Microsoft Azure DNS private zones enable creating zones inside the private networks that can span multiple Azure virtual networks and on-premises DCs (using VPN or Express Route).
With private DNS zones, you can use your custom domain names rather than the Azure-provided names that are available today. Using custom domain names, you can customize the virtual network architecture to best suit your organization’s needs. It provides name resolution for VMs within a virtual network and between virtual networks. Additionally, you can configure zone names with a split-horizon view, which allows a private and a public DNS zone to share the same name. For more information, see Using Azure DNS for Private Domains.
Integrated Solution for GSLB in Azure
In collaboration with Microsoft Azure, Avi Load Balancer has devised a solution to provide a highly available, optimal user experience. This solution seamlessly combines on-premises systems and services across multiple locations within your Azure private DNS zone. The solution enables you to balance the load across application instances that have been deployed in multiple locations (within a private DNS zone and on-prem DC) without any need for an FQDN or public IP address.
As networks and applications scale, this solution also helps with the challenges such as performance, resiliency, migration, and application testing without downtime and helps gain application insights.
Deploying Avi Load Balancer GSLB alongside Azure private DNS zones provides you with the following enterprise-grade benefits:
- Not Limited to a Region or Subscription ID
-
The virtual networks belonging to different subscription IDs or regions can be part of the same solution.
- Increased Application Availability
-
The joint solution delivers high availability for your critical applications by monitoring your endpoints and providing seamless failover so that only healthy servers are returned on lookups.
- Improved Application Performance
-
The solution improves application responsiveness by directing traffic to the endpoint within the lowest proximity for the client.
- Service Maintenance Without Downtime
-
The solution enables you to perform planned maintenance operations on your applications without downtime by directing traffic to alternative endpoints.
- Distribute Traffic for Complex Deployments
-
GSLB methods can be combined to create sophisticated and flexible rules to scale to the needs of larger and more complex deployments using two-level algorithms.
- Elasticity and Autoscaling
-
The analytics-driven, scale-out approach allows the load balancers to elastically provide on-demand autoscaling based on real-time traffic patterns.
- Split-horizon DNS Support
-
This solution works seamlessly for the zones with a split-horizon view.
Capabilities
Functions across all peered VNets and on-prem DC
Provides seamless name resolution
Between VMs located in the same virtual network.
Between VMs in different virtual networks.
For Azure hostnames from on-premises clients.
Provides access to applications hosted in one VNet from other VNets and vice versa. Also, access to applications hosted on-prem from Azure VNets and vice versa
Provides reliable health checks for endpoints supporting Ping, TCP, HTTP(S), and customs checks
Provides seamless DNS-based failover without any production impact
In case the VNet in a peered group is down, provides seamless operation as the endpoints present in that affected VNet will not be included in any DNS query until it is back up
Ensures high availability and reliability
Allows an option to fall back to any site or refuse query
Enables DNS based policies. For more information, see DNS Policy in the VMware Avi Load Balancer Configuration Guide.
Accelerates CI/CD deployment with the support of A/B testing for new features using a priority algorithm
Provides autoscaling capabilities during peak traffic
Provides centralized provisioning with automated discovery of applications across sites
Supports application monitoring, logs, and analytics across sites
Supports customizable TTL
Allows the option to send one or more DNS records
Primary Components
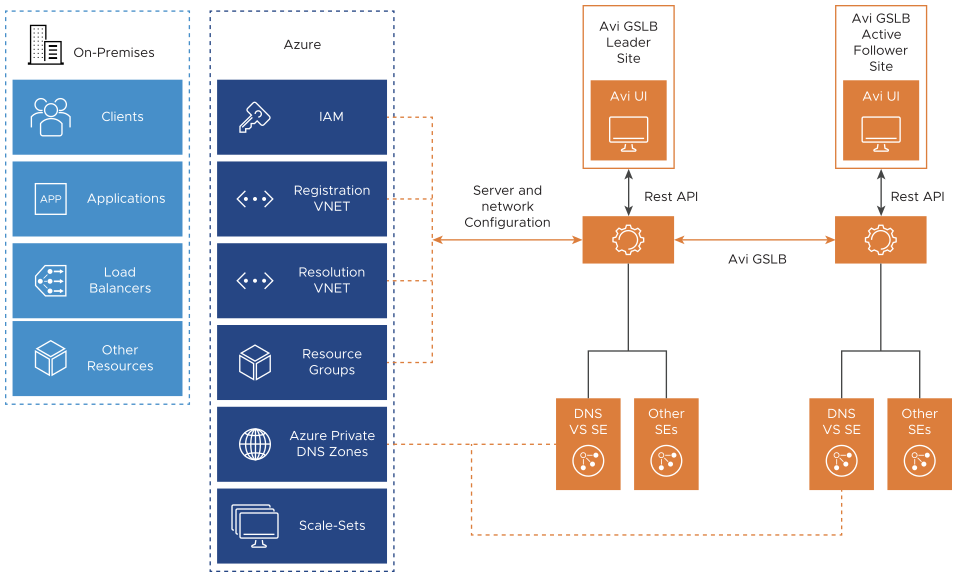
Avi Load Balancer GSLB Components
Azure Private Zone Components
This service can be used in conjunction with your DNS servers (such as Avi Load Balancer DNS virtual service as shown in the topology above), to resolve both on-premises and Azure hostnames. We can use name resolution between VMs and role instances within the same cloud service, without the need for an FQDN.
