If you run the VMware Aria Automation Quickstart, the wizard configures cloud accounts, some infrastructure, a project, and some cloud templates. It also deploys a cloud template. Follow the steps in this procedure to see what was added. You can also use this tour to learn about some of the Automation Assembler and Automation Service Broker features.
The information presented in this tour is based on the vCenter Server Quickstart, but the results are similar if you run the VMware Cloud Foundation Quickstart.
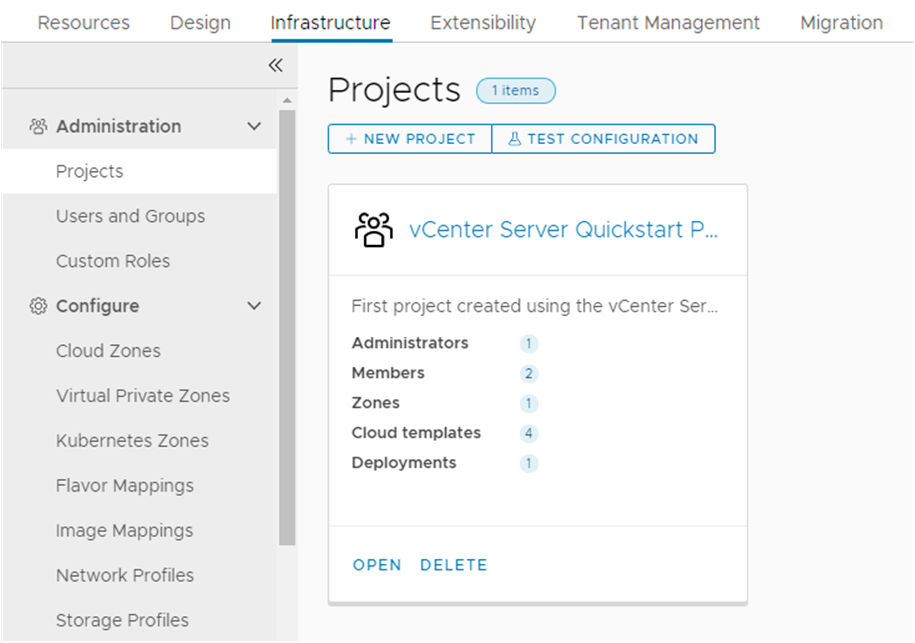
The tour follows the basic workflow that you use as you add new cloud accounts, develop your own cloud templates, and make them available to your consumers as a catalog. To expand your configured infrastructure to support a diverse range of development operation team projects, you must broaden your infrastructure so that you can create more refined cloud templates. This tour is only a starting point. It is intended to familiarize you with the user interface and how to use it.
You begin with the console, then Automation Assembler, where cloud administrators and cloud template developers do most of their work. This is followed by Automation Service Broker, which you configure to provide catalog items that your consumers can request and manage.
Prerequisites
- The procedure assumes that you ran the Quickstart. See How do you get started with VMware Aria Automation using the VMware vCenter Server Quickstart.
- If you did not, you can use the Guided Setup to get started creating your cloud infrastructure. See How do you get started with Automation Assembler using the Guided Setup.
- Log in as a user with a cloud administrator role.
