After completing an initial assessment, you can then remediate the advisories that were detected in the assessment.
Before you begin
Automation for Secure Hosts Vulnerability triggers nodes to receive the latest advisories from an operating system. Windows nodes in particular can receive these updates in one of two ways:
- Windows Update Agent (WUA) - By default, Windows nodes connect directly to Microsoft using the WUA, which is automatically installed on all Windows nodes. The WUA supports automated patch delivery and installation. It scans nodes to determine which security updates are not installed and then searches for and downloads the updates from Microsoft’s update websites.
- Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) - A WSUS server acts as an intermediary between Microsoft and the minion. WSUS servers allow IT administrators to deploy updates to a network strategically to minimize down time and disruptions. See Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) in the official Microsoft documentation for more information.
- Ensure that the WSUS is enabled and running. If needed, you can configure the Windows minion to connect to a WSUS using a Salt state file provided by Automation Config. See Enabling Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) for this state file. After running this state file, verify that your minion is successfully connecting to the WSUS server and is receiving updates.
- Approve updates related to advisories from Microsoft on the WSUS server. When the WSUS server receives updates from Microsoft, the WSUS administrator must review and approve those updates in order to deploy the updates in the environment. In order for Automation for Secure Hosts Vulnerability to detect and remediate advisories, any updates that contain advisories must be approved.
Remediate supported advisories
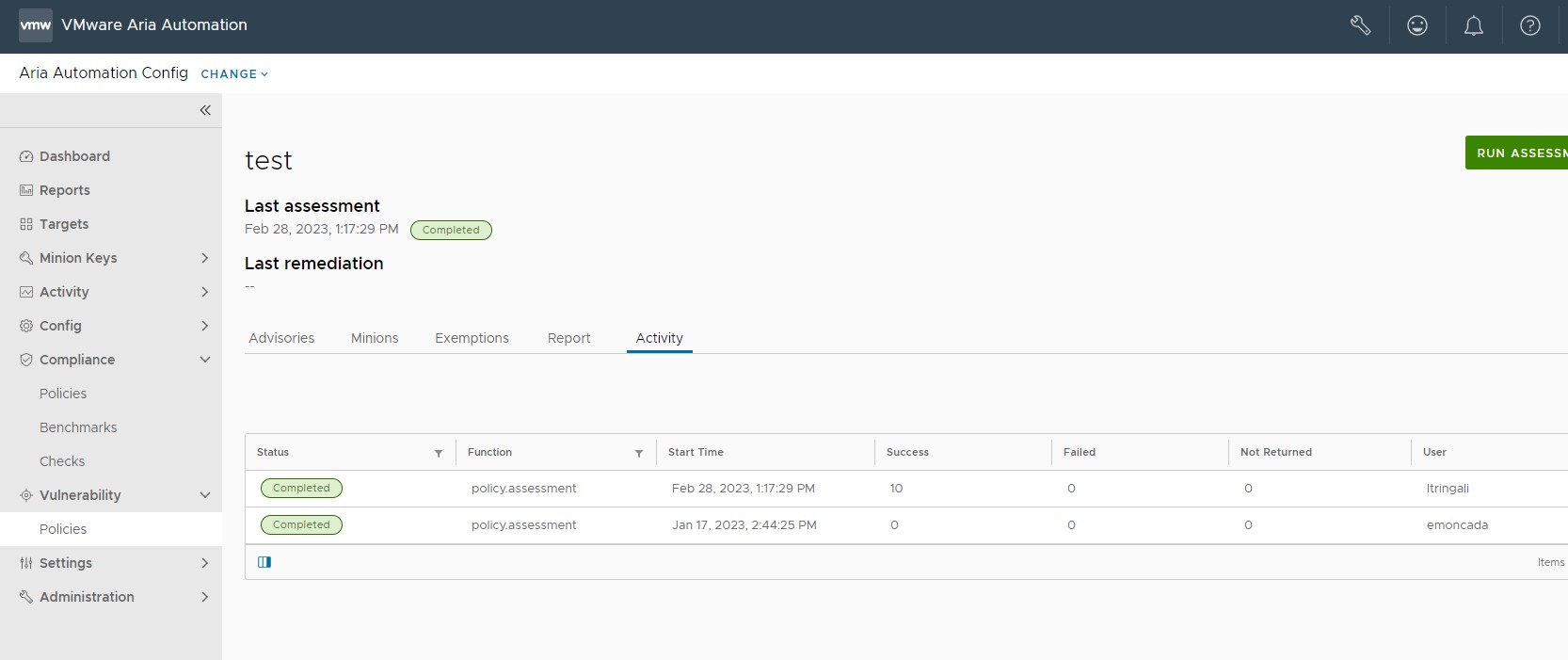
On the policy home page, the Activity tab shows a list of completed or in-progress assessments and remediations and their statuses:
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
| Queued | The operation is ready to run but the minions have not started the operation. |
| Completed | The operation is finished running. |
| Partial | The operation is still waiting for some minions to return, although the operation has finished running. |
| Failed | The operation failed to complete. |
During the remediation, all packages that are part of that advisory are applied to the selected nodes. You can remediate all advisories at once or you can remediate a specific advisory, a specific minion, or set of minions as needed. You may also select state files to apply as both pre and post-remediation actions to guarantee dependencies or ensure a service or system restarts after being patched.
Automation for Secure Hosts Vulnerability always installs the latest available version that is available from a vendor, even if the advisory was fixed by an earlier version.
After remediating an advisory, you must run another assessment to verify the remediation was successful.
- Remediating all advisories at once
- Remediating a specific minion
- Remediating a set of minions
From the policy dashboard, when you run Remediate all, Automation for Secure Hosts Vulnerability remediates all advisories on all minions in your policy, which may result in long processing times.
- In the Vulnerability workspace, click a policy to open the policy's dashboard.
- From the policy's dashboard:
- To remediate by advisory, click the checkbox next to all advisories you want to remediate.
- To remediate by minion, select the Minions tab, click a minion, and select all advisories you want to remediate for the active minion.
- To remediate by both advisory and minion, click an advisory ID and click the checkbox next to all minions you want to remediate for the active advisory.
- To run pre or post remediation actions:
- Click the Optional pre/post actions toggle.
- Select an environment.
- Choose state files to apply before and/or after the remediation.
- Click Remediate.
Results: Your vulnerability advisories are remediated. Occasionally, remediation might require a full system or minion reboot. If you're aware of this in advance, you can configure a reboot in state file to run as a post-remediation action. Otherwise, see How do I reboot a minion as part of remediation.
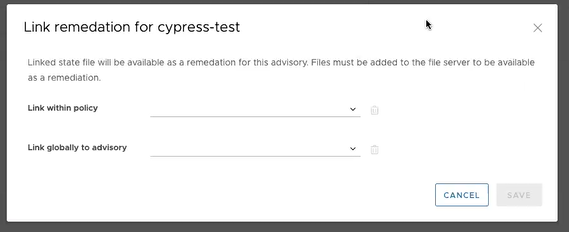
Custom remediation
- Link within policy - The remediation file is only used to remediate the specified advisory in the current policy. For example, if a duplicate policy was created with the same the unsupported advisory, the remediation file will only remediate the advisory in the first policy and not in the duplicate.
- Link globally to advisory - The remediation file is used to remediate the specified advisory across all policies.