- Registration virtual networks
-
When you designate a virtual network as a registration virtual network at the time of creating a private zone or later when you update the zone, Azure will dynamically register DNS A records in the private zone for the VMs within this virtual network. This will keep track of VM additions or removals within the virtual network to keep your private zone updated. This is done automatically without any intervention.
- Resolution virtual networks
-
You can also designate up to 10 virtual networks as Resolution virtual networks while creating or updating a private zone. Forward DNS queries will resolve against the private zone records from any of these virtual networks.
DNS VM Forwarder
DNS VM forwarder is a BIND DNS server hosted on Azure. It is deployed for conditionally forwarding DNS queries based on the subdomains. This is the first point of contact for all the requests coming in for *.azure .com. Once the requests are received by the DNS forwarder, it will check for the FQDN names and based on the rules will forward the requests either to Azure DNS or Avi Load Balancer DNS virtual service. Avi Load Balancer DNS virtual service will handle all the traffic related to applications that need to be handled by GSLB. Azure DNS will handle all internal hostname resolution. For instance, for the azure.com zone, there are two DNS VM forwarders configured to forward requests from gslb.azure.com to Avi Load Balancer DNS and Azure DNS.
You can configure multiple DNS VM forwarders.
If you are planning to host Avi Load Balancer DNS virtual service, it is recommended to configure the forwarders in the same VNets. (See sample topology provided below)
The DNS VM Forwarder IP addresses need to be configured as custom DNS for all VNets in Azure. Similarly, it needs to be configured on corporate DNS for on-prem clients.
Sample Topology
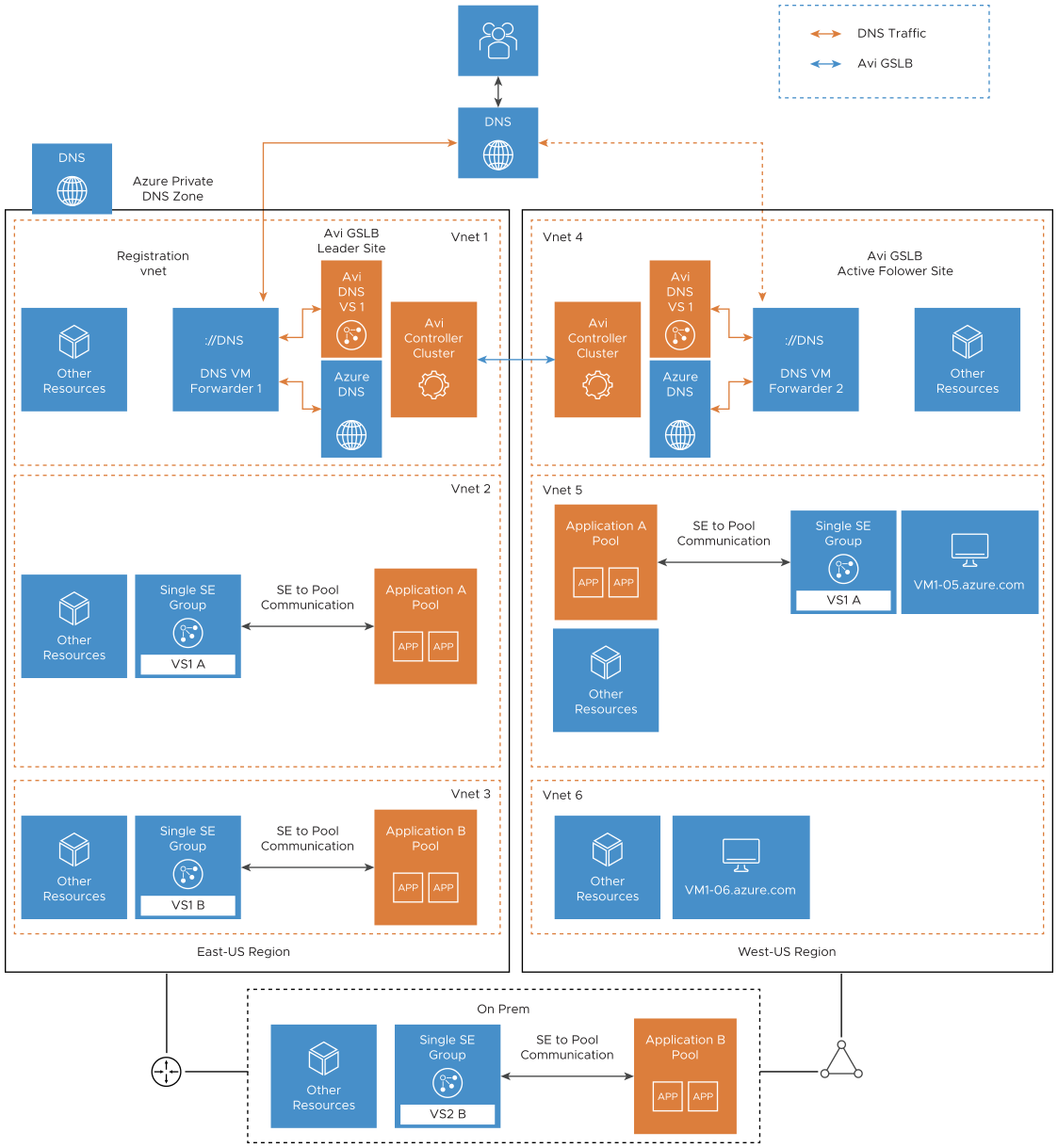
Topology details:
Two Avi Load Balancer GSLB sites - one in Azure Vnet1 (GSLB leader site) and the other in Vnet4 (Avi Load Balancer GSLB active follower site).
One on-prem DC is connected to Azure VNets using an express route/VPN gateway.