Tour of the Quickstart changes to Automation Assembler
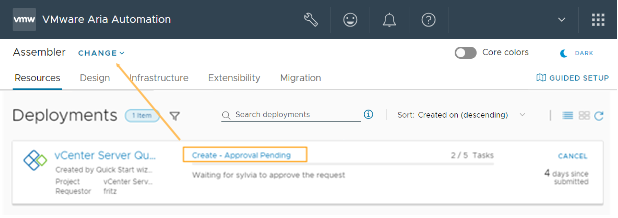
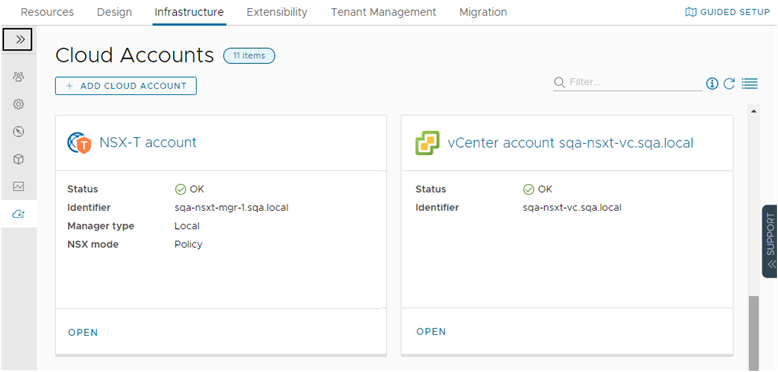
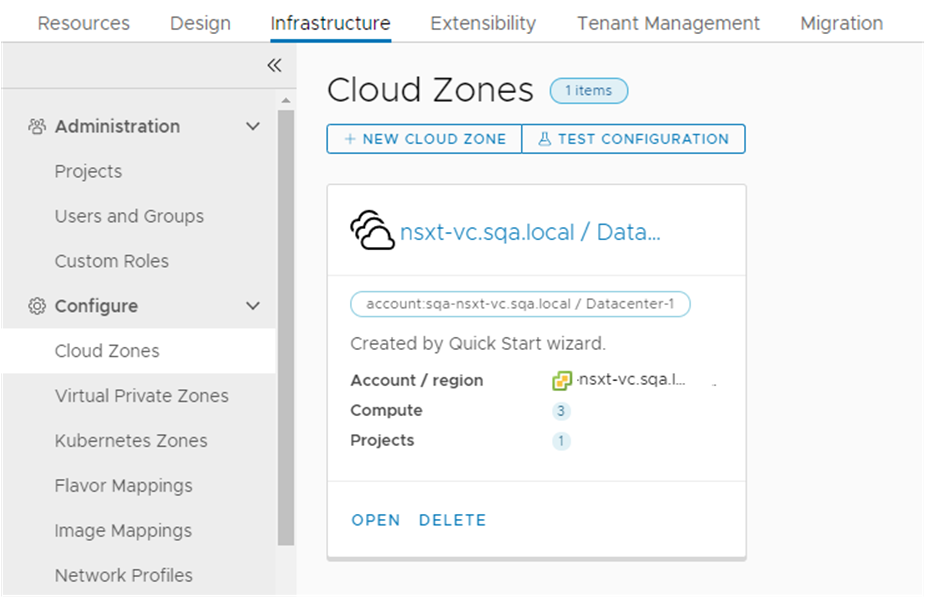
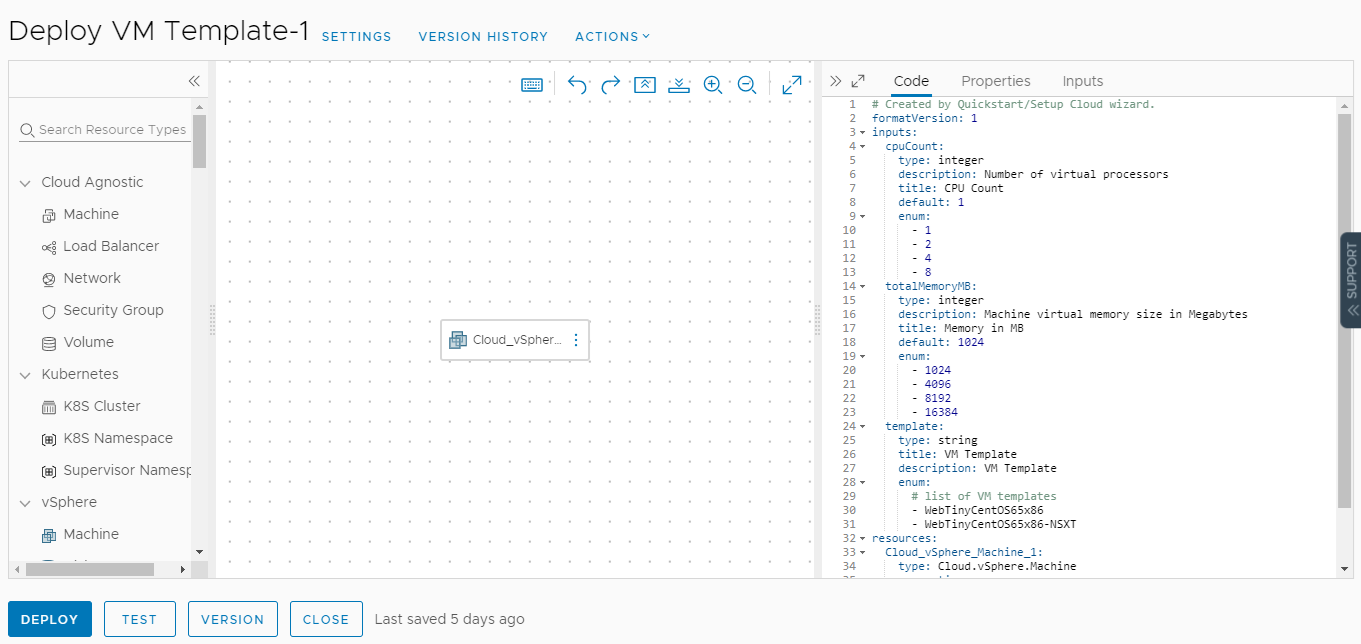
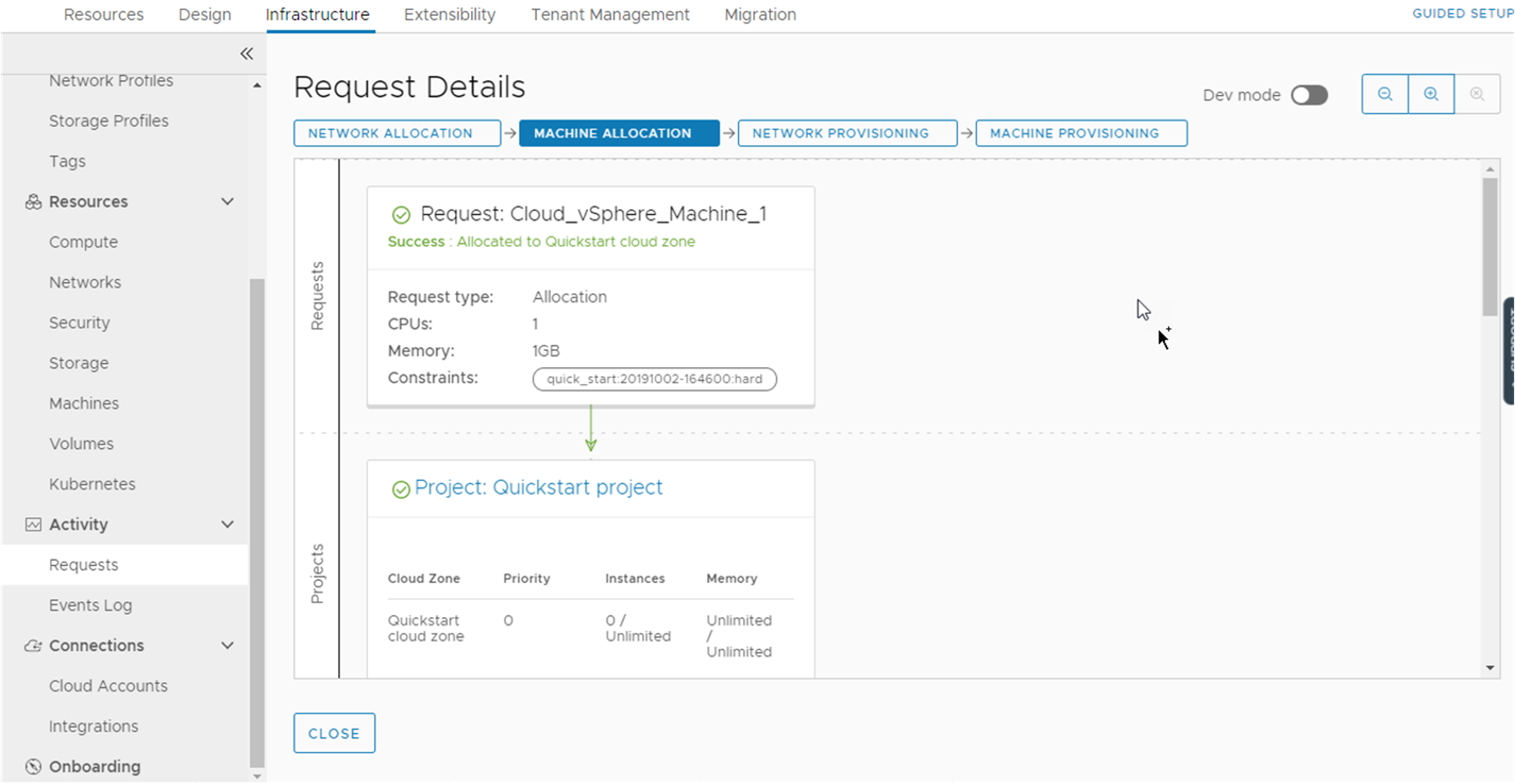
This tour of Automation Assembler shows you what the Quickstart configured and deployed. It is designed to guide your through the user interface and help you understand some of the tasks you might later perform on your own.
