b-40b4-9ab4-75c31205a02a as admin...
OK
name requested state instances memory disk urls
config-server started 1/1 1G 1G config-server-c0795bce-127b-40b4-9ab4-75c31205a02a.apps.example.com
Application health and status
For more visibility into how Spring Cloud Services service instances backing apps are behaving, or for troubleshooting purposes, you may wish to access those apps directly. See below for information about accessing their output.
Read backing application logs
To access logs for service instance backing apps, target the "p-spring-cloud-services" org and its "instances" space: Access the service instance backing app as described in the Access Service Instance Backing Applications Using the cf CLI section.
Then you can use cf logs to tail logs for the backing app:
$ cf logs config-server
Retrieving logs for app config-server in org p-spring-cloud-services / space 24a322c8-c875-4aeb-955f-b8b9b497c838 as admin...
If the backing app is not running properly, it will write detailed health information to its log on each GET request sent to its health Actuator endpoint. If the backing app is healthy, it will not log any health details.
Access Actuator endpoints
Service instance backing apps use Spring Boot Actuator. For information about accessing the Actuator endpoints that are activated on service instance backing apps, see the Service Instance Endpoints section of Spring Boot Actuator endpoints.
Capacity requirements
Below are usage requirements of the apps backing a single service instance (SI) of each Spring Cloud Services service type.
| Service Type | Memory Limit / SI | Disk Limit / SI |
|---|---|---|
| Config Server | 1 GB | 1 GB |
| Service Registry | 1 GB | 1 GB |