Client machine that can be present on-prem or in Azure.
Multiple VNets (Registration and Resolution) in Azure as part of the private DNS zone.
Application (Application B) residing on-prem must be accessible from the Azure VNets.
Application (Application A) residing in Azure must be reachable from on-prem clients and clients in Azure (same VNet and other VNets).
VMs hosted in Azure must have inter-VNet and Intra-VNet communication.
Considerations
- Avi Load Balancer Controller and GSLB
-
It is not required to have Avi Load Balancer Controller/GSLB site in all VNets, locations.
GSLB site can be present either on-prem or in Azure or at both places.
One GSLB site/Avi Load Balancer Controller can take care of all GSLB functioning. In such a case, no further GSLB configuration would be possible until the site is functional. So, it is recommended to have at least two sites that are designated as the leader site and the active follower site for any GSLB configuration changes, if required. For more information, see GSLB Site Configuration.
- Clouds
-
Create different clouds on the Avi Load Balancer Controller to specify the network and location details for one cloud per VNet. For more information, see Installing NSX Advanced Load Balancer in Microsoft Azure in the VMware Avi Load Balancer Installation Guide.
Avi Load Balancer SEs
Avi Load Balancer SEs will be deployed in all VNets that are load balancing resources and applications.
DNS virtual service can be deployed in two or three VNets depending on the deployment size and traffic volume. Avi Load Balancer DNS virtual service is not required for all VNets. For topologies discussed in this document, Avi Load Balancer DNS virtual services are deployed in two locations.
You can have the application pools, Avi Load Balancer SEs running in the same VNet as that of the Controller.
As explained in the topology, the DNS VM forwarder component conditionally forwards the traffic either to Avi Load Balancer DNS virtual service or to Azure DNS.
Request Flow
This section covers the request flows for the resolution of applications hosted in the following:
One VNet from other VNet
Azure VNets from on-prem
Virtual machines in different virtual networks