When you log in to VMware Aria Automation, you might see the Identity and Access Management and Branding tab. These tabs are not covered as part of the tour. You use them as you add users and manage your organizations.
For more about identity management and branding, see Administering VMware Aria Automation
Prerequisites
- This procedure assumes that you ran the Quickstart. See How do you get started with VMware Aria Automation using the VMware vCenter Server Quickstart.
- Log in as a user with an administrator role.
Procedure
What to do next
Continue your tour in Automation Service Broker.
Tour of the Quickstart changes to Automation Service Broker
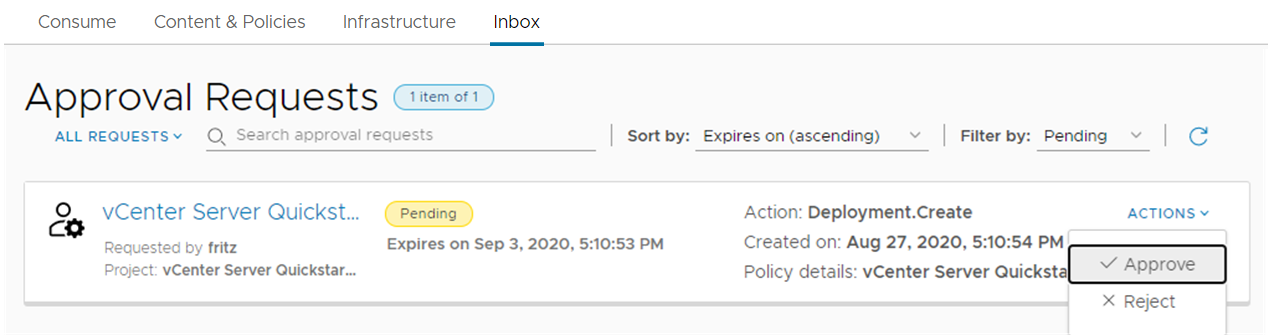
Automation Service Broker is where you provide your users with a catalog of templates that they can deploy to the cloud accounts that you provide. In this part of the tour, you can see what the Quickstart configured for you.
The tour gets you started learning the user interface and understanding some of the tasks you can later perform on your own.
If you run the Quickstart wizard more than once, you will see representative examples for each run as you progress through this tour.
Prerequisites
Review the tour of Automation Assembler. See Tour of the Quickstart changes to Automation Assembler.
Procedure
- To see how your consumers deploy templates, navigate to Automation Service Broker.
- Click the service drop-down menu in the upper left corner.
- Select Service Broker.
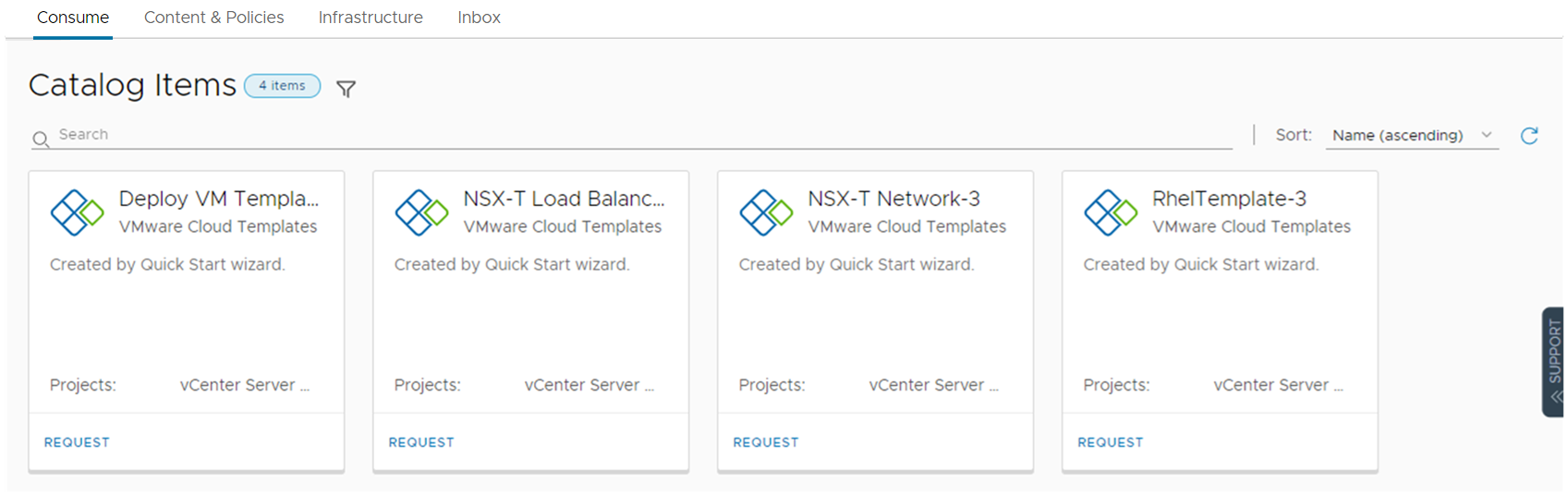
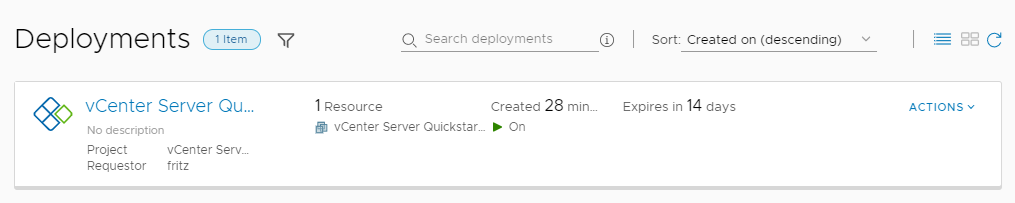
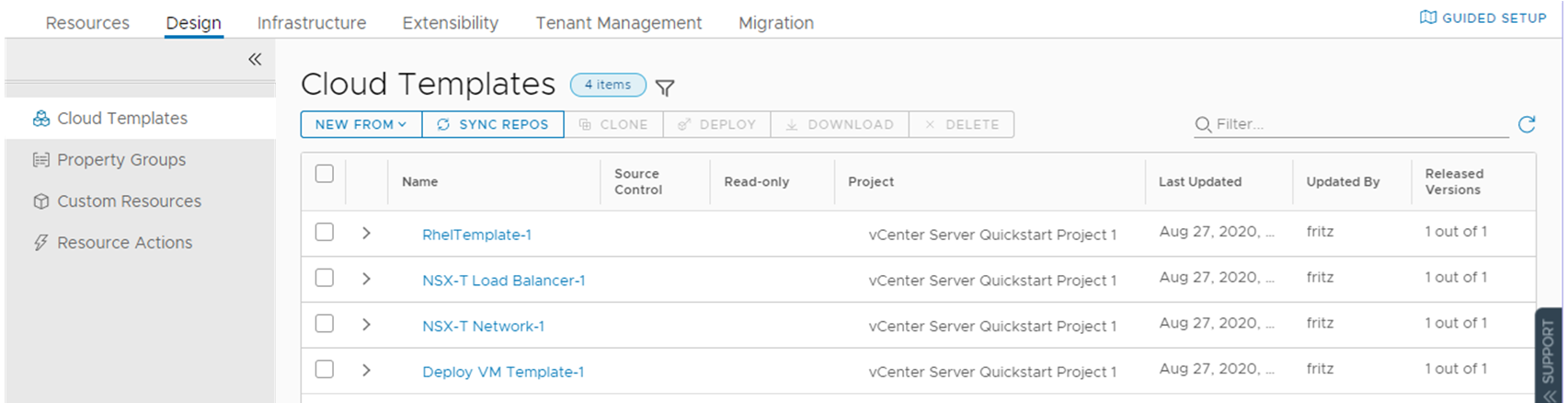
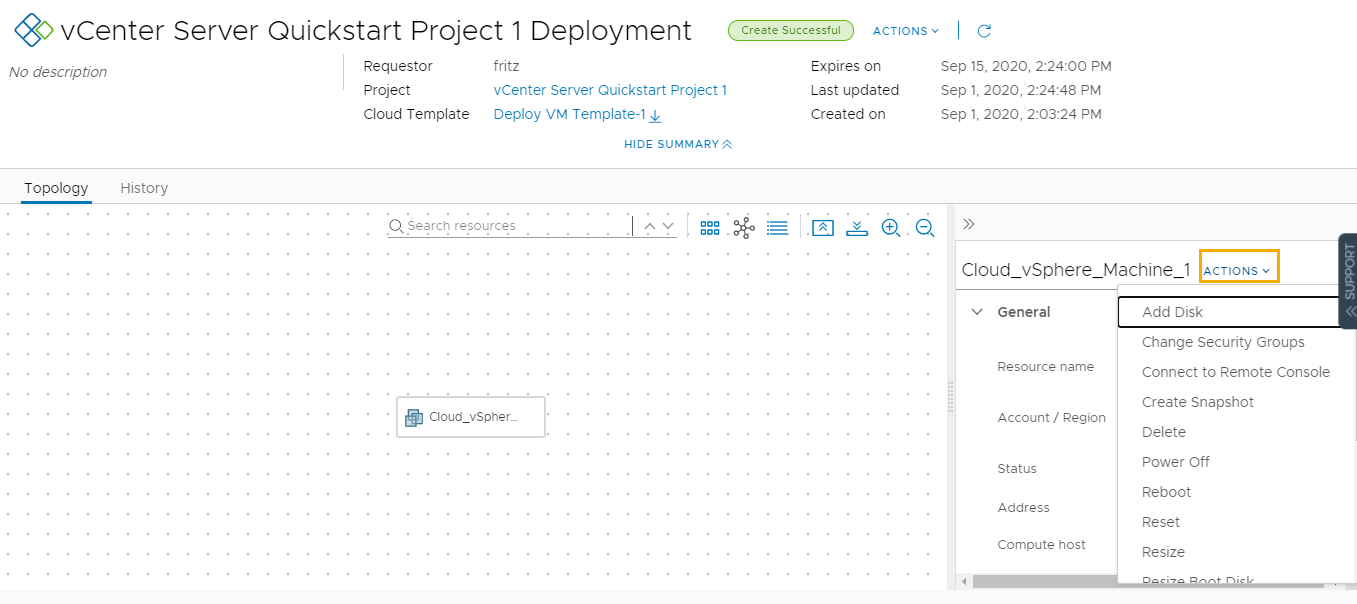
Notice that the three catalog items are the released VMware cloud templates from Automation Assembler.
- To see what the Quickstart deployed, select .
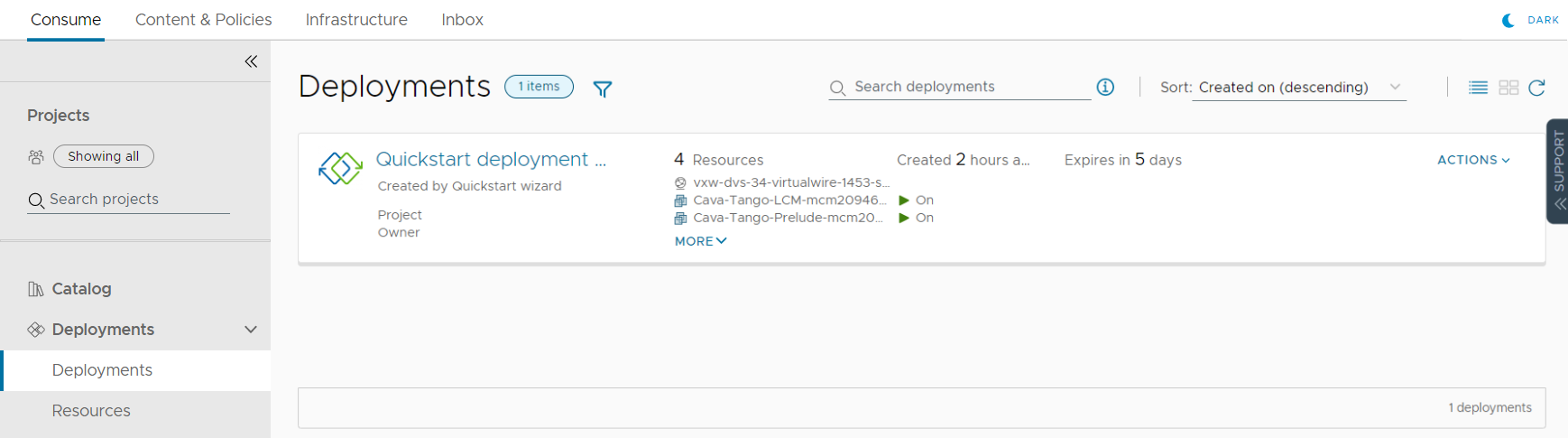
Notice that this deployment is the same one that we saw in Automation Assembler.
- To review how Quickstart configured Automation Service Broker to provide the templates in the catalog, select .
- Click Content Sources.
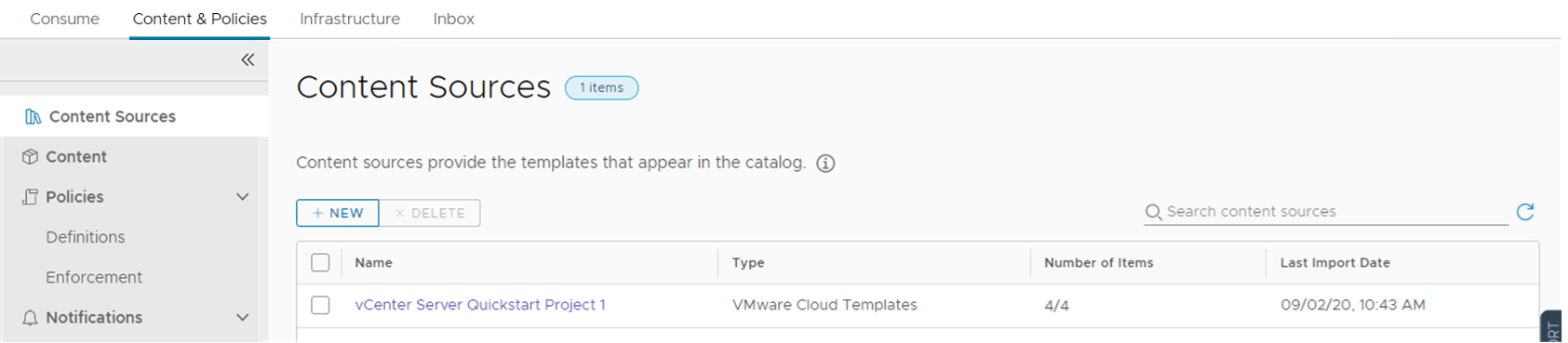
In this case, the templates are the content source. You can also add Amazon Web Services CloudFormation templates, Automation Orchestrator workflows, and templates that you want to provide to your consumers.
- Click Content.
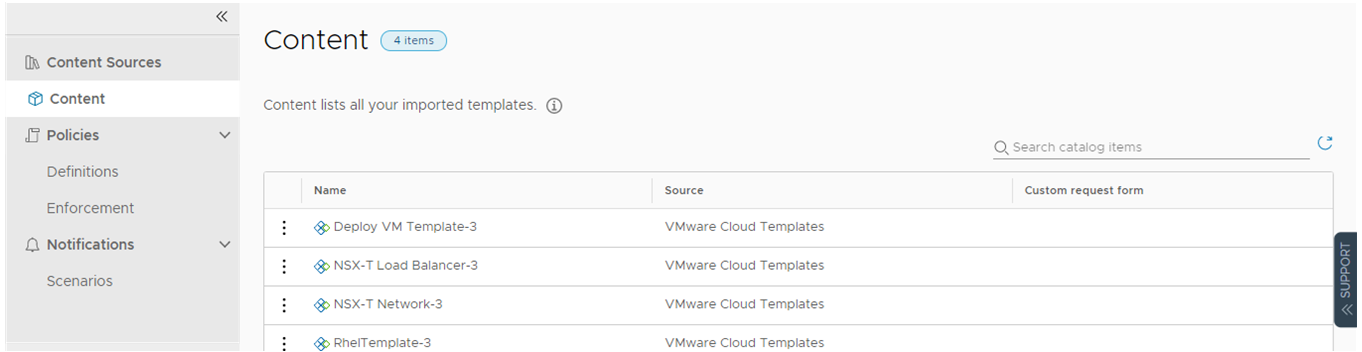
This list is where you see the list of all the content in Automation Service Broker, including the templates from Automation Assembler.
- Select .
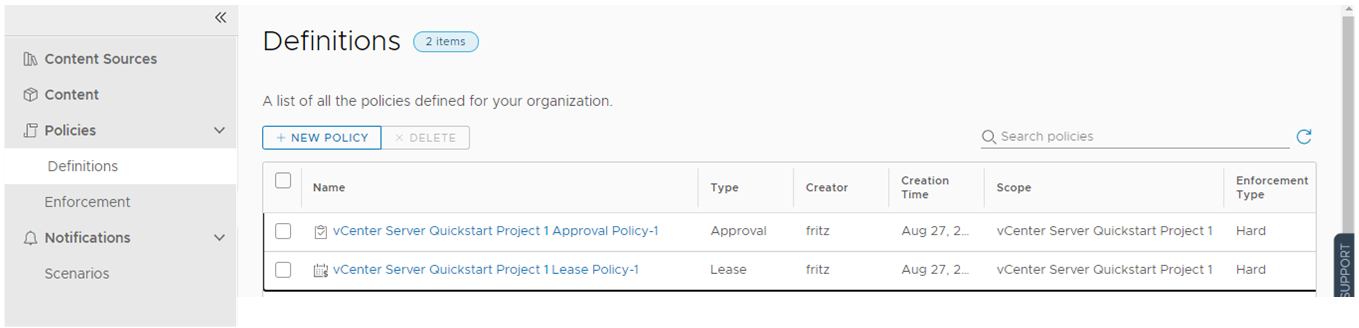
You create and manage policies in Automation Service Broker, including lease policies that apply to Automation Assembler deployments.
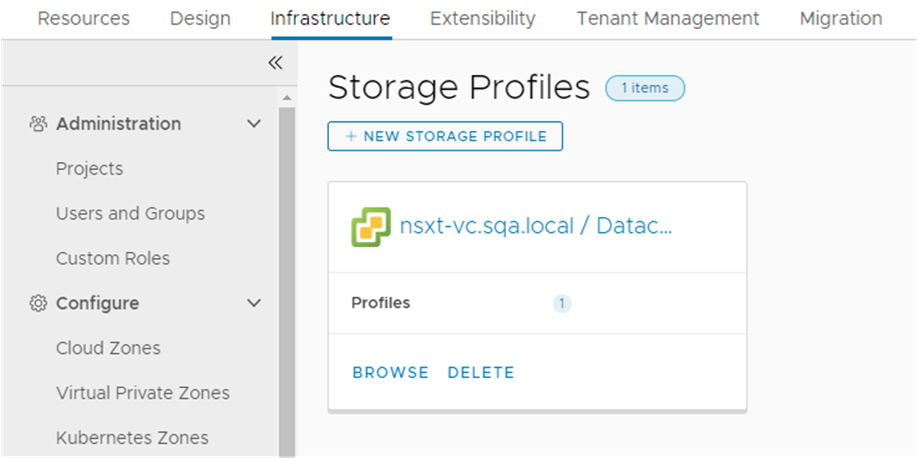
- To review the project and the custom name that you created in the Quickstart, and that you saw in the Automation Assembler part of the tour, select .
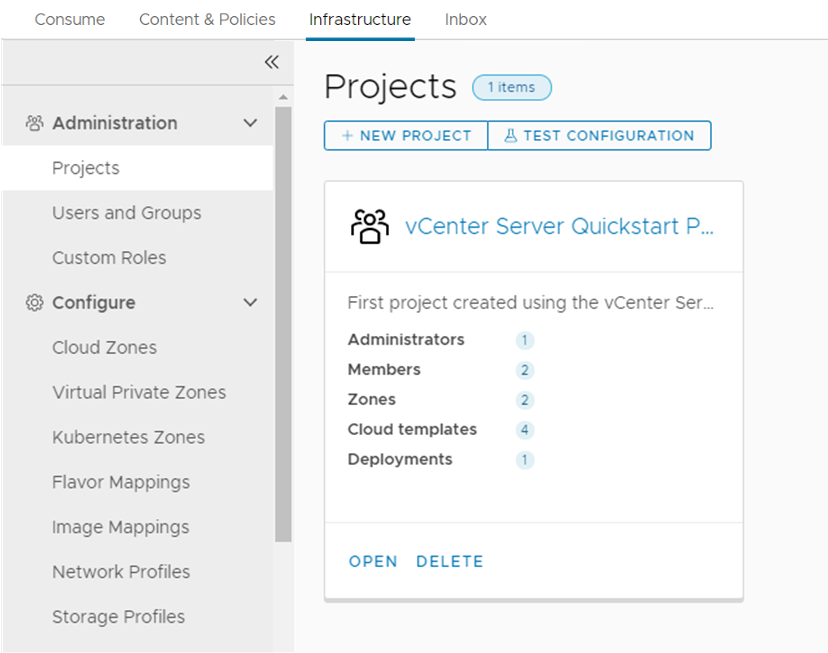
Notice that only a limited number of the infrastructure options that you saw in Automation Assembler are available in Automation Service Broker. Only the options that you must use to set up the catalog for your consumers are provided.
- Click Content Sources.
What to do next
To add another cloud account, configure the infrastructure to support it, and deploy a template to support it, use the guided setup. See How do you get started with Automation Assembler using the Guided Setup.